Last Updated on: 13th June 2024, 07:24 am
✓ Fact Checked 🕓
❙ Our team of writers, editors, and medical experts rigorously evaluates each article to ensure the information is accurate and exclusively cites reputable sources.
❙ We regularly assess how the content in this article aligns with current scientific literature and expert recommendations in order to provide the most up-to-date research.
When faced with various dental problems, there is a quick, aesthetic, and viable solution: dental bonding.
This technique has revolutionized the way dentists approach dental restoration, allowing for less invasive and more conservative treatments compared to conventional restorations.
In this article, we’ll tell you everything you need to know about dental bonding.
What is Dental Bonding?
Dental bonding is a cosmetic dentistry technique in which an adhesive material is used to bond a restorative material, such as composite resin or ceramic, to the natural tooth structure.
How does Dental Bonding Work?
Dental bonding is based on the principle of chemical bonding of a restorative material to the tooth structure using dental adhesives.
Dental adhesives are substances that are applied to the prepared tooth surface.
Creating a thin layer that acts as a bridge between the tooth and the restorative material. These adhesives allow for strong and durable bonding, ensuring that the restorative material stays in place even under the pressure of chewing.
What Materials are Used in Dental Bonding?
1. Composite resin
Composite resins are restorative materials that mimic the color of the tooth. They are used not only in cosmetic treatments but also in other common dental treatments, such as restoration of decayed teeth, replacement of traditional metal fillings, or coating of sensitive dental areas.
Restorations made of composite resin can usually be completed in a single appointment, as they are applied in layers on the prepared tooth and sculpted to the appropriate shape and size.
2. Ceramic
Dental ceramic is a type of aesthetic and resistant material commonly used in the manufacture of dental restorations, such as crowns, veneers, inlays or onlays, and bridges.
It has a good aesthetic appearance, as it is translucent and emits a shine similar to natural tooth enamel.
Ceramic restorations often involve more than one appointment, as they require impressions of the prepared tooth, the creation of a plaster model from the impressions, the sculpting of the restoration on the plaster model, and the baking of the restoration in a high-temperature dental oven to harden it.
Then, the ceramic restoration is cemented in place on the prepared tooth using dental bonding techniques.
When is Dental Bonding Used?
Dental bonding is used in a wide variety of situations, including:
1. Smile makeovers: Dental bonding can be used to make composite resin restorations that allow for the modification or improvement of the shape of teeth.
2. Cosmetic restorations: Dental bonding is ideal for cosmetic restorations, which can repair chipped or broken teeth, restoring their shape and functionality.
3. Closing gaps between teeth: Sometimes, it is not possible to perform orthodontic treatments to move teeth and close gaps between them. For these cases, the use of composite resin restorations can help eliminate those annoying gaps between teeth, helping to build a more
aesthetic smile.
4. Cementation of indirect restorations: Indirect dental restorations are those that are not performed in the dental office but in a laboratory.
These include inlays, veneers, or ceramic crowns, which can be cemented using dental bonding techniques to ensure proper retention and durable bonding.
5. Dental fillings: Composite resins can be used to make dental fillings or restorations in teeth affected by decay, allowing for a conservative and aesthetically pleasing restoration.
6. Dental sensitivity: Sometimes, the gum covering the necks of the teeth can retract, and when this area is exposed, dental sensitivity may occur.
Dental bonding facilitates the placement of composite resin on the surface of the tooth, reducing dental sensitivity.
7. Covering discolored teeth: When teeth have formation defects or stains that cannot be solved with teeth whitening, the placement of ceramic or composite veneers using dental bonding is the indicated solution.
Steps for the Dental Bonding Procedure
The dental bonding procedure involves several steps, which may vary depending on the type of restoration, the material used, and the technique employed by the dentist.
The general steps for bonding with composite resin are described below
1. Color selection: When performing cosmetic restorations, the color of the restorations must be as identical as possible to the color of natural teeth.
To achieve this, the dentist should select the color of the material to be used in the restoration with a good source of daylight, always with the patient’s approval.
2. Tooth preparation: Any decay or previous restoration is removed, and an adequate surface is created for bonding. This may involve removing dental enamel and applying conditioning agents to improve material adhesion.
3. Dental adhesive application: The dental adhesive is applied to the prepared tooth surface. The adhesive is evenly distributed, allowing a thin and robust layer to form.
4. Polymerization of adhesive material: The adhesive material is exposed to a special polymerization light that hardens and fixes it to the tooth. This is typically done using an LED or halogen light lamp.
5. Restorative material application: Once the dental adhesive is in place, the restorative material, such as composite resin, is applied and molded to obtain the desired shape. The material is photopolymerized to harden it.
6. Adjustment and polishing: After the restorative material is polymerized, the final adjustment is made to ensure that the restoration fits correctly, eliminating discomfort or biting problems.
Additionally, proper polishing ensures that the restoration has an aesthetic appearance.
What are the Post-operative Care Requirements for Dental Bonding Procedures?
After undergoing a dental bonding procedure, it is essential to follow appropriate post-operative care to ensure the restoration’s durability and success. Some post-operative care includes:
• Maintaining good oral hygiene: It is essential to brush teeth at least twice a day, and use dental floss and mouthwash regularly to prevent the accumulation of bacterial plaque and cavities in the restored area.
• Avoiding harmful foods and beverages: Foods and beverages that can damage the restoration, such as hard, sticky, or high-sugar foods, should be avoided. In addition, smoking should be avoided, and alcohol consumption should be limited.
• Scheduling regular check-ups with the dentist: It is important to schedule regular check-ups with the dentist to evaluate the restoration’s integrity and make adjustments or repairs if necessary.
• Limiting the consumption of foods with colorants: Some restorative materials may be more susceptible to taking pigments from the environment, so it is recommended to reduce the consumption of beverages and foods such as coffee, cola, blackberries, beets, among others, that may alter the color of composite resins.
The use of straws (preferably reusable) or proper dental hygiene after consuming pigmented foods is advisable.
 Benefits of Dental Bonding
Benefits of Dental Bonding
1. Conservation of dental tissue
One of the most significant benefits of dental bonding is that it allows for the preservation of healthy dental tissue.
Unlike conventional restorations that require the removal of large amounts of healthy dental enamel, dental bonding allows for minimal tooth preparation.
It also, preserves natural dental structure and reduces the risk of sensitivity after the procedure.
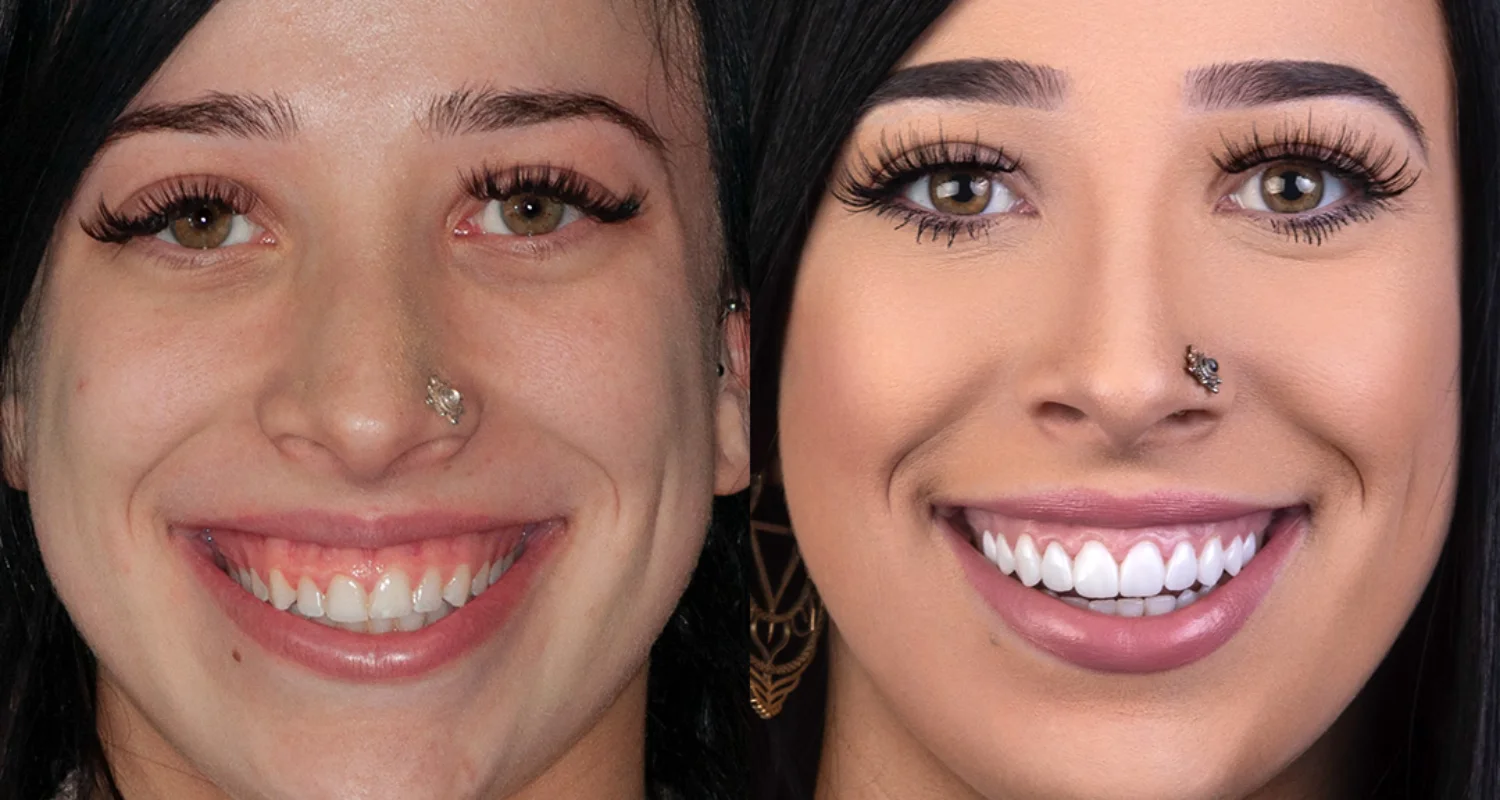
2. Natural and enhanced aesthetics
Dental bonding allows for the application of aesthetic restorative materials, such as composite resins, that can be adapted to the color and shape of natural teeth.
This allows for virtually invisible restorations, providing highly satisfying aesthetic results.
3. Greater retention and durability
Dental bonding creates a strong chemical bond between the restorative material and the tooth, resulting in greater retention of the restoration and greater long-term durability. It is estimated that they can last between 10 to 15 years or more.
Limitations of Dental Bonding
1. Requires dentist skills and experience
Dental bonding is a technique that requires skills and experience from the dentist to obtain optimal results. Proper selection of the restorative material, and precise preparation of the tooth.
Also, the proper application of the dental adhesive, and proper polymerization (hardening) of the restorative material are critical elements of the dental bonding procedure.
Therefore, it is important that the dentist be well-trained and have experience in this technique.
2. Higher cost
Compared to conventional restorations, dental bonding may have a slightly higher cost due to the need for specific adhesive and restorative materials, as well as the higher skill and experience required by the dentist.
However, many patients consider the aesthetic result and preservation of dental tissue worth the additional investment.
The average cost of dental bonding is estimated to be around $300 to $600 per tooth, but other payment options may be available depending on the type of dental insurance or other payment methods.
Conclusion
Dental bonding is a modern and conservative technique that offers several benefits related to the aesthetic restoration of the shape and function of teeth. This technique is a treatment option for various clinical situations.
However, it is important that the dentist carefully evaluate each case and select the appropriate restorative technique according to the patient’s needs and conditions.
Share:
References
1. Dental bonding. (Abr 14, 2022). Cleveland Clinic. Recuperado el 8 de abril de 2023, de https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/10922-dental-bonding
2. Higuera, V. (Mar 12, 2019). Teeth bonding: What to expect if you have your teeth bonded. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/dental-and-oral-health/teeth-bonding
3. Learn more about dental bonding for teeth. (Abr 2, 2023). WebMD. Recuperado el 8 de abril de 2023, de https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/dental-bonding
4. Tahhan, R. (Sep 18, 2017). The pros and cons of dental bonding. Titan Dental Care Sterling, Virginia. https://www.titandentalcare.com/blog/pros-cons-dental-bonding/
5. Cadenaro, M., Josic, U., Maravić, T., Mazzitelli, C., Marchesi, G., Mancuso, E., Breschi, L., & Mazzoni, A. (2023). Progress in Dental Adhesive Materials. Journal of dental research, 102(3), 254–262. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/00220345221145673
6. Swain, E. (Dic 16, 2022). Dental Bonding Cost. NewMouth. https://www.newmouth.com/dentistry/restorative/bonding-cost/