Last Updated on: 16th December 2025, 10:06 am
The symptoms of addiction in the mouth - like dry mouth, tooth decay, gum disease, bad breath, and mouth sores - appear early. Recognizing these symptoms and getting timely dental and addiction support is essential to protect your smile and overall health.
People with substance abuse issues usually suffer oral health issues. The symptoms of an addiction frequently manifest first in the mouth before other parts of the body show damage.
Because the mouth is vital for nutrition, communication, and self-esteem, understanding how addiction can harm it is important for early intervention and recovery.
This article explores the most common symptoms of addictions for oral health, how different substances and behaviors cause damage, and provides practical steps to prevent and treat these effects.
What are addictions and how do they affect oral health?

Addictions are chronic disorders that involve the compulsive use of substances or behaviors despite knowing the harm they cause.
The most common addictions that impact oral health include alcohol, tobacco, recreational drugs, and behaviors like eating disorders or ludomania.
Many additive substances reduce saliva production. This is especially dangerous because saliva is the mouth’s first line of defense against cavities and infections. Others suppress the immune system or lead to neglect of oral hygiene. Together, these effects create the perfect environment for oral diseases and problems.
What are the most common oral symptoms of addiction?
Addiction-related damage often shows up clearly in the mouth. Many of the signs are early warnings of deeper health issues. Let’s see the most common symptoms.
Why is dry mouth so harmful?

Dry mouth (xerostomia) happens when saliva production decreases. It’s especially common in people who use alcohol, marijuana, methamphetamines, or certain medications.
Without enough saliva, the mouth can’t:
- neutralize acids
- wash away food debris
- remineralize teeth
This creates the perfect environment for:
- cavities
- gum disease
- oral infections
What does addiction-related tooth decay look like?
Addiction can severely damage teeth. The main culprits include:
- sugar cravings, especially from stimulants
- acid erosion from drugs or vomiting
- poor oral hygiene habits
This often leads to:
- deep cavities
- widespread decay
- tooth sensitivity or pain
- teeth needing root canals or extractions
How do addictions affect the gums?
Substances like tobacco, alcohol, and drugs weaken the immune system, making gums vulnerable. Common signs include:
- redness and swelling
- bleeding when brushing
- gum recession
If untreated, this can develop into periodontitis, which damages the bone and can lead to tooth loss.
Can addiction cause tooth loss?
Yes. Long-term substance use increases the risk of losing teeth due to:
- advanced gum disease
- bone loss around teeth
- untreated decay
- fractures from clenching or trauma
Tooth loss isn’t just aesthetic; it can affect chewing, speech, and self-esteem.
Why are mouth sores and ulcers common?
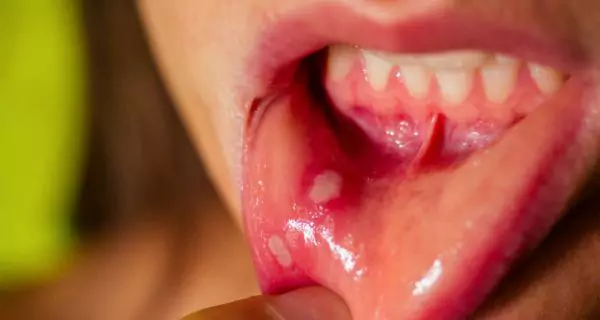
People with addictions may develop:
- painful ulcers
- cracked corners of the mouth
- sores that don’t heal
This happens because of:
- poor nutrition
- immune suppression
- chemical irritation from smoking or drug use
These sores increase the risk of infection and may signal more serious conditions.
What causes tooth staining and discoloration?
Addiction often affects the color of teeth. Common causes include:
- Tobacco: yellow or brown stains
- Poor hygiene: plaque buildup darkens teeth
- Meth or cocaine: can turn teeth gray, black, or mottled
Stains may be superficial, or are signs of deeper enamel damage.
Why do people with addictions often have bad breath?
Bad breath (halitosis) in people with addiction is usually caused by:
- dry mouth
- bacterial buildup
- tooth decay or infections
- smoking and alcohol residue
It’s often persistent, even after brushing.
How is bruxism connected to drug use?

Bruxism (grinding or clenching teeth) is especially common with stimulants like MDMA (ecstasy), cocaine, and methamphetamine.
It can cause:
- worn or fractured teeth
- jaw pain or fatigue
- TMJ disorders (temporomandibular joint problems)
Studies show that up to 89% of ecstasy users clench their jaws, and 68% of meth users grind their teeth.
Can addictions lead to mucosal lesions or oral cancer?
Yes, regular use of tobacco, alcohol, cannabis, or cocaine can damage the soft tissues of the mouth, leading to:
- Leukoplakia: white patches inside the mouth, sometimes precancerous
- Erythroplakia: red patches with a high cancer risk
- Oral cancer: often found on the tongue, gums, or throat
The combined use of alcohol and tobacco dramatically increases the risk of oral cancer.
How do specific substances damage oral health?
The symptoms of an addiction in the mouth depend on the type of substance. While they all tend to reduce saliva and weaken the immune system, each one affects oral tissues, teeth, and gums in different ways.
How does alcohol affect your mouth?

- Reduces saliva and alters pH levels.
- Encourages plaque buildup and cavities.
- Weakens immune response in the gums.
- When combined with tobacco, it raises oral cancer risk.
What does tobacco do to your oral health?
- Causes gum recession and bad breath.
- Stains teeth yellow or brown.
- This is the major cause of gum disease and oral cancer.
How does marijuana affect teeth and gums?
- Leads to dry mouth and more plaque buildup.
- Increases the risk of gum disease.
- May cause mucosal changes and leukoplakia (white patches).
What does methamphetamine use cause in the mouth?
- Extreme dry mouth and acidic environment.
- Rapid decay, especially near the gum line.
- Serious gum disease and tooth loss.
- Often worsened by poor hygiene and teeth grinding.
How does cocaine affect the mouth?
- Causes mouth and nasal ulcers.
- Can lead to tissue death in the palate or gums.
- Increases the risk of gum disease and oral lesions.
Why does MDMA (ecstasy) harm your teeth?
- Causes intense muscle activity, leading to jaw clenching and bruxism (grinding).
- Leads to enamel wear and jaw pain.
- Reduces saliva, causing dry mouth and increasing risk of decay.
What are the oral risks of heroin use?
- Triggers dry mouth and sugar cravings.
- Users often skip brushing or dental visits.
- Strongly linked to cavities and gum disease.
Each drug affects your mouth differently, but all can cause serious damage. Getting care early and asking for help can prevent bigger problems.
How to protect and restore your smile when facing addiction?

The symptoms of addictions are visible and can be recognized before other symptoms in the body. Protecting your oral health during recovery is not just cosmetic; it’s a crucial part of healing.
Let’s look at how you can restore and care for your smile.
What dental treatments can help?
If addiction has affected your oral health, your dentist may recommend treatments tailored to your needs, such as:
- Professional cleanings to remove plaque, tartar, and stains.
- Deep cleanings (scaling and root planing) for advanced gum disease.
- Fillings, crowns, or bridges to repair decayed or broken teeth.
- Tooth extractions or dentures when teeth can’t be saved.
- Fluoride treatments to rebuild enamel and reduce sensitivity.
- Oral surgery or biopsies if unusual sores or growths appear.
- Custom night guards for teeth grinding related to stress or withdrawal.
These treatments help you to restore your smile,reduce pain, improve your ability to eat and speak, and support your overall recovery.
How can you prevent more damage?
Even if you’ve already seen the symptoms of addictions in your mouth, small changes in your routine decrease oral damage. You can protect your oral health by:
Brushing and flossing gently but consistently
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush twice a day for two minutes.
- Floss once a day to remove plaque between your teeth.
- Use alcohol-free mouthwash to reduce bacteria without drying out tissues.
- If your gums are sensitive, go slow; consistency is more important than pressure.
Staying hydrated
- Many substances cause dry mouth, which increases the risk of cavities and gum disease.
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day and consider sugar-free gum or lozenges to stimulate saliva.
Limiting sugary and acidic foods
- Cravings for sweets or soda are common during withdrawal.
- Try to replace them with healthier options like fruit, yogurt, or cheese, which are better for your teeth.
Avoiding smoking and alcohol
- Tobacco and alcohol make oral symptoms worse and slow healing.
- Reducing or quitting these can significantly improve your oral and overall recovery
Don’t forget to look for signs like ulcers, white patches, gum swelling, or bleeding. If you notice any of these symptoms, contact your dentist early. It could prevent bigger problems later on.
Who can support you?
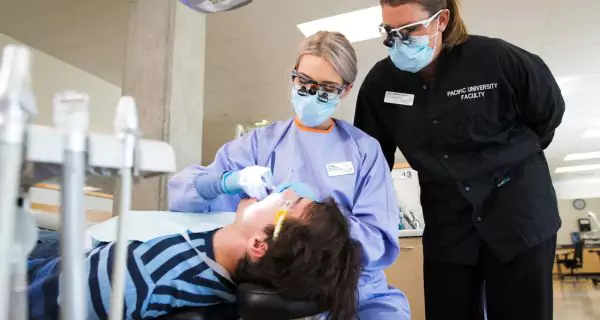
Healing from addiction needs the help of different specialists, such as:
- Dentists and hygienists to restore your oral health.
- Therapists or counselors to address emotional triggers.
- Addiction specialists for medical treatment and guidance.
- Support groups for motivation and shared experiences.
This support not only helps with recovery, but it also reduces the risk of future symptoms of addictions affecting your body and mouth.
What products can support oral recovery?
In recovery, your mouth may be more sensitive, dry, or prone to infection. These over-the-counter products can help:
- Alcohol-free mouthwash (like Listerine Zero or TheraBreath): avoids burning and keeps breath fresh.
- Fluoride toothpaste (such as Colgate Total or Sensodyne): strengthens enamel and reduces sensitivity.
- Xylitol gum or lozenges: help stimulate saliva and reduce cavity risk.
- Biotène oral rinse or gel: designed to relieve dry mouth.
- Interdental brushes or floss picks: make cleaning easier if your gums are tender.
Using the right tools at home can support your recovery and reduce the visible symptoms of addictions in your smile.
Why does taking care of your mouth matter when dealing with addiction?
The symptoms of addictions often show up in your mouth before other parts of your body. Paying attention to these signs can help you protect your teeth and gums from serious damage.
Taking care of your mouth every day, visiting the dentist regularly, and getting help for addiction are the best ways to protect your smile and improve your health. Don’t ignore these symptoms. Acting early gives you a better chance at recovery and maintaining a healthy smile.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is meth mouth and how does it happen?
Can dental treatment help reverse damage caused by addictions?
How does sugar intake linked to addiction affect teeth?
Can addiction cause changes in taste or smell?
Is it safe to get dental work done while in addiction recovery?
Voice and Search (Q&A)
How does addiction cause bad breath?
Addiction causes bad breath mainly through dry mouth, infections, decayed teeth, and strong odors from substances like tobacco and alcohol.
What oral infections are common with addiction?
Common infections include oral thrush (candidiasis) and slow-healing sores caused by dry mouth and immune suppression.
How can I prevent tooth decay during addiction recovery?
Maintain good hygiene, use fluoride toothpaste, avoid sugary foods, stay hydrated, and visit the dentist regularly.
Share
References
1. Amiri, S., & Shekarchizadeh, H. (2021). Oral health-related quality of life among a group of patients with substance use disorders in rehabilitation treatment: a cross-sectional study. BMC Oral Health, 21(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-021-01764-0
2. Axtell, B. (2024, October 15). How drug abuse affects your mouth. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/drug-abuse-mouth
3. D’Alessandro, M., Greene, K., & Hraber, M. (2025, July 15). Making the connection to care: Oral health and substance use disorder. NASHP. https://nashp.org/making-the-connection-to-care-oral-health-and-substance-use-disorder/
4. McFarland, K. K., Giannini, P. J., Fung, E. Y. K. (2018, January 10). Addiction and oral health care. Decisions in Dentistry. https://decisionsindentistry.com/article/addiction-oral-health-care/
5. Shekarchizadeh, H., Khami, M. R., Mohebbi, S. Z., Ekhtiari, H., & Virtanen, J. I. (2013, September 1). Oral Health of Drug Abusers: A Review of Health Effects and Care. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4453891/
- Dr. Yeidy Carolina Mesa [Author]
DDS Yeidy Carolina Mesa Passionate Dentist | Advocate for Accessible Oral Health Education Graduating from Universidad CES in 2022, I am a dedicated general dentist with a lifelong passion for helping others and making a meaningful impact in the world. My journey into dentistry began at the age of 7, inspired by my own experience with braces and overcoming a fear of the dentist. This personal journey shaped my mission to help patients conquer their own dental anxieties and embrace a healthier,...
View all posts
- Nayibe Cubillos M. [Medical Reviewer]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...Recent Posts
















