Last Updated on: 3rd January 2026, 09:02 am
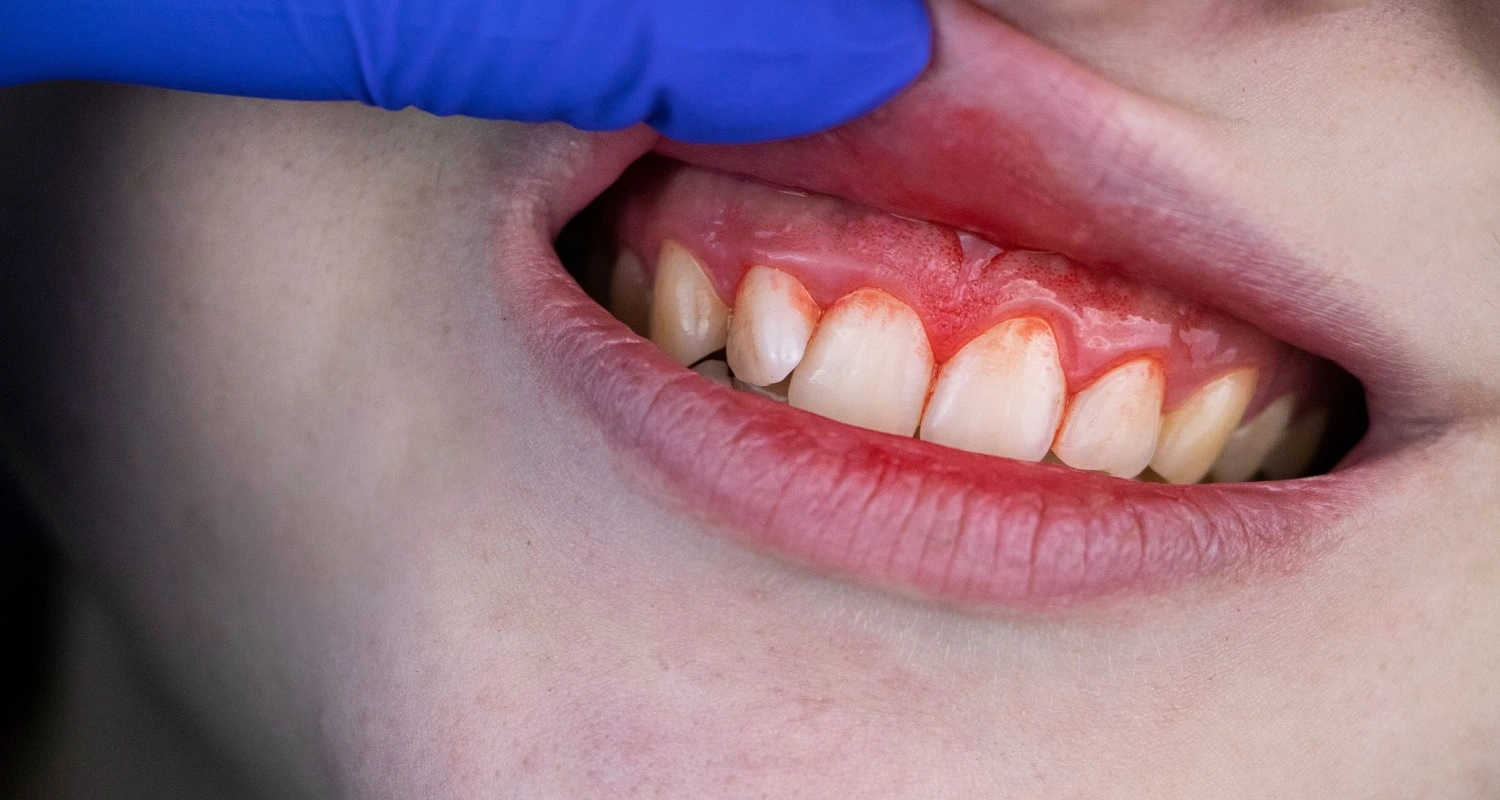
The recession of the gums is often indicated by tooth sensitivity to hot or cold foods, bleeding during tooth brushing, and changes in the color of your gums. These signs should never be overlooked, as they may signify the presence of gum recession, a silent oral health disease that affects a significant population. It is crucial to determine the underlying causes of these symptoms to address them effectively.
What is the Recession of the Gums?
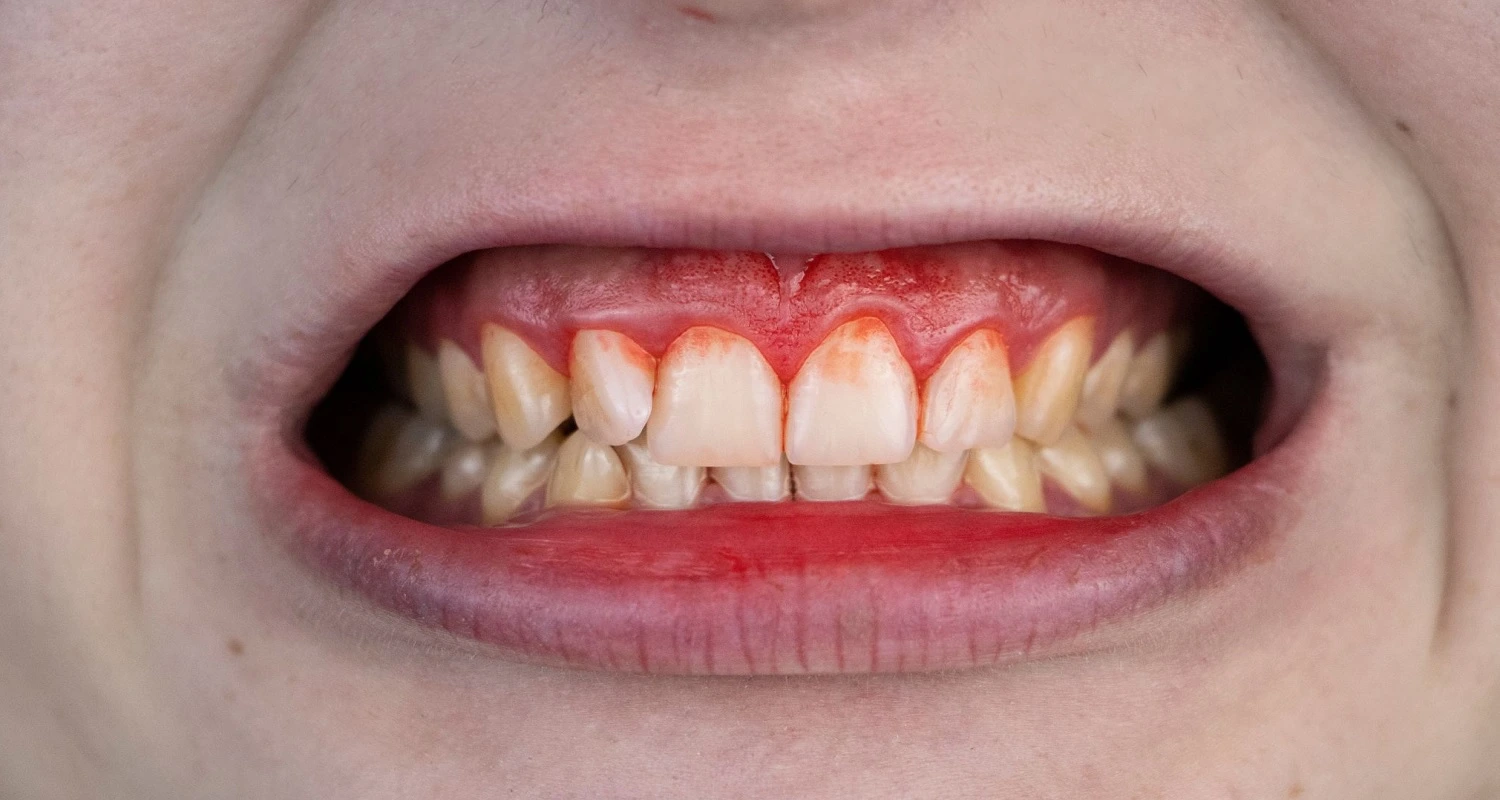
Gum recession, also known as gingival recession, is a progressive disease of gum loss, leaving the roots of the teeth exposed.
This pathology is a consequence of periodontitis (another gum disease) and can be mild, moderate, or severe.
Gingival recession causes the tissue (gums) to detach from the tooth, exposing the root and making it look longer. This facilitates the accumulation of bacteria and increases dental sensitivity and the risk of infections and cavities. If not treated in time, it can lead to tooth loss.
The California Dental Association estimates that 75% of adults have gum disease, including receding gums. It is a common oral health condition in people aged forty and over, which is why some specialists link its cause to aging.
What Causes Gum Recession?
This type of gum disease can be the consequence of factors such as poor or very aggressive dental hygiene, previous untreated periodontitis, or genetics.
Other predisposing situations are:
• Bruxism
• Hormonal changes in women: puberty, pregnancy, or menopause – stages that generate greater sensitivity in the gums.
• Brushing too hard, wearing away tooth enamel.
• Tobacco use
• Crooked teeth or a misaligned bite
• Poor oral hygiene increases the formation of tartar.
• Periodontitis, is a bacterial condition that affects the soft tissues surrounding the teeth, including the gums, causing them to recede.
• Genetic predisposition
• Piercings on the lips or tongue facilitate rubbing against the gums and cause tissue damage.
The consumption of some medications that cause xerostomia (dry mouth), a diagnosis of diabetes, lupus, or HIV are also conditions that cause gum recession.
What are the Symptoms of Gum Recession?
Identifying the symptoms of this disease is relevant to address it properly with timely treatment, and avoid complications. One of the most obvious signs is the increase in the length of the visible part of the teeth.
Other symptoms are:
• Color change in the gums, going from a healthy pink to a darker or reddish tone
• Red and swollen gums
• Gum pain
• Bad breath
• Bleeding after brushing or flossing
• Dental sensitivity when brushing, with heat, cold, or something hard.
• Exposed dental roots
How to Prevent a Gum Recession?
Although gingival recession is a common condition, the measures to prevent it are within everyone’s reach. Here are some practices that should help in the prevention of this pathology:
• Brush your teeth twice a day, with a soft bristle brush.
• Do dental cleanings at least twice a year.
• Do not use tobacco.
• Floss regularly.
• Use antimicrobial mouthwash daily.
• Eat a balanced diet.
• Visit the dentist at least twice a year.
What are the Treatment Options for Receding Gums?

The dentist will give indications regarding practices that improve and even stop the progression of the disease. In advanced cases, treatment with drugs is an option
If the gingival recession is a consequence of periodontitis, it is necessary to perform a root scaling.
Other alternatives for the therapeutic management of gingival recession are:
• Restoration through a composite resin the color of the tooth, covering the root of the tooth.
• The application of a material that is the same color as the gums to fill in the spaces where the gums have receded.
• Use of acrylic or silicone veneers superimposed on the teeth affected by the disease.
• In cases of dental misalignment, you can resort to orthodontic appliances to correct the position of the teeth. Subsequently, the adjustment of the gums is possible.
In advanced cases, the treatment is surgical, in which case, there are two options:
1. Flap surgery: Experience the transformative power of Deep Dental Cleaning, a meticulous procedure specially designed to eradicate bacteria and plaque from the gums, ensuring optimal oral health.
2. A gum graft is the most frequent option. A is made with tissue taken from the roof of the mouth or other donated human material. The recovery time is generally two weeks, although it depends upon the number of teeth involved in the procedure, the origin of the graft tissue, and the age of the recipient.
• Guided bone regeneration, a highly effective solution for bone loss around teeth, offers a therapeutic alternative. This innovative procedure incorporates the placement of regenerative material in the affected area, facilitating the growth of new bone and tissue, making it an ideal choice for individuals considering dental bone graft.
Home Remedies for Receding Gums

Some home remedies provide relief and help stop gum recession.
• Mouthwash with salt water: Mix a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and rinse with this mild mouthwash several times a day.
• Coconut oil has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. Mouthwashes with the oil can be used for a few minutes every day to help reduce inflammation.
• Chamomile infusion can be used as a mouthwash twice a day to relieve inflammation and reduce gum discomfort.
• Aloe vera gel is applied to the affected gums. It has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce irritation and promote healing.
A Timely Diagnosis is Essential
If you notice that your teeth have a “longer appearance” and you see changes in the color of the gums or bleeding during tooth brushing, be alert and consult your dentist. These are some of the symptoms of gum recession, a disease that also offers other signs.
An early diagnosis and proper treatment help prevent the progression of gum recession and maintain good oral health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the consequences of not treating a gingival recession?
Gingival recession is an unwanted problem that exposes the root surface. It usually has an unsightly impact and can lead to the development of tooth sensitivity plus the increased risk of abrasion and root caries.
Is gum recession an indication of cancer?
No, gum recession alone is not an indication of cancer. Oral cancer is typically associated with symptoms such as white spots or persistent open sores in the mouth that do not heal. However, it’s important to note that severe gum disease, a common cause of gum recession, is believed to increase the risk of certain cancers over time. This is just one of several reasons why it is crucial to promptly evaluate and treat any signs of gum disease and maintain a strong oral hygiene routine to prevent periodontitis in the future.
How long does it take for gum recession to begin?
The timeframe for gum recession varies, depending upon the underlying cause. If you brush your teeth too aggressively, it may take time for your gums to recede. However, if you already have gum disease, the recession can occur relatively quickly. In certain instances, your gums may recede within a few weeks or months.
Will my gums regenerate?
Once the gums have receded, they do not naturally regenerate on their own. However, there are measures you can take to assist in the process. Laser treatments are the primary solution for correcting a “gummy smile,” and they can also be used to improve minor gum recession. The laser stimulates gum growth during the healing process. In cases of significant gum recession, gum grafts are the only method of restoration. This type of gum contouring can enhance the appearance of your smile by preventing teeth from appearing too long. Additionally, it safeguards your future oral health by covering any exposed areas of the tooth roots.
Share:
References
1. Bueno Rossy Luis, Ferrari Roberto, Shibli Jamil (November 2015) Treatment of recessions and mucogingival defects through connective tissue grafts in teeth and implants /http://www.scielo.edu.uy/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1688-93392015000200005
2. Caffaso Jaqueline (Mayo 23 de 2017) Overview of receding gums / https://www.healthline.com/health/periodontitis#outlook
3. Cleveland Clinic (Abril 14 de 2022) Gum Recession / https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22753-gum-recession#:~:text=Gum%20recession%20is%20when%20your,antimicrobial%20mouth%20rinses%20and%20surgery
4. Marks Hedy (October 31, 2021) Receding Gums / https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/receding_gums_causes-treatments
5. Segovia Carreño Rina E., Salazar V Carmen Rosa, Paz de Gudiño Mercedes (June 2022) Precipitating factors in the development of gingival recession / http://ve.scielo.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0001-63652002000200006
6. Ubertalli James (May 2022) The recession of the gums / https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/mouth-and-dental-disorders/temporomandibular-disorders/temporomandibular-disorders-tmds
-
Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...Recent Posts