Last Updated on: 12th December 2025, 05:31 am
Chewing gum is an activity that many people enjoy, but have you ever wondered what the impact is on your dental health? In this article, we will cover several aspects related to, is chewing gum bad for your teeth?, including dentists’ perspectives, the effects on tooth enamel, and much more.
1. Is chewing gum bad for your teeth?

Is chewing sugar-free gum bad for your teeth?
Chewing sugarless gum has several benefits for oral health. Studies suggest that it can help reduce dental plaque and cavities by stimulating saliva production. Xylitol, a sweetener commonly used in sugar-free gum, has also shown benefits in preventing tooth decay.
The dentist’s perspective
From the dentist’s perspective, Is chewing sugar-free gum bad for your teeth? It is generally acceptable and can be considered part of good oral hygiene, as long as it does not replace conventional practices such as brushing and flossing. Sugared gum, however, is a very different matter, and most dentists advise against it.
2. Chewing gum and tooth decay
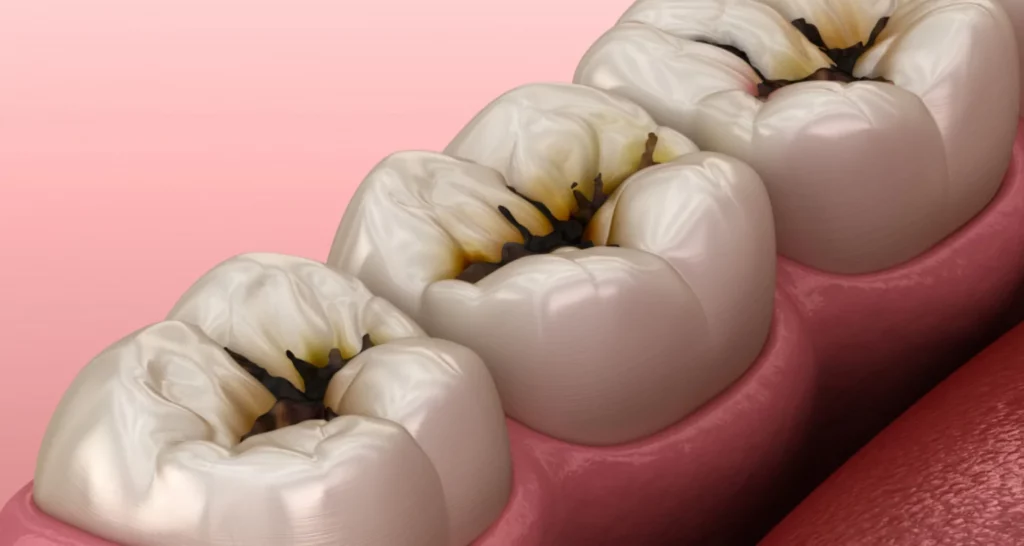
The risk of tooth decay
One of the biggest concerns when it comes to chewing gum is the risk of tooth decay. Chewing gum that contains sugar can contribute to the formation of cavities by providing a breeding ground for bacteria.
How to avoid it? Is chewing gum bad for your teeth?
The key is to choose sugar-free gum that contains xylitol. This sweetener is not only safe for your teeth, but it also has antibacterial properties that help fight tooth decay.
3. Oral hygiene and chewing gum

Basic oral hygiene
Regular brushing and flossing are essential for good oral hygiene. Is chewing gum bad for your teeth? Although chewing gum can help clean teeth to some extent by stimulating saliva, it should not be considered a substitute for these practices.
Complement with gum. Is chewing sugar-free gum bad for your teeth?
Chewing gum can be a good addition to your oral hygiene routine, especially if you opt for sugar-free gum with xylitol. These gums can help clean teeth and gums between meals, but should not replace regular oral hygiene.
4. Benefits of sugar-free gum

Saliva and cavity prevention
Is chewing sugar-free gum bad for your teeth? Chewing sugarless gum can stimulate saliva flow by 10-12%, which is beneficial for cleaning the mouth and neutralizing cavity-causing acids (ADA, 2021). The increase in saliva production can also help neutralize acids in the mouth, wash away food particles, and strengthen tooth enamel thanks to the minerals it contains.
Xylitol and additional benefits
Xylitol is a sweetener commonly found in sugar-free gum and has additional benefits for dental health. Not only is it safe for your teeth, but it also has antibacterial properties that help fight tooth decay.
5. Chewing gum and enamel erosion
Short term effects
Is chewing sugar-free gum bad for your teeth? In the short term, chewing gum (especially sugarless) does not appear to have a significant negative impact on tooth enamel erosion. In fact, as mentioned above, it can help clean teeth and stimulate saliva production, which is beneficial for enamel.
Long-term effects
Is chewing gum bad for your teeth? Few long-term studies evaluate the impact of chewing gum on tooth enamel erosion. Additionally, constantly chewing gum can lead to temporomandibular joint problems, which could impact the alignment of your teeth and cause muscle pain.
6. The best and worst gums for your teeth

Is chewing sugar-free gum bad for your teeth? The best chewing gum
If you decide to chew gum, opt for sugar-free options. Look for gum that contains xylitol, as this sweetener has been shown to be beneficial for oral health. These are the most recommended by dentists to complement good oral hygiene.
Is chewing gum bad for your teeth? The worst chewing gum
On the other hand, gums with sugar or containing fruit acids can be harmful to your teeth. These gums can contribute to tooth decay and enamel erosion, so it’s best to avoid them if you’re concerned about the health of your teeth.
7. Chewing gum and jaw health

Temporomandibular joint problems
Chewing gum excessively can lead to problems in the temporomandibular joint, causing pain and other jaw problems. This is something to keep in mind if you are an avid gum chewer.
Tips to minimize risks
To minimize the risk of jaw problems, try to chew gum only occasionally and avoid chewing gum for long periods of time. You can also alternate sides to distribute the effort more evenly.
8. Oral care while chewing gum

Ideal frequency and tips
As for frequency, try not to chew gum all day. Doing it occasionally, especially after meals, can be beneficial. But remember, gum is not a substitute for brushing and flossing. Use gum as a complement, not as a substitute.
Select the correct gum
Is chewing gum bad for your teeth? Always opt for gum recommended by dental associations or that contains xylitol. They are the ones most likely to benefit your dental health, while gums with sugar or fruit acids are the ones you should avoid.
9. Benefits of xylitol gum

Cavity prevention
Xylitol is a sweetener that has antibacterial properties that can help fight tooth decay. In addition, being a safe sweetener for teeth, it does not contribute to enamel erosion.
General oral health
Xylitol gum can also help combat bad breath and is a good addition to your overall oral hygiene regimen. Some studies even suggest that xylitol may have a positive effect on overall oral health, although more research is needed to confirm this.
We have also a comprehensive guide about toothpaste with xylitol. In this article, we will explore how toothpaste with xylitol has become a popular and effective option for maintaining oral health and preventing cavities.
Conclusion
About, Is chewing gum bad for your teeth? Chewing gum can have both positive and negative effects on oral health, depending upon how and what type of gum you chew. Opt for sugar-free gum with xylitol and use this activity as a complement to your regular oral hygiene regimen for maximum benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is chewing gum bad for your teeth?
There are situations in which it is best to refrain from chewing gum: If the gum contains sugar, there is a greater risk of developing tooth decay. Additionally, if you have problems with your temporomandibular joint (TMJ), excessive chewing of gum could intensify jaw discomfort.
Is chewing gum bad for your teeth daily?
According to Dr. Kahn, parafunctional behaviors such as chewing gum can trigger or aggravate temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. The continuous act of chewing gum puts excessive pressure on the temporomandibular joints, muscles and teeth, which can lead to overload, imbalance and misalignment.
Is chewing sugar-free gum bad for your teeth?
Some sugar-free gums are sweetened with synthetic sweeteners, such as aspartame and acesulfame-K, instead of sugar alcohols. Recent studies, including one from 2022, have established a correlation between high consumption of these artificial sweeteners and an increased risk of developing cancer.
Does chewing gum contribute to dental cleaning?
Sugar-free gum can help clean your mouth. Consuming sugar-free gum after eating or snacking can help eliminate and neutralize the acids generated by bacteria in dental plaque that damages tooth enamel. The chewing process and the taste of the artificial sweeteners in gum promote saliva production.
Share:
References
1. Helen West, R. D. (Jun 14, 2022). Chewing gum: Good or bad? https://health.clevelandclinic.org/is-chewing-gum-bad-for-you/
2. Kaput, K. (2022, julio 1). Is chewing gum bad for you? Cleveland Clinic. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/is-chewing-gum-bad-for-you/
3. Dodds, M. W. (2012). The oral health benefits of chewing gum. Journal of the Irish Dental Association, 58(5). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23573702/
4. Miller, C. S., Danaher, R. J., Kirakodu, S., Carlson, C. R., & Mumper, R. J. (2022). Effect of chewing gum containing Xylitol and blackberry powder on oral bacteria: A randomized controlled crossover trial. Archives of Oral Biology, 143(105523), 105523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2022.105523
5. Persaud , N. , Azarpazhooh , A. , Keown-Stoneman , C. , Birken , C. S. , Isaranuwatchai , W. , Maguire , J. L. , Mamdani , M. , Allen , C. , Mason , D. , Kowal , C. , . Jaleel , M. ,
Bazeghi , F. , Thorpe , K. E. , Laupacis , A. , & Parkin , P. C. (2023). Xylitol for the prevention of acute otitis media episodes in children aged 1–5 years: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Diseases in Childhood, archdischild-2023-3 https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2023-325565
6. Wu, Y.-F., Salamanca, E., Chen, I.-W., Su, J.-N., Chen, Y.-C., Wang, S. Y., Sun, Y.-S., Teng, N.-C., & Chang, W.-J. (2022). Xylitol-containing chewing gum reduces cariogenic and periodontopathic bacteria in dental plaque—microbiome investigation. Frontiers in nutrition, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.882636
- Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...Recent Posts















