Last Updated on: 2nd January 2026, 09:14 am
Discover effective gum disease treatment at home with simple remedies and tips. Learn how to manage gingivitis naturally and improve your oral health.
Gum disease is a common oral health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. While it often starts as gingivitis, an early stage characterized by redness and swelling of the gums, it can progress to periodontitis if left untreated. The good news is that gum disease, especially in its early stages, can often be managed and even reversed with diligent gum disease treatment at home.
In this guide, we’ll explore practical, science-backed ways to treat gum disease from the comfort of your home and help restore your gums to optimal health.
What is gum disease?
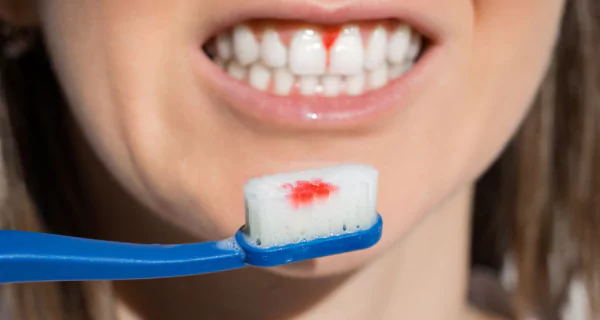
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a progressive condition that affects the tissues that surround and support the teeth. It typically begins with plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, that builds up on the teeth and gums due to poor brushing and flossing habits. If not removed, plaque hardens into tartar, irritating the gums and causing inflammation.
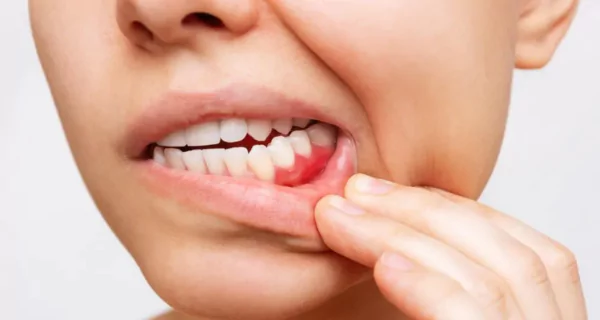
Early signs include swollen, red, and bleeding gums. Without treatment, the infection can progress to affect the bones surrounding the teeth, making it painful to chew and potentially leading to loose teeth.
Gingivitis vs. Periodontitis
- Gingivitis: The mildest form of gum disease, gingivitis, involves swelling, redness, and bleeding gums. It doesn’t affect the underlying bone or tissue and is reversible with proper care.
- Periodontitis: If untreated, gingivitis can advance to periodontitis. This severe stage involves damage to the bone and tissues that support the teeth, potentially leading to tooth loss.
Gum Disease Causes
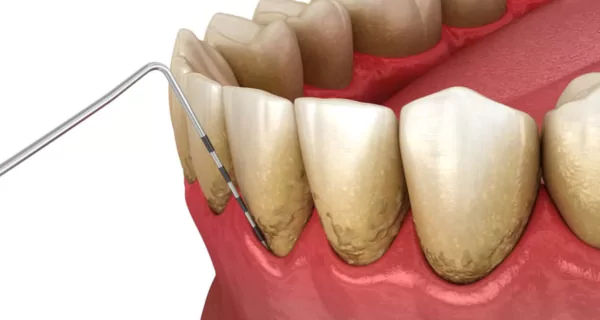
The main cause of gum disease is plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth and gums. Gum disease starts with a condition called gingivitis, which progresses through the following steps:
- Bacteria accumulate on teeth: after eating and don’t clean your teeth, bacteria collect on it.
- Plaque forms: if you don’t brush and floss thoroughly, these bacteria form plaque on your teeth, especially near the gumline.
- Tartar develops: when plaque isn’t removed, it hardens into tartar (calculus), which sticks to your teeth and gums. Of note, tartar provides an environment where bacteria thrive.
- Gum irritation and inflammation: the bacteria in plaque and tartar release toxins that irritate the gums. This causes redness, swelling, and bleeding, which are early signs of gum disease known as gingivitis.
- Gum pockets form: if gingivitis isn’t treated, the gums pull away from the teeth, forming small pockets. These spaces become traps for bacteria, plaque, and tartar, leading to infections.
- Bone and tissue damage: at this stage, the disease has progressed to periodontitis. As the infection worsens, it breaks down the connective tissue and bone that support the teeth.
- Tooth loss: Over time, the teeth lose their support and may become loose or fall out. Gum disease is the leading cause of tooth loss in adults.
Risk Factors of Gum Disease
- Poor oral hygiene: inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to accumulate, worsening gum disease.
- Smoking and tobacco use: weakens the immune system and impairs healing, exacerbating gum disease.
- Genetic predisposition: some individuals are genetically more prone to gum disease.
- Hormonal changes: pregnancy, menstruation, menopause, and puberty can make gums more sensitive and inflamed.
- Diabetes: Poorly managed diabetes increases susceptibility to infections, including gum disease.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as those that reduce saliva flow or affect gum tissue, can increase the risk.
- Poor nutrition: Deficiencies in essential nutrients, especially vitamin C, can weaken gums and the immune system.
- Stress: Chronic stress weakens the immune system, reducing the body’s ability to combat infections.
- Clenching or grinding teeth (bruxism): Excessive pressure can damage gum tissues and exacerbate the condition.
- Age: Older adults are more susceptible to gum disease due to longer exposure to risk factors.
- Existing dental problems: Crowded teeth or poorly fitted dental appliances make it harder to clean teeth, increasing risk.
Symptoms of Gum Disease

Recognizing the symptoms of gum disease early is crucial for effective treatment. Common signs include:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums.
- Bleeding during brushing or flossing.
- Persistent bad breath or a metallic taste in the mouth.
- Receding gums that make teeth appear longer.
- Painful chewing or sensitivity near the gum line.
If you notice these symptoms, act quickly to prevent the condition from worsening.
Effective Gum Disease Treatments at Home
While severe gum disease requires professional intervention, gingivitis and mild cases can often be managed with at-home remedies:
Practice proper oral hygiene
Good oral hygiene is essential for preventing and managing gum disease. Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Brush twice daily: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to clean along the gum line without causing irritation. Consider an electric toothbrush for more thorough cleaning.
- Floss daily: Flossing removes plaque and food particles from between teeth where your toothbrush can’t reach.
- Use a tongue scraper: Cleaning your tongue can help eliminate bacteria contributing to gum disease.
- Rinse with antibacterial mouthwash: Mouthwashes containing chlorhexidine or essential oils can reduce bacteria and inflammation in the gums. Swish for 30 seconds after brushing to maximize its benefits.
Natural Remedies for Gum Disease
Home remedies can be a cost-effective and helpful way to manage plaque and treat the gum disease, particularly in its early stages. By taking proactive measures at home, you can support your gum health and lower the risk of diseases like gingivitis. However, it’s wise to seek advice from a healthcare professional before trying these remedies if you’re pregnant, breastfeeding, or have any existing health conditions. Gum disease treatment at home include:
- Saltwater rinses: A saltwater rinse is a simple yet effective remedy for reducing gum inflammation and killing bacteria.
Instructions: Mix 1/2 teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth thoroughly twice a day.
- Hydrogen peroxide rinses: Hydrogen peroxide is a mild antiseptic that can reduce plaque and bacteria while whitening teeth.

Instructions: Mix equal parts of hydrogen peroxide and water to create a rinse. Swish this solution in your mouth 2-3 times a week, but do not swallow it.
- Baking soda paste: Baking soda has antibacterial properties and can help neutralize acids in your mouth.
Instructions: Mix baking soda with water to create a paste. Apply it to your gums to reduce plaque buildup. Use this method sparingly to avoid enamel damage.
- Aloe vera gel: Aloe vera is well-known for its soothing properties and ability to reduce gum inflammation.
Instructions: Apply pure aloe vera gel directly to the gums and let it sit for a few minutes before rinsing.
- Oil pulling: An ancient Ayurvedic practice, oil pulling can help reduce harmful bacteria in the mouth.
Instructions: Swish a tablespoon of coconut or sesame oil in your mouth for 15-20 minutes, then spit it out and rinse with warm water.
- Turmeric paste: Turmeric’s anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties make it ideal for irritated gums.
Instructions: Mix turmeric powder with water to form a paste. Apply the paste to your gums for about 10 minutes, then rinse thoroughly.
- Green tea: Green tea is rich in antioxidants that promote gum healing and reduce harmful bacteria.
Instructions: Drink a cup of green tea daily or use it as a rinse to support gum health.
While these remedies can help alleviate symptoms and improve gum health, they are not a replacement for professional dental care. If you suspect gum disease, consult a dentist for a thorough evaluation and treatment plan.
Foods That Promote Gum Health
Your diet plays a crucial role in maintaining and improving gum health. Choosing nutrient-rich foods can accelerate healing, strengthen oral tissues, and combat gum disease. On the other hand, avoiding certain foods can reduce irritation and the risk of further gum damage.

Nutrient-rich foods for healthier gums
- Fresh fruits and vegetables: Eating a colorful variety ensures you get a range of nutrients for optimal gum health.
- Dairy products: Milk and cheese are rich in calcium, which fortifies teeth and bones. They also contain antibacterial enzymes that help reduce harmful bacteria in your mouth.
- Fish: Salmon and other fatty fish are high in omega-3 fatty acids, potent anti-inflammatories that support the immune system and help combat the effects of gum disease.
- Nuts and seeds: are a great source of omega-3s. Just chew carefully to avoid irritating sensitive gum tissues.
- Probiotic-rich foods: Fermented foods like yogurt introduce healthy bacteria into your mouth, helping to balance the microbiome and keep gums healthy.
- Chicken: is an anti-inflammatory nutrient linked to gum health, and collagen, which supports the structural integrity of gum tissues.
- Water: Staying hydrated with plenty of water helps flush out bacteria and food debris, promoting cleaner gums and overall oral health.
Foods to avoid for gum health
- Sugary snacks and drinks: Sugar feeds the bacteria in plaque, worsening gum disease and leading to tooth decay.
- Acidic foods: While citrus fruits like oranges are healthy in moderation, excessive consumption can irritate sensitive gums.
- Hard or sticky foods: Sticky foods can remain trapped in teeth, encouraging bacterial growth, while hard foods may damage or irritate tender gums.
By incorporating these gum-friendly foods into your diet and avoiding harmful ones, you can support your oral health, prevent gum disease, and strengthen your gums. Combined with regular oral hygiene and dental check-ups, a balanced diet plays a key role in maintaining a healthy smile.
How to Monitor Your Gum Health at Home
Regular self-checks can help you identify early signs of gum problems and take action before they escalate. Here’s how to monitor your gum health effectively:
- Observe your gums: Watch for signs of irritation like redness, swelling, or bleeding during brushing or flossing. Additionally, check if your gums appear to be receding, exposing more of your teeth or their roots, which could indicate a problem.
- Be aware of unusual symptoms: Stay alert to unusual symptoms such as persistent bad breath or an unpleasant taste in your mouth, as these could indicate a gum infection. Additionally, pay attention to any sensitivity near the gum line or discomfort while eating or chewing, as these may signal underlying issues.
- Evaluate your efforts: Monitor your progress if you’ve begun with a gum disease treatment at home, by noting improvements. If symptoms persist or worsen after two weeks of consistent care, it’s important to consult a dentist for further evaluation and treatment.
By staying attentive to these changes, you can ensure your gums remain healthy or address potential problems early.
When to see a Dentist

Recognizing the need for professional care and seeking timely treatment can prevent severe damage and help restore gum health effectively. While gum disease treatment at home can be effective for mild cases, regular dental check-ups are key to catching problems early and avoiding more invasive procedures. You should consult a dentist if you experience:
- Persistent swelling, redness, or bleeding gums despite consistent home care.
- Pain in your gums or teeth that doesn’t improve over time.
- Loose teeth or noticeable gaps forming between teeth.
- Pus around the gum line, which may indicate a serious infection.
Professional Interventions
Scaling and root planing: A deep cleaning procedure that removes tartar and bacteria from below the gum line. It smooths the tooth roots to prevent further bacterial buildup, allowing the gums to heal.
Laser therapy: This minimally invasive treatment targets and removes infected gum tissue while promoting faster healing and reducing discomfort.
Surgical options: In advanced cases of gum disease, surgical treatments may be required to restore gum health and prevent further damage:
- Flap surgery involves lifting the gums to thoroughly clean deep beneath them, then repositioning the tissue to reduce pockets and make maintenance easier.
- Gum grafts use healthy tissue, often taken from another part of the mouth, to repair areas of severe gum recession, protecting exposed tooth roots and improving overall gum structure. These procedures aim to restore functionality, prevent further progression, and enhance oral health.
Conclusion
Gum disease is a common but manageable condition, especially in its early stages. With consistent gum disease treatment at home as oral hygiene, natural remedies, and a gum-friendly diet, you can effectively treat mild cases of gum disease. However, it’s essential to stay vigilant and seek professional care if symptoms persist or worsen.
By taking proactive steps to care for your gums, you not only protect your oral health but also contribute to your overall well-being. Start implementing these tips today for healthier, stronger gums and a confident smile!
Frequently Asked Questions
Can gum disease be reversed at home?
What’s the fastest way to treat gum inflammation?
Is oil pulling effective for gum disease?
What foods help improve gum health?
When should I stop home treatment and see a dentist?
Share
References
1. Brazier, Y. (2024, january 4). What is periodontitis?. Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/242321
2. Cleveland clinic staff. (2024, September 9). Gingivitis. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10950-gingivitis-and-periodontal-disease-gum-disease
3. Cronkleton, E. (2024, september 3). 10 Home Remedies for Gingivitis. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/dental-and-oral-health/gingivitis-home-remedy#takeaway
4. Fletcher, J. (2024, july 22). Medical news today. How to relieve gum pain fast. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326107
5. Rani, N., Singla, R. K., Narwal, S., Tanushree, N., Kumar, N., & Rahman, M. M. (2022, september 6). Medicinal Plants Used as an Alternative to Treat Gingivitis and Periodontitis. Evidence-based Complementary And Alternative Medicine, 2022, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2327641
- Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...Recent Posts