Last Updated on: 12th June 2024, 08:37 am
✓ Fact Checked 🕓
❙ Our team of writers, editors, and medical experts rigorously evaluates each article to ensure the information is accurate and exclusively cites reputable sources.
❙ We regularly assess how the content in this article aligns with current scientific literature and expert recommendations in order to provide the most up-to-date research.
Understanding Blue or Gray Teeth: A Complete Guide with Solutions
Dental pigmentation is one of the main reasons for a dental consultation, as it directly affects the aesthetics and self-esteem of patients. Depending upon the cause of the discoloration, there are various solutions to combat stains on teeth, and the success of the treatment depends upon a correct diagnosis. Join us to discover everything about gray or blue teeth.
What Causes Stains on Teeth?
There are many causes of stains and pigmentation on the teeth. There are two types of stains:
1. Extrinsic dental stains
Extrinsic stains are acquired after the tooth is formed; they are associated with the consumption and/or use of medications, drinks, materials, and some foods. The pigment that causes the stain is called chromogen. Some examples are those generated by:
• Tobacco consumption
• Coffee
• Wine
• Chocolate
• Iron supplements
2. Intrinsic dental stains
They are the stains that originate during tooth formation; they appear mainly on permanent teeth and sometimes on temporary teeth. The most common causes of intrinsic dental stains are:
• Use of some medications
• Excessive oral fluoride consumption
• Genetic issues
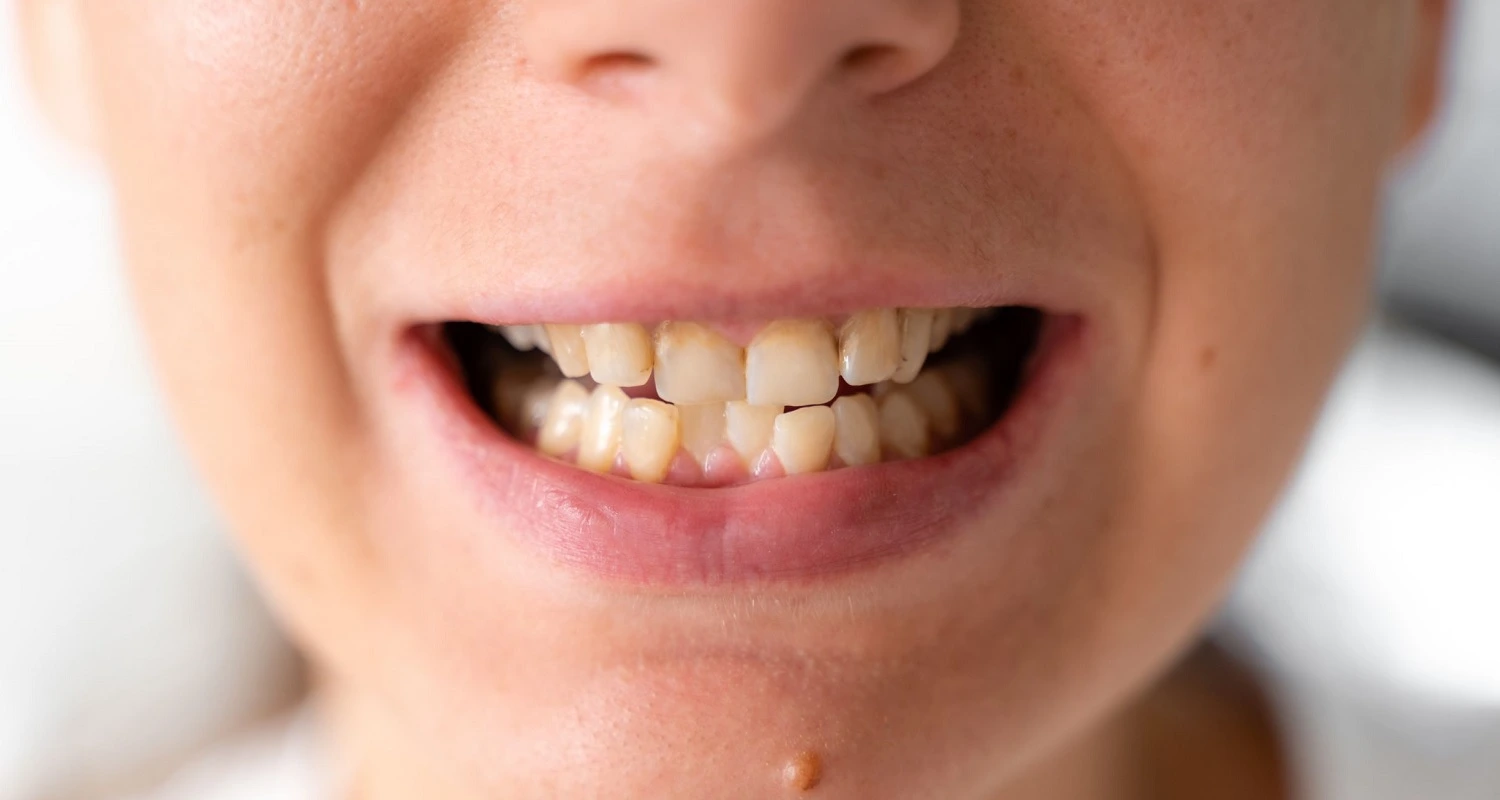
Gray Teeth
1. Teeth may take on a grayish color due to
2. Dental trauma
3. Amalgam restorations
4. Dental cavities
5. Restorations in poor condition
6. The use of some endodontic materials
7. Fluorosis
Blue Teeth
The main causes of blue teeth are:
1. Genetic alterations: Genetic defects that alter dentin formation (Dentinogenesis imperfecta)
2. Oral consumption of antibiotics: The use of medications such as tetracycline, and minocycline.
3. Placement of medications inside the tooth: Remains of antibiotics (triantibiotic paste) used to manage dental trauma and infections.
4. Chromogenic bacteria: Some authors claim that some bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa. They could cause pigmentation on the teeth.
What is Dental Fluorosis?
Dental fluorosis is a disease that affects the formation of the hard tissues of permanent teeth, such as the dentin and enamel. It is caused by excess fluoride consumption, which produces a characteristic pigmentation that ranges from white, grayish, bluish or even brown tones. This is one of the main reasons of blue or gray teeth.
What are Tetracycline Stains?
Tetracycline stains are pigmentations specific to the tooth (intrinsic), secondary to the use of a group of antibiotics called tetracyclines, used to treat infections. These pigmentations can cover one or several teeth. Its treatment depends upon the severity and extent.
How is Tooth Color Evaluated?
• Tooth color evaluation is carried out through observation and comparison with pre-established color guides.
• It is subject to the dentist’s experience, visual acuity and even eye strain.
• Instruments such as the colorimeter or spectrophotometer can be used; they are more efficient but require expensive equipment.
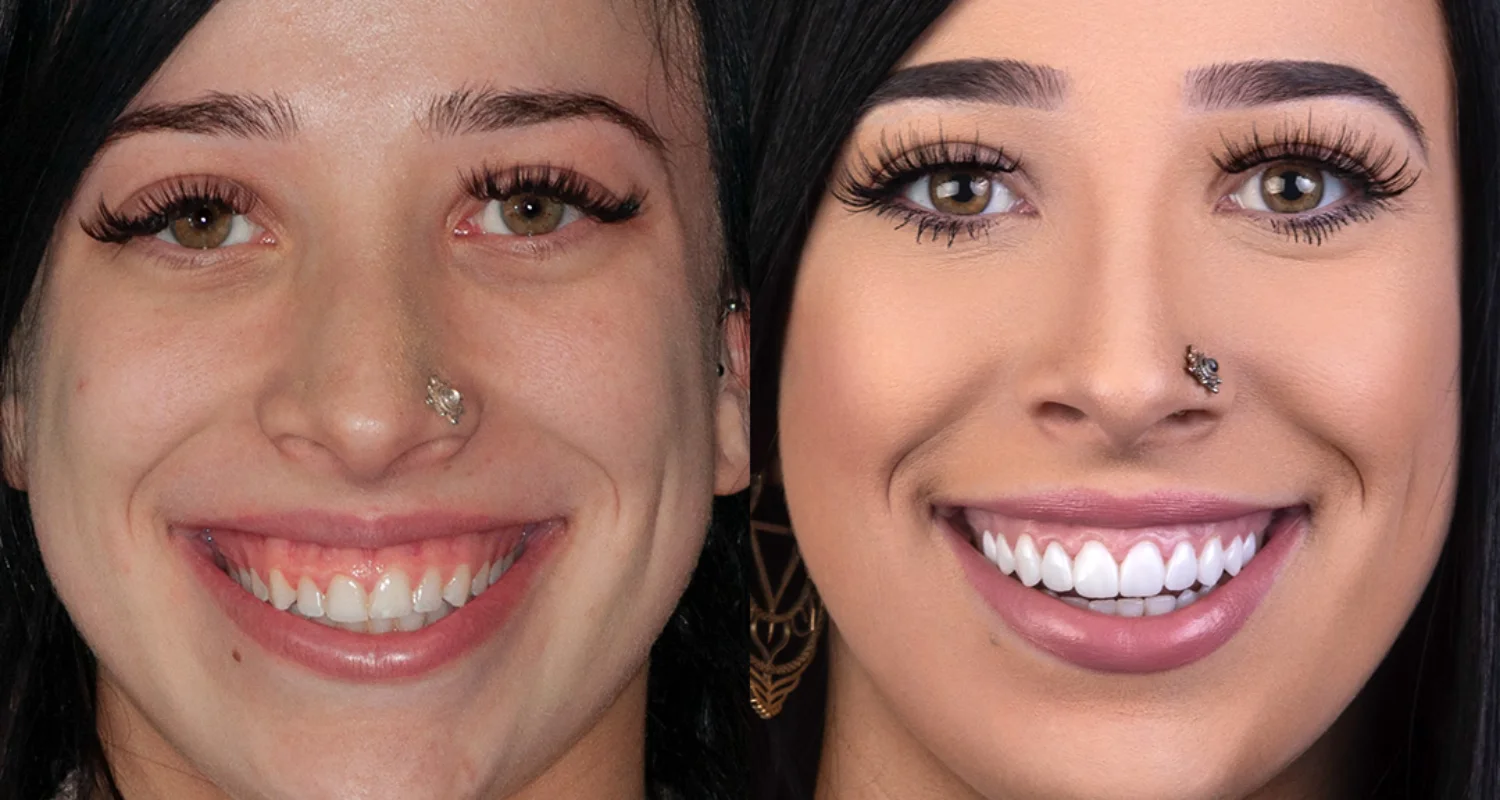
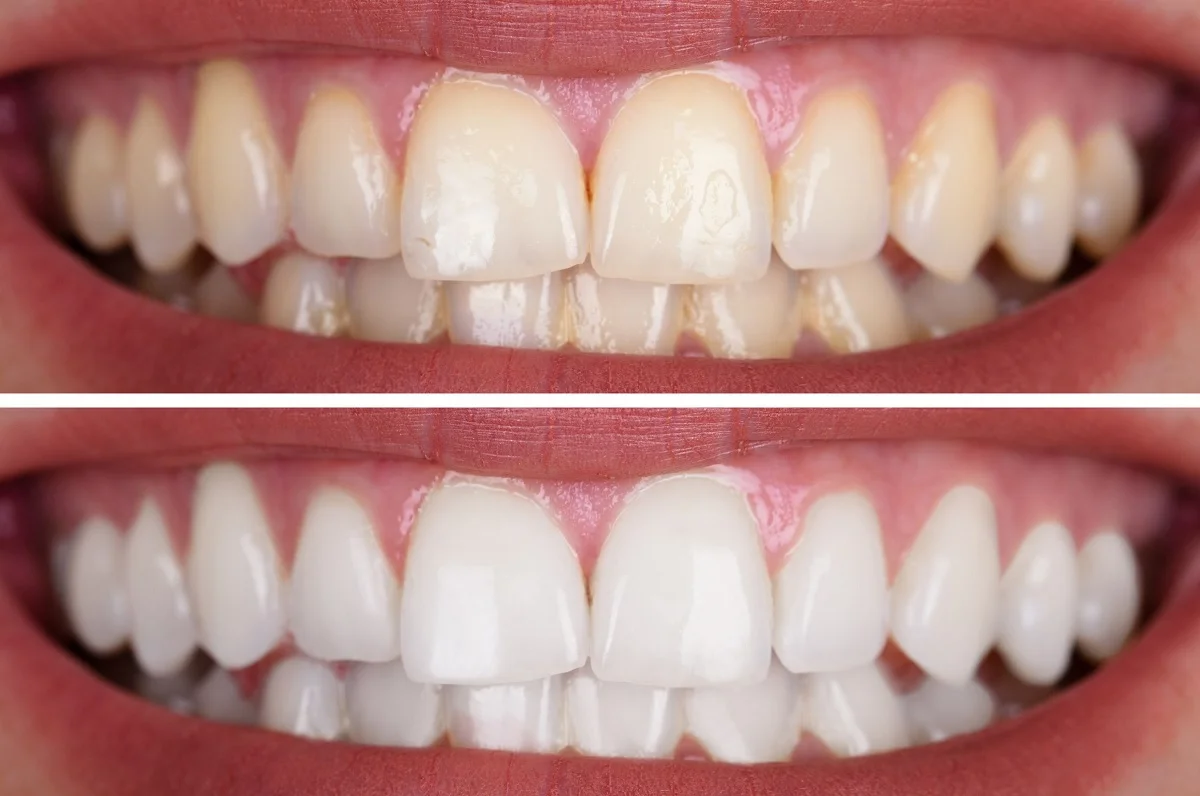
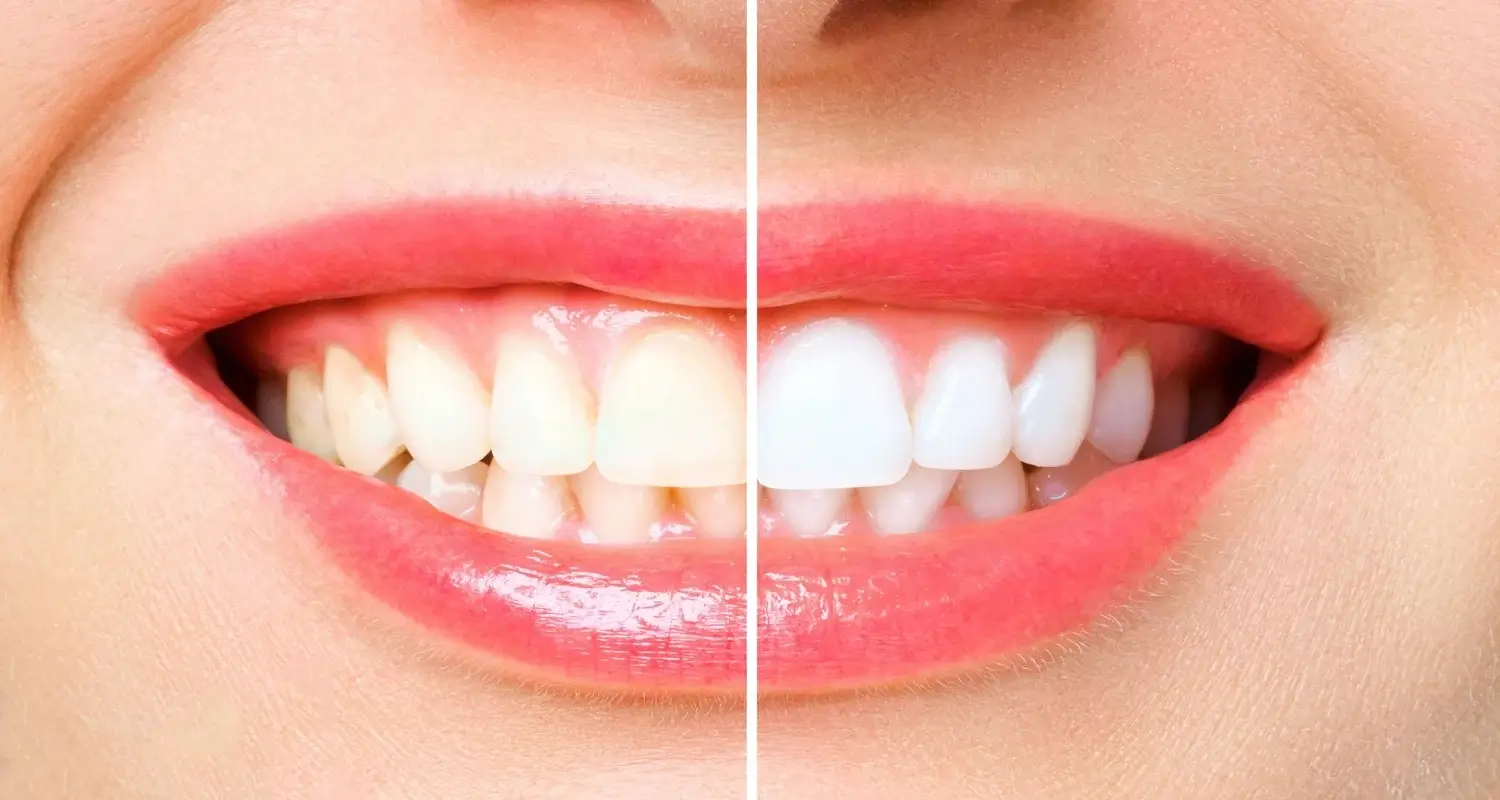
Teeth Whitening
Teeth whitening as a procedure seeks to eliminate extrinsic dental stains and in some cases, intrinsic dental stains. Products based on hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide are usually used to destroy the substance that causes the stain, also called chromogen. It is not recommended for children under 15 years of age or pregnant women.
Can Teeth Whitening be Done at Home?
There are home teeth whitening and dental office teeth whitening procedures. In fact, many teeth whitening protocols include in-office sessions combined with at-home treatment, for greater effectiveness. However, home teeth whitening should also be supervised by the dentist for best results and fewer unwanted effects. If you want to know more about teeth whitening both professional and at-home methods, click here.
How to Avoid Sensitivity After Whitening?
Tooth sensitivity is the most common unwanted effect after teeth whitening since it affects the most superficial layer of the tooth: the tooth enamel. A patient is more likely to experience tooth sensitivity after whitening if:
• There is a long-term use of a teeth whitening agent.
• Excessive treatment sessions
• Whitening in teeth with previous sensitivity or with exposure of the root.
Sensitivity Treatment
• Application of fluorides such as fluoride varnish, gel fluoride, or neutral PH fluoride.
• Avoid citrus drinks or drinks with high acid content such as citric or phosphoric.
• Use caution and inform the dentist if your teeth have or have previously had tooth sensitivity.
• Do not carry out whitening sessions continuously and without recovery periods.

What Products can be Used to Whiten Teeth?
To treat tooth stains, some of the following products can be used:
• Whitening toothpaste
• Specialized rinses
• Whitening strips
• Personalized gel and splints for home whitening
• In-office teeth whitening
For best results and greater safety during teeth whitening, the procedure should be supervised by a dentist. The above will also avoid unwanted effects in the future such as tooth sensitivity.
What is Dental Microabrasion?
Dental microabrasion is a procedure that aims to partially or eliminate intrinsic dental stains, by polishing the tooth surface where the stain is located then abrading and chemically treating the dental stain. In most cases, substantial improvements in tooth color are achieved.
When to Use Microabrasion or Teeth Whitening?
• Microabrasion is recommended for permanent teeth with defects in their development, that is, stains that have not been acquired due to eating habits.
• Dental whitening is usually indicated in cases of extrinsic stains and in some cases of stains specific to the tooth.
Remember that both procedures must be supervised and carried out by a dentist.
Conclusion
• Identifying the root of the problem is the first step in successfully addressing pigmentation in your teeth such as blue or gray teeth.
• Teeth whitening is an effective option for removing extrinsic dental stains like blue or gray teeth, but it should be performed with caution and professional supervision to avoid tooth sensitivity and other unwanted side effects.
• The choice between microabrasion and whitening depends on the nature of the stains, either blue teeth or gray teeth, and should be determined by a dentist.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are GRAY-blue stains on my teeth?
Over time, teeth can naturally change color as the enamel thins, revealing more of the color of the dentin. Your teeth can also take on blue or gray tones. These alterations can be the result of extrinsic or intrinsic stains, caused by disorders, medications, trauma, among other factors.
Why do some of my teeth have blue or GRAYY shades?
Teeth without vitality: If you notice that one or a few teeth are taking on a gray or blue hue, they may have lost their vitality. Contrary to what many might think, teeth have living pulp and nerves inside. When damaged due to trauma or infection, these nerves and pulp can cease to be alive, resulting in a tooth that turns dark pink, gray, or even black.
Why do my teeth turn blue?
A natural reason for teeth to change color is a rare genetic disease called dentinogenesis imperfecta. This condition impacts the appearance and structure of the teeth, causing the enamel to show shades from yellowish brown to blue-gray. Having teeth that are not completely white can affect our self-esteem.
Why do teeth acquire gray tones over time?
As we age, the enamel, which is the hard, outer layer of our teeth, wears away, revealing the darker underlying dentin. This can cause teeth to appear more grayish or yellowish instead of white. Additionally, some medications can cause dental stains.
Share:
References
1. DIt isntinogenesis imperfecta. (2023). Medlineplus.gov. https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/dentinogenesis-imperfecta/
2. Larson, J. (Sep 15, 2021). Blue light teeth whitening: Is it safe, and does it work? Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/dental-and-oral-health/blue-light-teeth-whitening
3. Tooth discoloration. (s/f). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/10958-tooth-discoloration
4. Torborg, L. (Jul 28, 2015). Mayo Clinic Q and A: Many safe choices available to help whiten teeth. Mayo Clinic News Network. https://newsnetwork.mayoclinic.org/discussion/mayo-clinic-q-and-a-many-safe-choices-available-to-help-whiten-teeth/
5. Mortazavi, H., Baharvand, M., & Khodadoustan, A. (2014).Colours in tooth discoloration: a new classification and literature review. International Journal of Clinical Dentistry, 7(1).
6. Bussell, R. M., & Deery, C. (2010). Case report: Blue chromogenic dental staining in child with West syndrome. European archives of paediatric dentistry : official journal of the European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry, 11(6), 298–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03262767