Last Updated on: 12th December 2025, 05:11 am
Treatment for Ranula: Management and Complications
Ranula is an oral condition that, although relatively uncommon, can cause significant discomfort to sufferers. In this article, we will talk about ranula, exploring its causes, diagnosis, and available treatment options. From surgery to non-invasive therapies, we will take an in-depth look at strategies to address this condition, as well as potential complications that patients and dental health professionals should be aware of. Our goal is to provide a complete overview of the management of ranula, allowing patients to learn about the solutions available for this pathology.
What is a Ranula?
A ranula is a mucus-filled bump that appears on the floor of the mouth, under the tongue. It manifests itself as a bluish mass, is usually painless, and has a fluctuating consistency.
What Causes a Ranula?
The underlying causes of ranulas are diverse and include trauma to the salivary ducts, which is the most common cause, as well as mechanical obstructions, due to stones or mucus plugs. They can also be generated by chronic inflammatory diseases such as Sjogren’s syndrome or HIV infections. Still, many ranulas have no known cause.
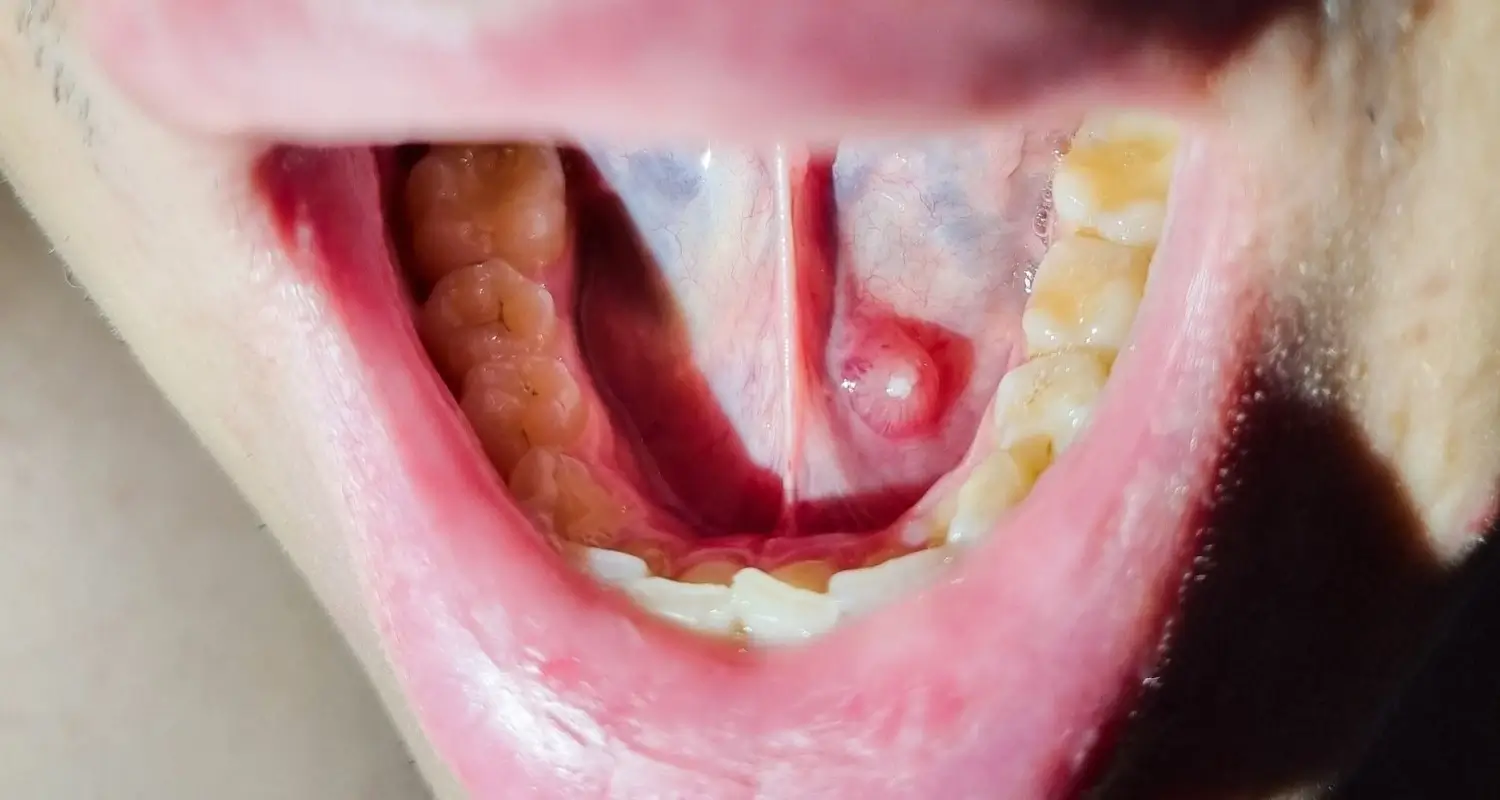
What are the Types of Ranulas?
There are two types of ranulas.
● Oral or simple ranulas: They generally originate from trauma to the salivary glands, although this is not always the case. They are seen inside the mouth.
● Cervical or sunken ranulas: The mucosal contents of the lesion penetrate the deeper tissues, behind the muscles under the tongue. They often do not present notable alterations in the oral cavity, but rather a bulge is observed in the neck area. According to experts, approximately half of cervical ranulas occur as a result of incomplete removal of oral ranulas.
Treatment of Ranulas
As for any medical condition, the treatment of a ranula will vary, depending upon the patient’s condition, that is: their general health, location, and size and cause of the ranula. A surgical approach is usually used to treat the condition, although less invasive procedures could be applied, according to the particular situation. Treatment options for a ranula include:
1. Sewer system
A treatment used as emergency management, in case the ranula is causing discomfort to the patient and definitive treatment is not possible at the time. It consists of making an incision that allows the contents of the ranula to drain, thus reducing its size. However, this is not considered a definitive treatment, and the injury could persist.
2. Surgical excision
Excision or surgical removal of the lesion along with the salivary gland causing the problem has been reported as the most effective treatment for ranulas. By eliminating the cause, the probability of the ranula appearing again is very low.
3. Marsupialization
A procedure in which a small window is opened and fixed with stitches, through which the liquid contained inside the ranula can drain continuously until the lesion disappears. However, if the ranula cannot be removed by this technique, it is necessary to perform surgical excision of the salivary gland. It has been shown that when ranulas are treated by marsupialization, they could return between 36.4% and 66.7% of cases.
4. Laser treatment
Lasers provide less aggressive therapies with shorter recovery periods that work for the treatment of small ranulas.
5. Injectable sclerosing therapy
Some medications can be injected into the area, producing an inflammatory reaction that helps resolve the ranula. However, more than one injection is usually required to achieve the desired effect. This therapy works in 91.2% of cases, but about 22% of cases could recur. Therefore, it is usually limited to the management of small ranulas.
Natural Treatments for Ranula:
Several natural treatments can be useful in alleviating symptoms associated with a ranula. An effective method is to use warm salt water mouth rinses. This solution can help reduce inflammation and promote healing. Simply dissolve a teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and rinse your mouth several times a day.
Tea tree oil is another natural option for treating a ranula. This oil has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce the size of the cyst. Apply a few drops of the oil directly to the affected area and gently massage.
Finally, aloe vera is an efficient home remedy for a ranula. Its anti-inflammatory properties can relieve swelling and pain. Apply a small amount of aloe vera gel to the affected area and leave it on for a few minutes before rinsing.
What do the Experts Say?
Although less invasive treatments have been proposed as compared to the surgical removal of the sublingual salivary gland, it has been shown that, in cases of superficial ranulas, if they are not removed along with the salivary gland that caused the problem, the condition can return between 25% and 56.7% of cases.
Do Deep Ranulas Require Neck Incisions?

No. Most deep ranulas can be treated through the mouth. An effective solution can be obtained by removing the sublingual gland by making a small incision in the floor of the mouth, just below the tongue. This access will allow the accumulation of mucus in the area to be evacuated.
What is the Recovery Time for Ranula Surgery?
Recovery after ranula surgery can take 1 to 2 weeks. Typically, your doctor will place stitches that will dissolve on their own within a few days. The following factors could modify recovery times:
● Patient age
● Other associated diseases, such as diabetes
● Diet
● Rest
Care After Ranula Surgery
Take into account the following tips after ranula surgery:
● Stay rested
● Avoid sleeping too much lying down, try to place 2 or 3 pillows under your head.
● Do not exert effort or physical exercise for two weeks.
● Prefers a soft and balanced diet, rich in vegetables, protein, and vitamin C.
Complications Associated with a Ranula
Before performing the treatment:
● Infections
● Rupture and reappearance of the ranula.
● Problems eating and breathing, when it comes to large ranulas.
During surgery:
● Hemorrhages
● Damage to adjacent salivary ducts, which can cause blockages.
● Damage to the lingual nerve, which can cause numbness or loss of sensation in the
● Tongue, temporarily or permanently.
● Damage to nerves that control movement of the lower lip and chin.
After surgery:
● Hematomas or bruises
● Infections
● Inadequate healing
Can Ranulas be Dangerous?
Although it is not common, cervical or sunken ranulas can become large, compromising respiratory function. They can also cause a condition called acute mediastinitis; this is a serious infection in the area of the chest called the mediastinum, where many vital organs are located, and it could be life-threatening.
Conclusion
Ranula treatment varies depending upon the patient’s situation, with a focus on surgery to remove the sublingual salivary gland as the most effective treatment, but less invasive alternatives are also explored, such as laser therapy or the injection of sclerosing substances.
Despite their relatively low incidence, ranulas can lead to significant complications, including infections, nerve damage, and, in severe cases, the possibility of life-threatening acute mediastinitis. Therefore, early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential to address this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most effective therapy for a ranula?
The way to treat a ranula varies, depending upon different factors such as its magnitude and the severity of the symptoms. In some cases, the ranula may fade spontaneously; but in most scenarios, medical intervention is required. Treatment alternatives may include needle aspiration, cutting and emptying of the cyst, marsupialization, or even complete removal of the ranula through surgery.
What is the therapeutic strategy for a ranula?
One of the alternatives to treat ranula is marsupialization, in which the health professional makes a cut in the cyst and then sutures its edges, thus allowing free drainage of the cyst contents. If pain occurs, your doctor may suggest giving a steroid injection into the tissue underlying the cyst.
What is the preferred diagnostic procedure method for ranula?
Various diagnostic imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT), ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be used to evaluate a ranula. At the level of surgical treatment, the alternatives vary from marsupialization to complete removal of the sublingual gland, including simple excision of the cyst.
What are the dangers associated with ranula surgery?
The potential risks of this type of surgical intervention include paresthesia or numbness of the lingual nerve, which has been reported in up to 25% of cases according to some studies, as well as damage to the Wharton duct, which could result in obstructive sialadenitis. . Additionally, there is the possibility of laceration of the salivary duct, which could cause saliva to leak.
Share:
References
1. Ranuli. (s/f-b). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23451-ranula
2. Baurmash, H. D. (2003). Mucoceles and ranulas. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: Official Journal of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons, 61(3), 369–378. https://doi.org/10.1053/joms.2003.50074
3. Bowers, E. M. R., & Schaitkin, B. (2021). Management of mucoceles, sialoceles, and ranulas. Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America, 54(3), 543–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2021.03.002
4. Higuera, V. (2017).Ranula: Plunging, cyst, and surgery. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/ranula
5. Huzaifa, M., & Soni, A. (2023).Mucocele and Ranula. StatPearls Publishing.
6. What is a ranula? (s/f). WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/what-is-ranula
7. Ranuli. (s/f-a). Nationwidechildrens.org. https://www.nationwidechildrens.org/conditions/ranula
- Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...Recent Posts