Last Updated on: 27th December 2025, 05:38 am
Most people will experience an episode of swollen taste buds at some point in their lives. It does not usually imply a serious health condition, but it can cause an unpleasant sensation when eating food. In this article, we will inform you about swollen taste buds, their most frequent causes, symptoms, and recommended treatment.
What are Taste Buds?
The tongue is the organ in charge of the sense of taste, and it is covered with small structures called taste buds. These tiny sensory organs can take various shapes and are responsible for perceiving the different flavors: sweet, salty, bitter, and sour.
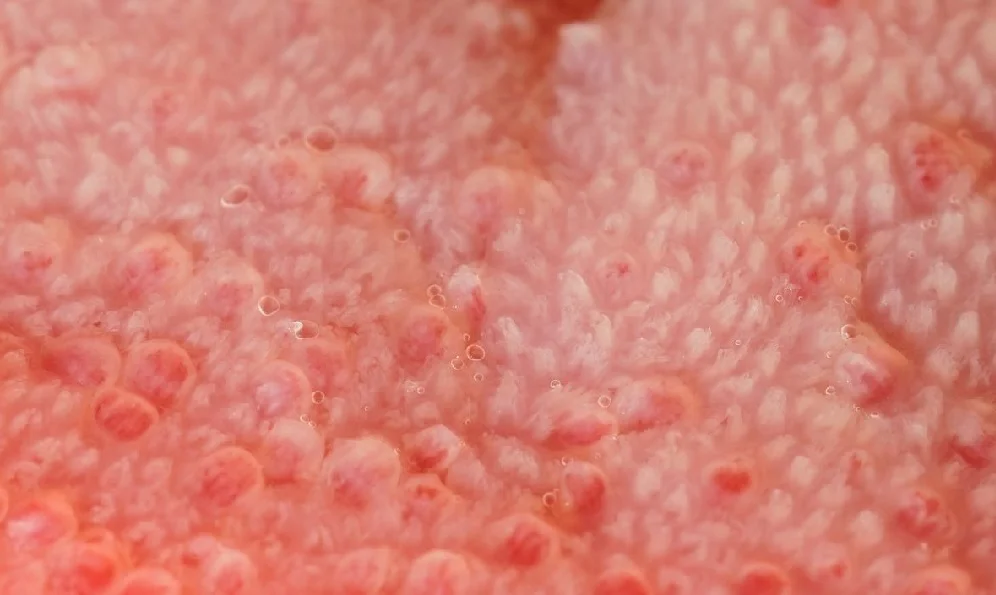
What are the Symptoms of Swollen Taste Buds?
This condition, also known as tongue papillitis, can occur in a small area of the tongue or in a generalized way. Typically, the duration of symptoms varies from a few hours to 2 weeks.
When taste buds become inflamed they can cause:
• Pain and tenderness, especially when eating hot food
• Increased size of the lingual papillae
• Changes in the sense of taste
• Burning sensation
What do Inflamed Taste Buds Look Like?
When the taste buds become inflamed, you will see:
• An increase in size
• A reddish, yellowish, or whitish appearance (although not always)
Why are Taste Buds Inflamed?
Inflammation of the taste buds can have multiple causes. The most frequent are:
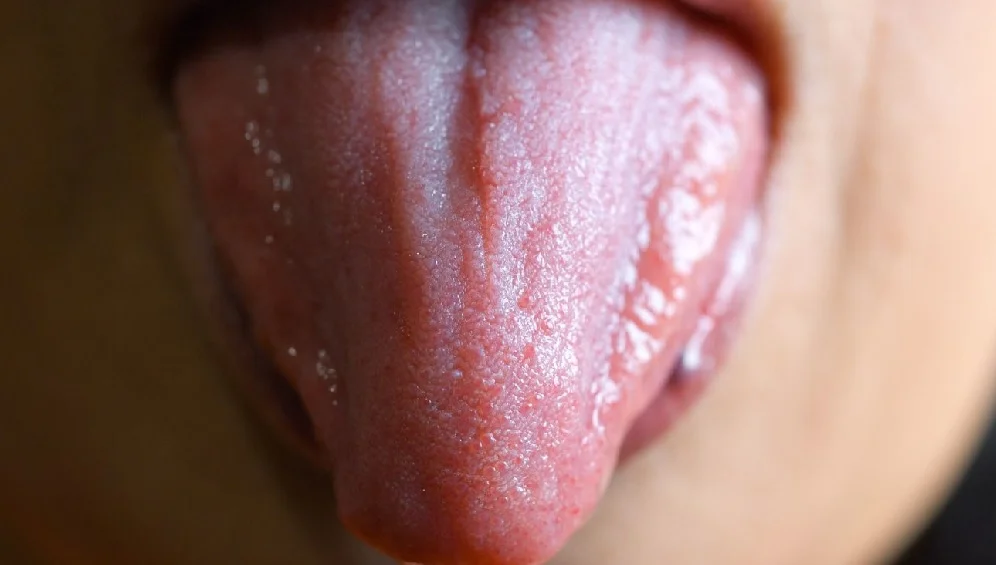
1. Gastroesophageal reflux
When stomach acid reaches the mouth as a result of reflux, it can irritate the tongue papillae.
2. Allergies
Some people tend to be more sensitive to certain substances than others. The papillae can become inflamed after coming into contact with irritating foods or chemicals.
3. Viral or bacterial infections
Infections with certain microorganisms can cause tongue problems. When tongue inflammation is caused by a microorganism, it is usually accompanied by other symptoms, such as fever and discomfort.
4. Very hot food or drinks
These can burn the papillae, causing them to swell.
5. Smoke
Chemical substances such as tobacco added to an increase in the temperature of the mouth can cause papillitis.
6. Nutritional deficiencies
When you don’t consume enough vitamins and minerals like iron, your tongue may swell.
7. Prostheses or restorations in poor condition
If these come into contact with the tongue, they can hurt the papillae and generate an increase in size, pain, and redness in the affected area.
8. Very acidic or spicy foods
Extreme flavors when consumed in excess can injure the taste buds and cause discomfort; it generally does not last more than a few hours.
What is Transient Papillitis of the Tongue?
When the inflammation of the tongue papillae lasts a few days (maximum one week) it is called transient papillitis of the tongue. Generally, it is caused by bites, burns, contact with irritating substances, or the consumption of certain foods.
Can Inflammation of the Tongue Papillae Imply a Serious Health Problem?
Although it is not a frequent reason for inflammation in the tongue papillae, it is important to mention that a tongue inflammation that does not heal can be one of the first signs of oral cancer. The risk of suffering from this condition increases in men over 50 years of age, with tobacco use being an additional predisposing factor.
How to Relieve Inflamed Taste Buds?
Here are 9 tips to ease the discomfort caused by swollen taste buds:
1. Rinse with warm water and salt 3 times a day.
2. Place ice on the tongue before eating since the cold has anesthetic properties.
3. See your doctor to manage acid reflux.
4. Avoid foods that are too sweet, sour, or hot.
5. Practice good oral hygiene habits, brushing your teeth after each meal.
6. Do not use mouthwashes with alcohol, as they can further irritate the tongue.
7. Apply over-the-counter topical anesthetics to decrease discomfort. This should be avoided in children since they can be toxic in young patients.
8. Make rinses with calendula infusions to reduce inflammation.
9. Limit consumption of cigarettes and vapers.
Medical Treatments

There are a few cases of inflammation of the tongue papillae that require medication. Symptoms usually resolve after a few days, but if treatment is required, it will depend upon the cause of the inflammation. If papillitis is caused by a viral or bacterial infection, a health professional may prescribe medication or a particular mouthwash to treat it.
When to See a Doctor?
Normally, the inflammation of the taste buds subsides without the need for treatment. However, it is advisable to seek medical attention if you have any of the following symptoms:
• Inflammation of the tongue papillae that does not resolve after one week
• Fever
• Swelling of the lymph nodes
• Recurrent inflammation (when the swelling of the papillae comes and goes)
• Localized or multiple growths of the tongue
• Changes in the taste of food
• Large lesions that are not painful
Conclusion
Tongue papillitis is a condition that can affect everyone at any time. It is advisable to identify the foods and substances that trigger this inflammation and avoid their consumption to maintain a healthy tongue. It is pertinent to note that when the inflammation of the taste buds occurs, accompanied by the symptoms mentioned above, it is advisable to seek medical attention.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical duration for inflamed taste buds to subside?
Normally, inflamed taste buds tend to heal on their own without any intervention and usually resolve within a few days to a couple of weeks. However, if you continue to experience them for more than 2-4 weeks or if they are increasing in size, it is advisable to consult a medical professional.
What could be the reason for the persistent presence of my swollen taste buds?
If you find that your swollen taste buds are not subsiding, it is important to seek medical attention. It is possible that inflamed taste buds may indicate a more serious underlying issue, such as tongue cancer. Therefore, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional when experiencing prolonged tongue pain.
Can taste buds become swollen during illness?
While it is uncommon, taste buds can swell as a result of a viral or bacterial infection. One notable cause is scarlet fever, which can occur in individuals with strep throat. In addition to swollen tonsils, fever, and rash, the tongue may become coated and experience peeling.
How do inflamed papillae appear?
Inflamed papillae usually manifest as small white or red bumps. “Lie bumps” occur when the papillae become irritated and swollen. Another type is called eruptive lingual.
Share:
References
1. Holland, K. (Feb 21, 2019). Supertaster: Definition, benefits, and drawbacks. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/food-nutrition/supertaster
2. Nall, R., MSN, & CRNA. (Jan 22, 2018). Swollen taste buds: Causes, diagnosis, and treatment. Medicalnewstoday.com. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320684
3. Swollen button bud. (2022). Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved May 29, 2023, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24544-swollen-taste-bud
4. Whitney DiFoggio BS, R. D. H. (Mar 9, 2023). 9 reasons for inflamed and swollen taste buds. Teeth Talk Girl. https://www.teethtalkgirl.com/dental-health/swollen-taste-buds
5. Bouquot , J. E. , Adibi , S. S. , & Sanchez , M. (2012). Chronic lingual papulosis: new, independent entity or “mature” form of transient lingual papillitis?Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology, 113(1), 111-117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2011.09.003
- Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...Recent Posts














