Last Updated on: 13th December 2025, 06:00 am
When we think of omega-3, the first thing that comes to mind are its benefits for the heart and brain. However, this essential fatty acid offers much more, especially when it comes to dental health. Integrating omega-3 for teeth into your dental care routine not only improves your smile, but they can prevent a number of oral problems. In this article, we tell you how omega-3 can strengthen your teeth and gums, prevent diseases, and improve general well-being.
Understanding Omega-3 for teeth Fatty Acids

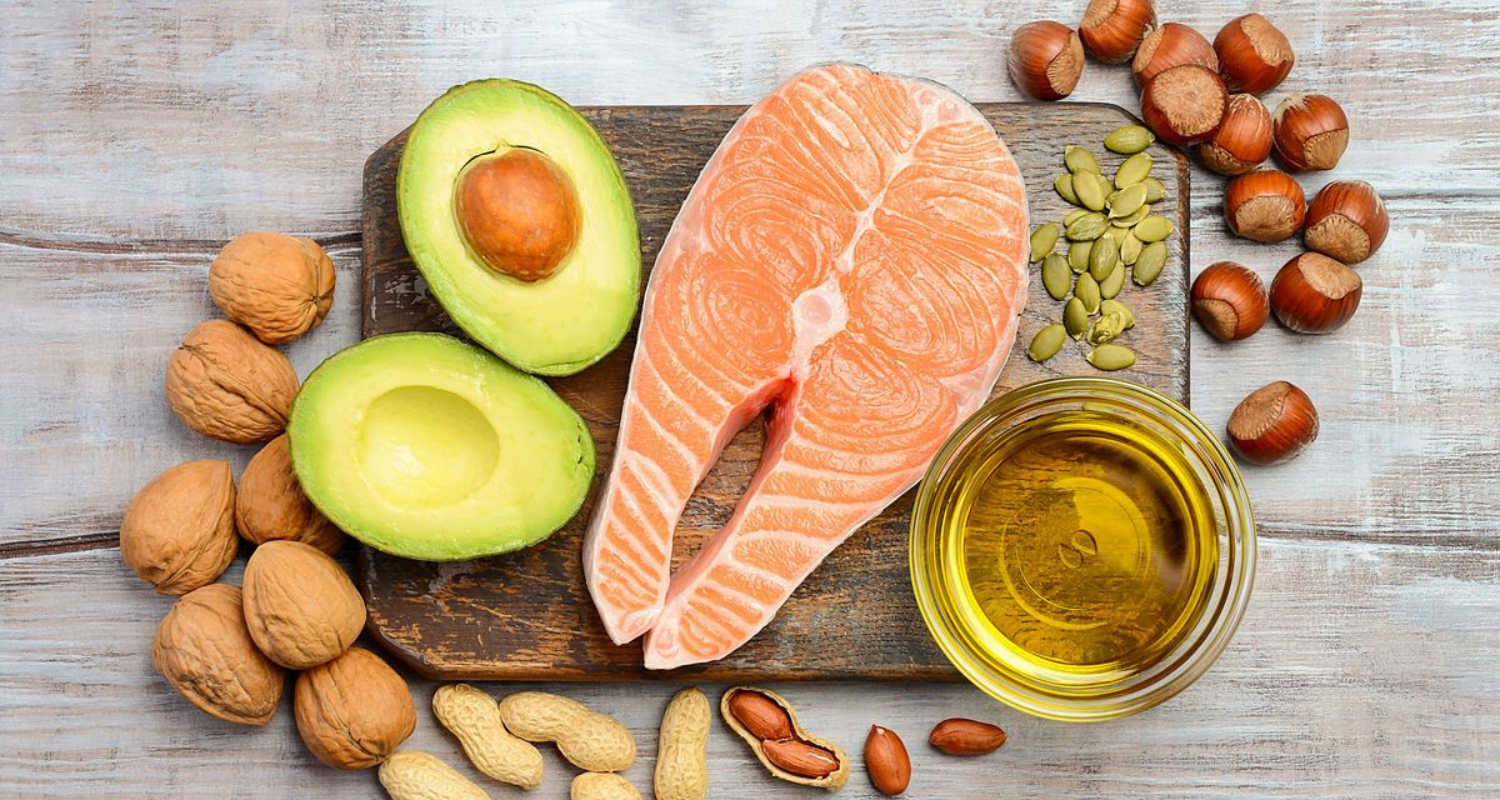
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of fat that is essential for the body, but it cannot produce them on its own. They are known for their extensive dental health benefits, including preventing gum disease and reducing inflammation. Of note, these nutrients play a crucial role in cardiovascular and brain health and keeping the mouth healthy and disease-free.
3 important reasons to include in you routine the omega-3 for teeth:
Incorporating omega-3 for teeth in your care routine offers multiple benefits that you cannot ignore:
1. It acts as a powerful ally in the prevention of gum disease, thanks to the anti-inflammatory properties that fight inflammation and infection.
2. It helps prevent cavities by inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth that contribute to tooth decay.
3. It offers a natural remedy for hyposalivation or dry mouth, stimulating saliva production and keeping the mouth hydrated.
The science behind omega-3 for receding gums
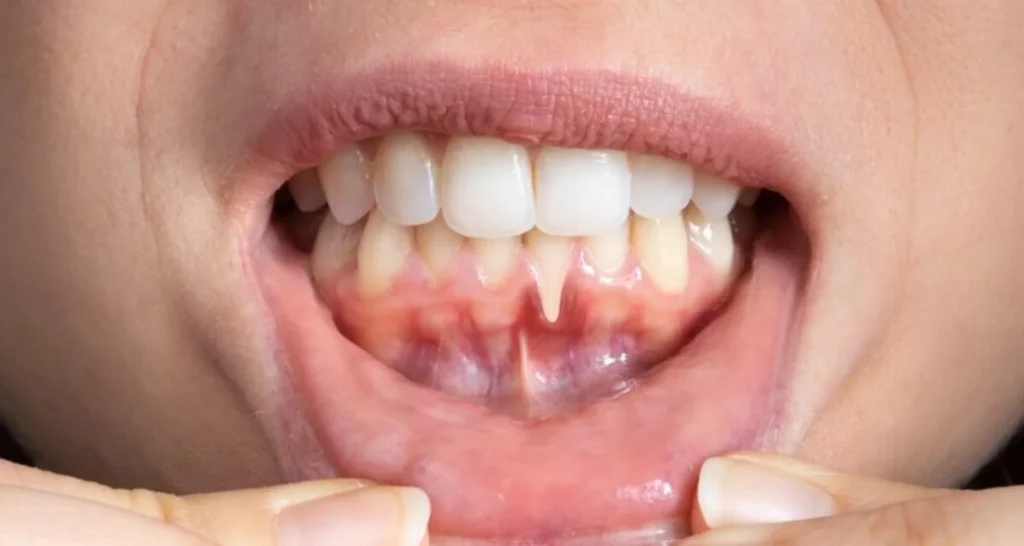
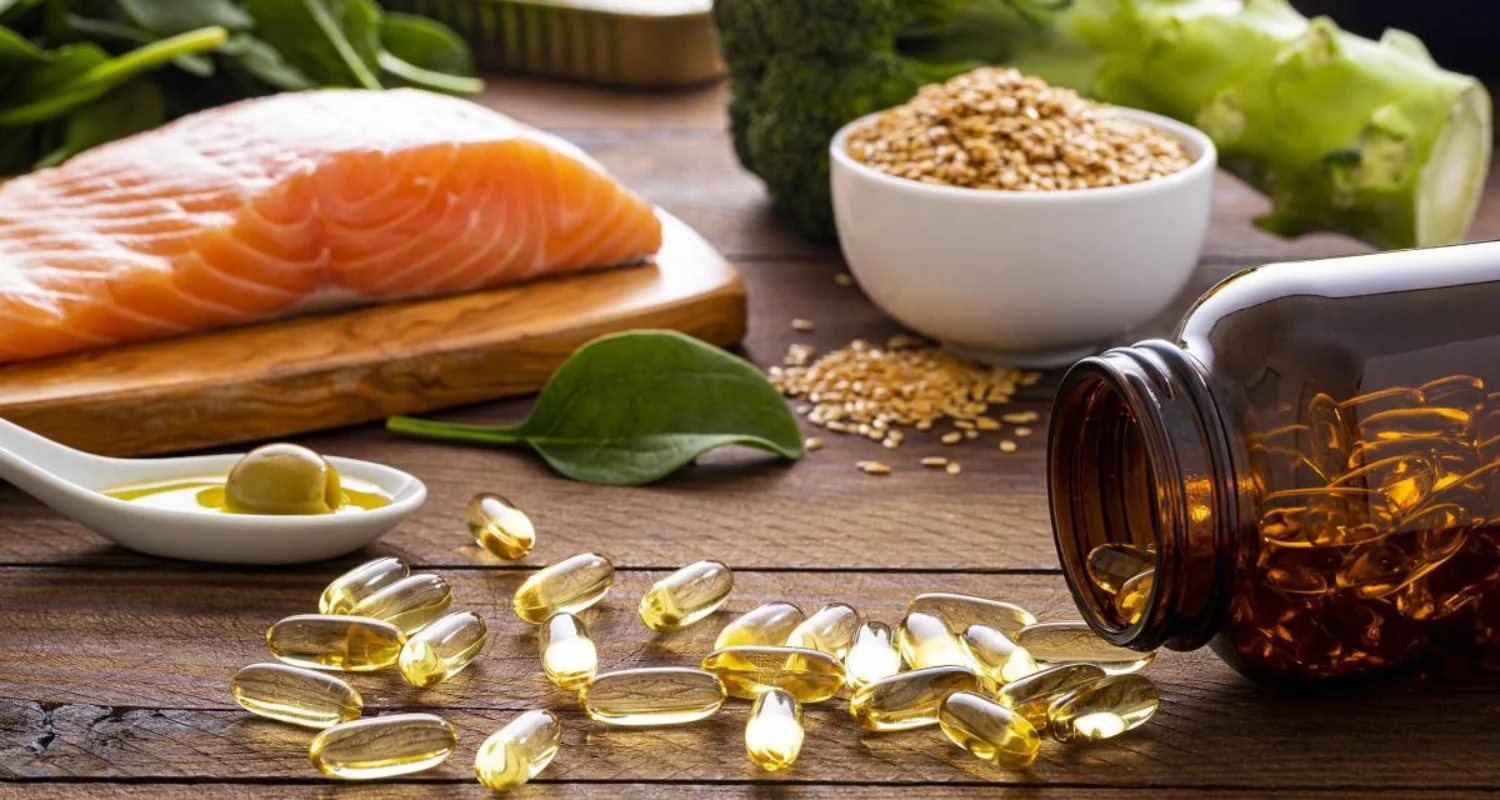
Omega-3 for teeth fatty acids are recognized for their ability to combat inflammation, a property that directly translates into oral health benefits. Research has shown that omega-3s are effective in preventing gum disease, one of the most common causes of tooth loss in adults. Gum disease, a chronic inflammation that affects the tissues that surround and support the teeth, can be mitigated by regularly incorporating them into the diet because they reduce inflammation, one of the key factors in the development and progression of this condition.
The relationship between omega-3 for teeth and periodontal disease is particularly important. Studies indicate that those who consume an adequate amount have a lower risk of developing periodontal disease, suggesting that this fatty acid may be protective against bleeding and receding gums. It is important to mention that the consumption of omega-3 not only prevents damage to gum tissues, but it is also beneficial for those who suffer from dry mouth or TMJ (temporomandibular joint) disorders.
How can omega-3 for teeth and prevent cavities?
The role of the Omega-3 for teeth and in preventing cavities is another fascinating aspect of its connection to oral health, as it helps reduce the amount of harmful bacteria in the mouth. A study carried out in 2019 showed that omega-3s can reduce the presence of Streptococcus oralis, a bacteria that causes cavities.
Additionally, there has been research into its effect in preventing dry mouth, a condition that can increase the risk of cavities and gum disease. Adding fish oil supplements to your diet or consuming more foods rich in omega-3s can be a great starting point to improve your oral health.
How much Omega-3 for teeth per day?
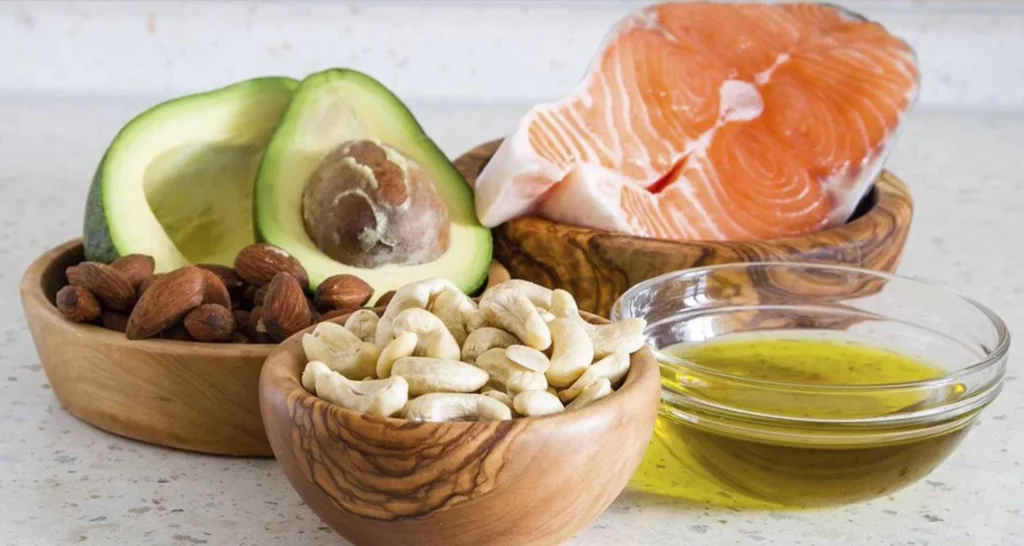

The question of how much per day is needed to obtain these dental health benefits is crucial. The optimal dosage will vary, depending on individual factors such as age, gender, and pre-existing health conditions. However, general guidelines suggest an effective range for both general and dental health. Incorporate omega-3 into your diet through foods such as:
● fatty fish (salmon or mackerel),
● walnuts and/or other seeds such as flax
● supplements
It can be an effective way to ensure you are getting the right amount. However, it is not advisable to start consuming these supplements without medical advice, since an excess of omega-3 can increase the risk of bleeding.
Incorporating omega-3 for teeth in your care routine: tips and tricks
Making omega-3 for teeth a part of your daily routine is easier than you think. Omega-3 foods are not only delicious, but they also offer a variety of options to suit all tastes. Rich sources of omega-3 include fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel, as well as flax seeds, walnuts, and fish oil supplements. For those who do not consume fish or are looking for a more concentrated dose, fish oil supplements are a convenient option that can ensure the recommended daily intake of omega-3.
The evidence is clear: omega-3 for teeth is good, but they are also a crucial ally in the fight against periodontal disease, preventing cavities, and treating receding gums. Whether through diet or supplements, making sure you get enough omega-3s can have a significant impact on your oral health. Remember, a healthy mouth is a reflection of a healthy body, and omega-3s are a fundamental pillar in this intrinsic connection between nutrition and dental health.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between omega-3 fatty acids and dental health is crucial to any comprehensive oral care routine. It’s not just about omega-3 for receding gums or combating bleeding gums but also about taking advantage of a holistic approach to health that includes nutrition as a fundamental pillar. At the end of the day, what you eat not only affects your general health but also the health of your mouth. Omega-3s are a clear example of how diet can be your best ally for a radiant smile.
Frequently Asked Cuestions
Does omega-3 benefit dental and gingival health?
Studies conducted by researchers at the University of Kentucky have revealed that omega-3 fatty acids have antibacterial qualities, capable of preventing and treating gingival diseases. These oral conditions not only compromise dental health, but are also linked to serious illnesses such as heart problems, pneumonia, and diabetes. Therefore, controlling gum disease with omega-3s not only protects teeth and gums, but they can also be a shield against other life-threatening disorders.
Do omega-3 fatty acids reduce the risk of dental disease?
You may already be familiar with omega-3 fatty acids for their ability to prevent heart disease, but did you know that they can also protect against gum disease? Periodontitis, a form of gum disease, can result in tooth loss, bad breath, as well as painful, swollen, and bleeding gums.
An added benefit of including omega-3s in your diet?
Studies suggest a connection between omega-3 consumption and improved gingival health; Adding moderate amounts of fish oil, rich in omega-3, to your diet can be an accessible and effective option to complement the treatment of periodontal diseases.
What happens if I take omega-3 every day?
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends the daily intake of DHA and EPA, combined, should not exceed 3 grams. Experts indicate that long term, omega-3s could dampen the ability of the immune system by reducing the body’s inflammatory reactions. Additionally, high doses can prolong the blood clotting period.
Can you take omega-3 tablets every day?
Yes, if consumed orally. Consuming fish oil is generally safe for most people when the dose does not exceed 3 grams daily. Ingesting amounts greater than 3 grams per day may increase the risk of bleeding. Side effects of fish oil include heartburn, diarrhea, and nosebleeds. Taking fish oil supplements during meals or freezing them can help minimize these drawbacks.
Share:
References
1. Azuma, M. M., Cardoso, C. de B. M., da Silva, C. C., de Oliveira, P. H. C., Jacinto, R. de C., Andrada, A. C., & Cintra, L. T. A. (2022). The use of omega‐3 fatty acids in the treatment of oral diseases. Oral Diseases, 28(2), 264–274. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/odi.13667
2. Naqvi, A. Z., Buettner, C., Phillips, R. S., Davis, R. B., & Mukamal, K. J. (2010). N-3 fatty acids and periodontitis in US adults. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 110(11), 1669–1675. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21034880/
3. Miller, L. M., Piccinin, F. B., Van Der Velden, U., & Gomes, S. C. (2022). The Impact of Omega-3 Supplements on Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy: A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 14(9), 1838. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/9/1838
4. Kruse, A. B., Kowalski, C. D., Leuthold, S., Vach, K., Ratka-Krüger, P., & Woelber, J. P. (2020). What is the impact of the adjunctive use of omega-3 fatty acids in the treatment of periodontitis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lipids in health and disease, 19(1), 100. https://lipidworld.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12944-020-01267-x
5. Ms, F. H. (Jan 17 2023). 17 Science-Based Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/17-health-benefits-of-omega-3
6. Professional, C. C. M. (Nov 17, 2022 Omega-3 fatty acids. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/17290-omega-3-fatty-acids
7. Naqvi, A. Z., Buettner, C., Phillips, R. S., Davis, R. B., & Mukamal, K. J. (2010). n-3 Fatty Acids and Periodontitis in US Adults. Journal Of The American Dietetic Association, 110(11), 1669-1675. https://www.jandonline.org/article/S0002-8223(10)01343-X/abstract
- Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...Recent Posts















