Last Updated on: 12th December 2025, 06:23 am
Do you want to learn how to reverse periodontitis?
Gum health is essential for a beautiful smile and good oral health. The gums are the soft pink tissues that cover the bones that house the teeth. Keeping them free of disease and inflammation is crucial. Prevention and maintenance of adequate oral hygiene are essential. However, if the gums are already affected by the disease, there are several options to treat and possibly reverse the condition. In this article, we’ll show you how to reverse periodontitis.
What is periodontitis?
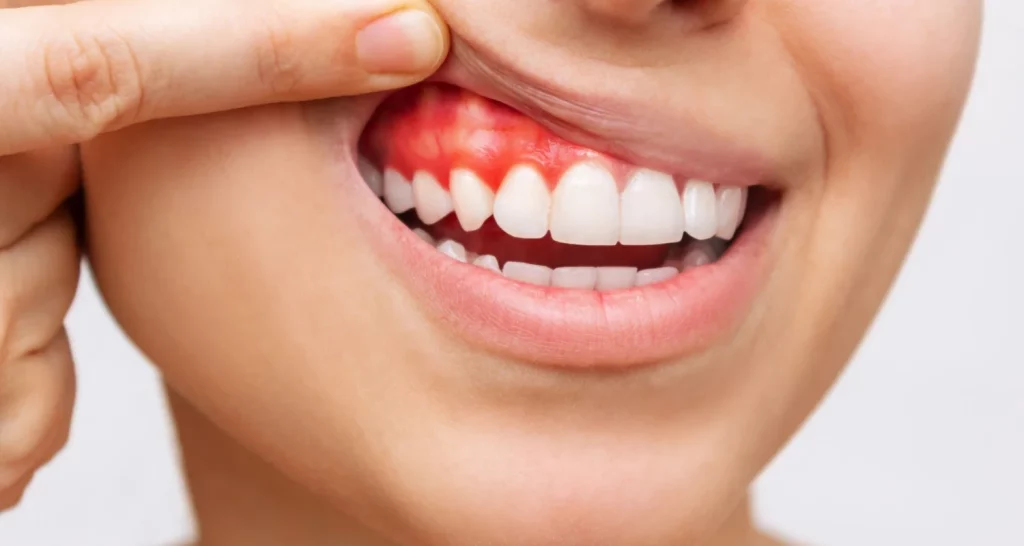
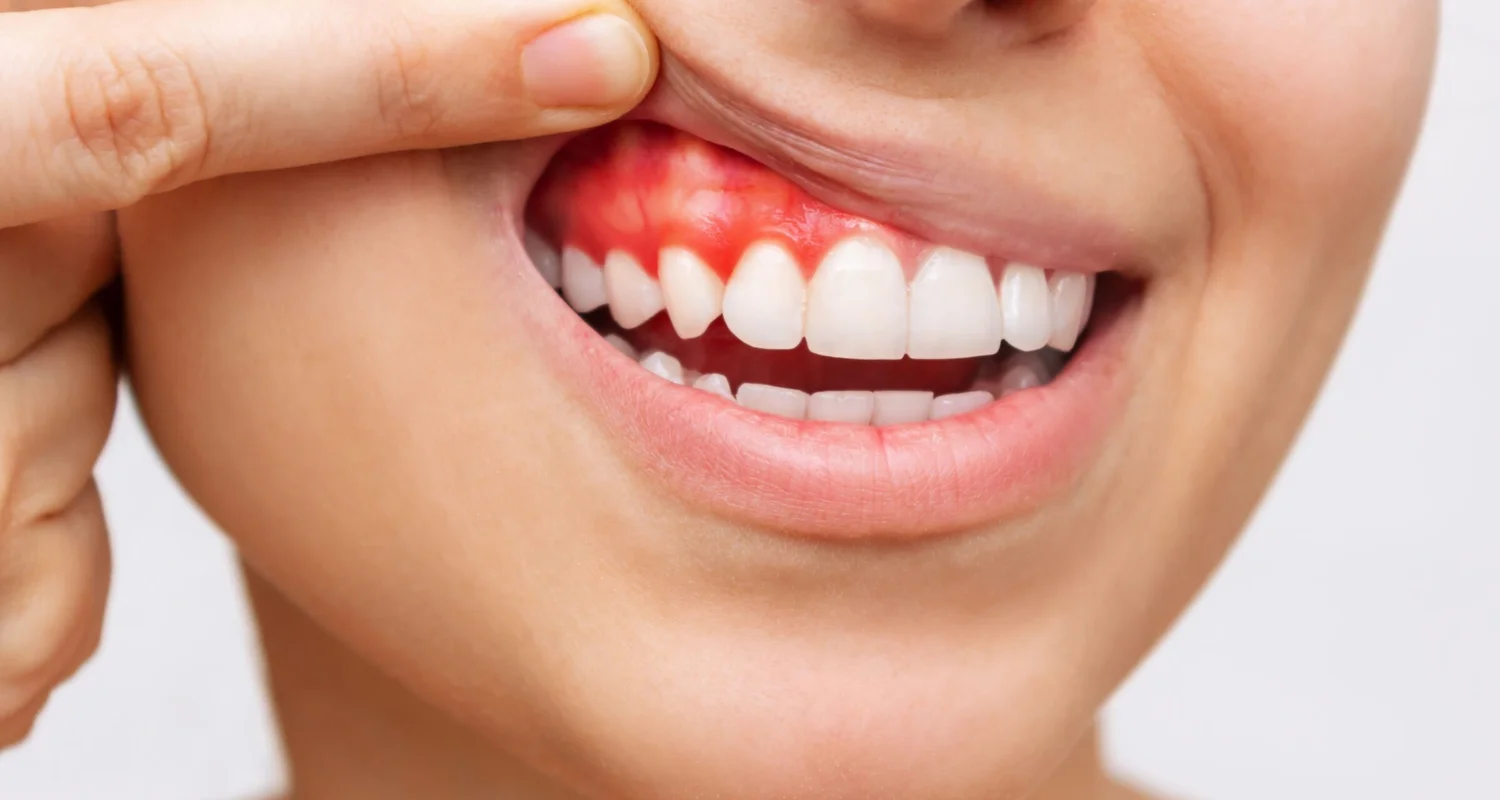
Periodontitis is a gum disease that is caused mainly by inadequate oral hygiene. The lack of effective dental cleaning leads to the formation of a layer of bacteria and food debris, known as calculus, that adheres to the teeth. This triggers an infection that attacks the gums, causing inflammation, bleeding, and the gradual destruction of the soft tissue around the teeth. If not treated in time, periodontitis can destroy the bone that supports the tooth, leading to tooth loosening and eventual loss.
Causative factors of periodontitis
Periodontitis is usually the result of poor oral hygiene, but other factors can increase the risk of developing this disease:
● Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or menopause.
● Tobacco and alcohol consumption.
● Genetic factors.
● Deficiencies in oral hygiene.
● Systemic diseases that can aggravate this condition, such as diabetes, AIDS, or in patients with weakened immune systems.
Symptoms
Characteristic symptoms of periodontitis include:
● Halitosis or persistent bad breath.
● Inflammation and redness of the gums.
● Bleeding gums, especially when brushing teeth.
● Dental sensitivity to extreme temperatures, whether cold or heat.
● Retraction of the gums, leaving the surface of the tooth more exposed.
● Mobility or loosening of teeth.
For more detailed information about gum disease, including its causes, classification, and initial signs, we invite you to explore specialized articles on our gum disease blog.
How to reverse periodontitis?
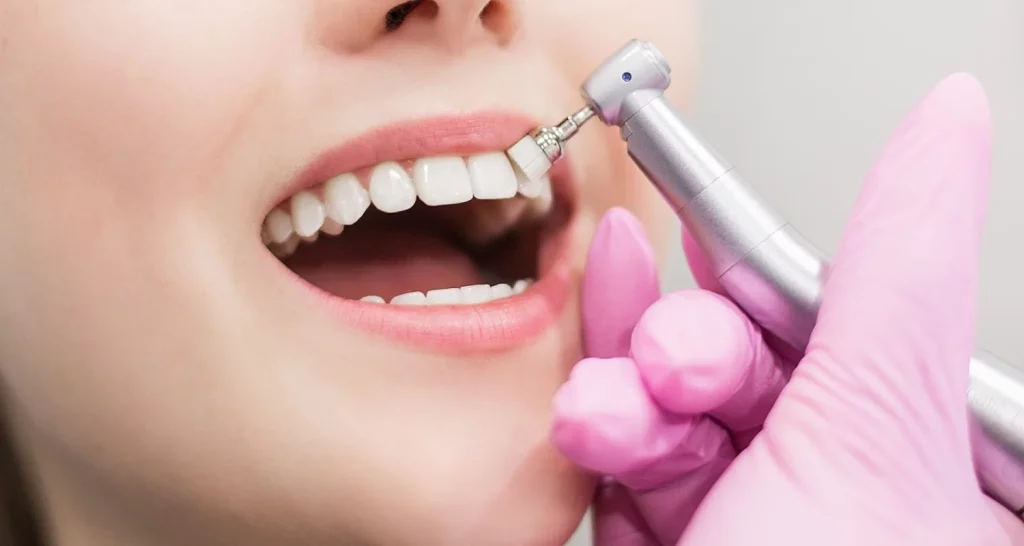
As mentioned, periodontitis is mainly due to the accumulation of dental plaque and calculus, a product of poor oral hygiene. Therefore, treatment focuses on improving oral hygiene and eliminating the cause of inflammation: plaque and calculus. Below are the most effective strategies to learn how to reverse periodontitis:
Accurate and personalized diagnosis
There are several types of periodontitis, each with a different level of severity. Treatment options will vary, depending upon the stage of disease progression. It is essential to visit the dentist to obtain an accurate diagnosis. Based on the severity of the disease, the oral health professional may recommend different treatments.
Professional cleaning in the office
While soft plaque can be removed at home by brushing, calcified plaque or calculus requires professional cleaning. To treat periodontitis, the dentist performs a deep cleaning with specialized instruments and equipment. In advanced cases, the periodontist may suggest a minor surgical procedure to expose the roots of the teeth and facilitate cleaning in the deeper areas.
Optimization of oral hygiene habits
After a professional dental cleaning, the dentist will provide essential recommendations to improve your oral hygiene. Following these instructions is crucial to prevent the formation of new bacterial plaque and calculus. Once the deep cleaning has been completed, the patient must make the commitment to keep their teeth free of plaque.
Some key tips include:
● Mechanical removal is the only effective method to eliminate dental plaque. This involves brushing your teeth three times a day, making sure that the bristles of the brush reach all tooth surfaces.
● Regular flossing is essential to eliminate food debris and bacteria in the interdental spaces.
● Your dentist may suggest alcohol-free mouthwashes to control infection-causing bacteria.
● Special toothpastes may be recommended to reduce gum inflammation.
In a nutshell, the best way to learn how to reverse periodontitis is by having correct oral hygiene since the beginning.
Maintenance and regular periodontal checkups
After a deep dental cleaning, the patient is advised to periodically visit the dentist for preventive maintenance. This includes less intense cleanings that preserve the results obtained initially; they are scheduled according to the evolution of the disease. Such care ensures the effectiveness of the treatment and should control possible factors that promote plaque accumulation, such as defective dental restorations.
Smoking cessation
Tobacco contains harmful substances that damage the gums and prevent proper healing. Even with proper treatment, smoking can impede the recovery of gingival health. Quitting smoking is beneficial not only for your gums, but for your overall health.
Management of bruxism and stress
The habit of clenching or grinding your teeth, known as bruxism, can intensify periodontitis by overloading the dental supporting tissues. It is important to consult with a dentist to evaluate treatment for bruxism. The condition is often related to stress, so finding ways to manage it is equally essential.
Natural remedies for periodontal disease
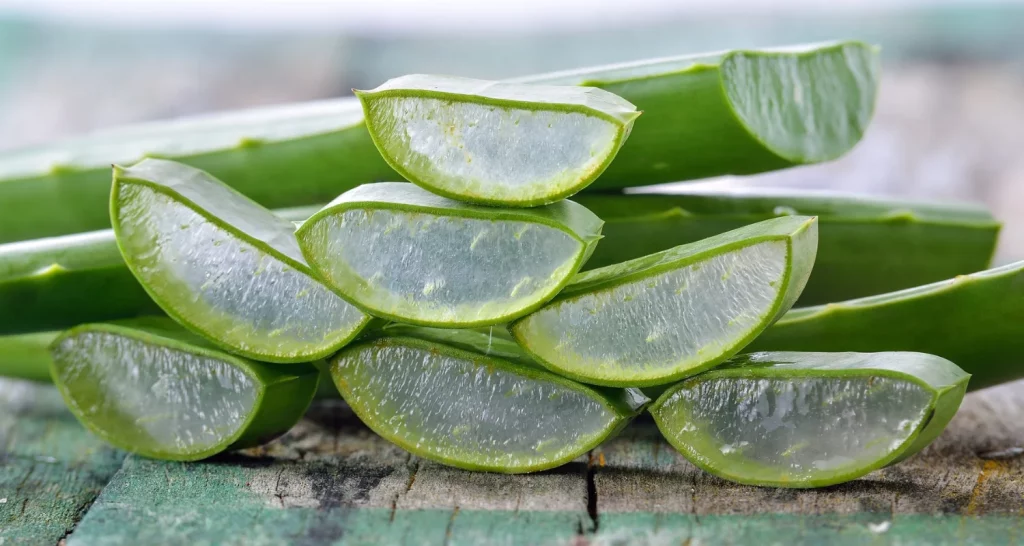

Although professional dental care is essential to understand how to reverse periodontitis, several natural remedies can help combat it and promote healthy gums.
An effective natural remedy for periodontal disease is the use of herbal treatments. Certain herbs have been shown to possess antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, making them beneficial in the treatment of gum disease. For example, tea tree oil is recognized for its antimicrobial effects. Applying this oil topically or rinsing with its extract helps reduce inflammation and fight gum infection.
In addition to tea tree oil, aloe vera, another herb, has shown promise in the treatment of periodontal disease. It contains bioactive compounds with anti-inflammatory properties that help relieve gum inflammation and promote healing. Regularly applying aloe vera gel to affected areas can reduce the severity of periodontal disease.
Chamomile is an herb that may be beneficial in managing gum disease. Known for its calming properties, chamomile helps relieve gum pain and inflammation. Rinsing with chamomile tea or applying chamomile extract to the gums provides relief and support the healing process.
Although herbal treatments can be effective, making dietary changes is also crucial to keeping gums healthy. One’s diet plays a significant role in overall oral health, including the condition of the gums. Include foods rich in vitamins C and D, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants as they help strengthen the gums and boost the immune system. This is a great way to learn how to reverse periodontitis even without a professional dentist’s advice.
Citrus fruits, such as oranges and grapefruits, are excellent sources of vitamin C, essential for collagen production and gum health. Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and kale, are packed with vitamins and minerals that support gum health.
Salmon, a fatty fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, can help reduce gum inflammation and promote gum healing.
Green tea, known for its antioxidant properties, is also beneficial for gum health when consumed regularly.
By incorporating these dietary changes into your daily routine, you will provide your gums with the nutrients they need to stay healthy and fight periodontal disease.
What does reversing periodontitis involve?
Periodontitis, an advanced inflammation of the gums, leads to the destruction of the hard and soft tissues that support the teeth. “Reversing periodontitis” refers to the process of relieving this inflammation and restoring gum health. However, note that, in its advanced stages, even if the infection is controlled, lost tissues are not completely regenerated with conventional treatments. So, learning how to reverse periodontitis in those stages could be useless.
Is it possible to recover Post tissues?
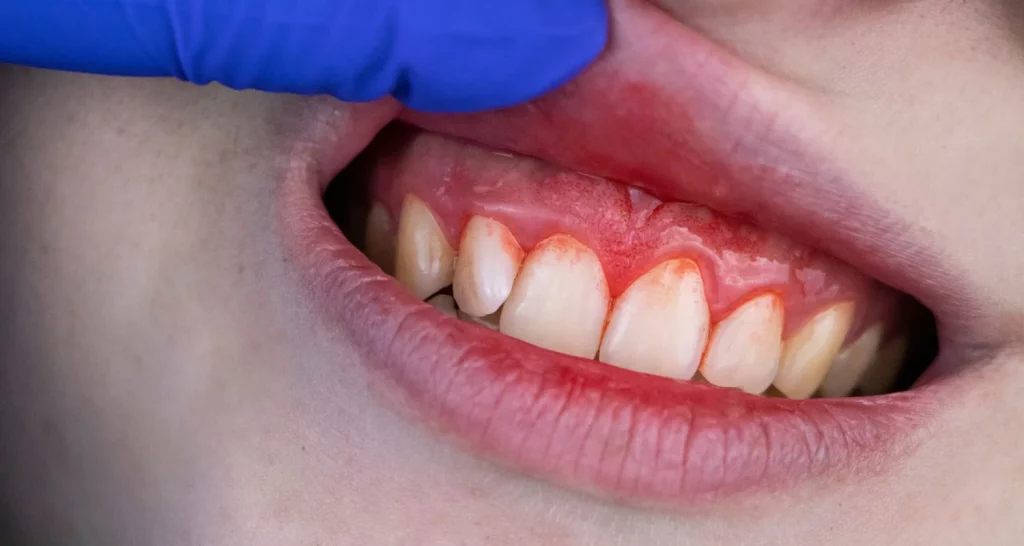
When intervened in time, the recovery of tissues lost due to periodontitis may be possible. This may require additional surgical procedures such as:
● Reconstructive surgeries: They include soft tissue or bone grafts and tissue regeneration techniques.
● Laser therapy: The technology is effective in improving gum response to treatment, tissue regeneration and healing.
Conclusion
The recovery of oral health in cases of periodontal disease is a collaborative effort between the patient and the dentist. There are no quick solutions to understanding how to reverse periodontitis. Instead, the treatment requires discipline, changes in oral hygiene habits, perseverance, and periodic dental cleanings.
Frequently Asked Questions
How are Periodontal Bacteria Eliminated?
The use of antibiotics, either topically or orally, is effective in combating the bacterial infection associated with periodontal diseases. Topical antibiotics can be administered by using specific mouthwashes or applying an antibiotic gel directly to the affected periodontal pockets. It may be necessary to resort to oral antibiotics to eradicate the bacteria responsible for infections.
Is It Possible to Live a Long Life with Periodontal Disease?
Don’t lose hope. It is possible to live a long, healthy life even with periodontal disease, as long as you maintain proper control of the condition through appropriate treatments and following your dentist’s recommendations. As with other chronic diseases, seeking treatment early significantly increases the chances of effectively controlling periodontal disease and, consequently, improving your quality of life.
How to Treat Periodontitis at Home
The most effective way to combat gum disease is by disrupting the activity of plaque bacteria daily. This can only be achieved through manual brushing and deep cleaning in both the periodontal pockets and the interdental spaces. Home remedies like oil pulling are not able to perform this function.
Can Periodontal Disease Be Cured?
Although periodontal disease has no definitive cure, it is possible to control it effectively with the appropriate treatment. It is not considered curable because once the structural support around the teeth is lost, it usually does not fully recover. However, periodontal treatments can reduce an infection and contribute to a partial regeneration of the affected bone and tissue. Genetics plays an important role in this condition.
Share:
Referencias
1. Gum Disease Prevention. (Feb 8, 2020). American Academy of Periodontology. https://www.perio.org/for-patients/gum-disease-information/gum-disease-prevention/
2. Gum Disease and Other Diseases. (Jun 21, 2019). American Academy of Periodontology. https://www.perio.org/for-patients/gum-disease-information/gum-disease-and-other-diseases/
3. Non-Surgical Treatments. (Jun 21, 2019). American Academy of Periodontology. https://www.perio.org/for-patients/periodontal-treatments-and-procedures/non-surgical-treatments/
4. Surgical Procedures. (Feb 5, 2020). American Academy of Periodontology. https://www.perio.org/for-patients/periodontal-treatments-and-procedures/surgical-procedures/
5. Periodontal Diseases. (s. f.). Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/periodontal-diseases
- Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...Recent Posts