Last Updated on: 10th December 2025, 06:36 am
Diabetes and Dental Extraction
People living with diabetes are more prone to dental injuries and diseases, a situation for which they must receive differential dental treatment that takes their unique health condition into account.
In people affected by diabetes, tooth decay, and gum disease are common diagnoses that can lead to tooth extraction. This procedure requires special attention and care, as high blood glucose levels affect the immune system, as well as blood clotting time and healing.
It is important to know the repercussions of diabetes on oral health, the care before and after a dental extraction to facilitate a successful evolution, as well as the importance of providing the dentist with information about the patient’s clinical history.
What is Diabetes?
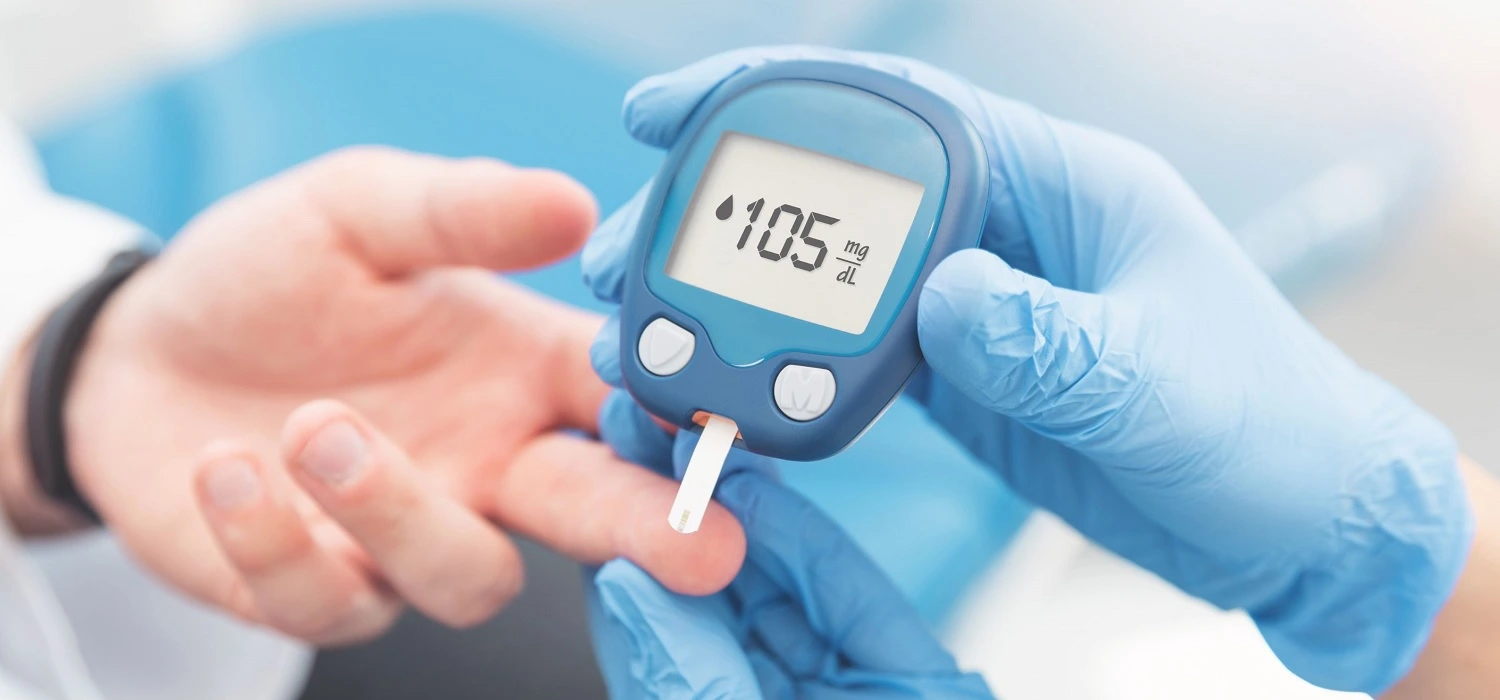
It is a disease characterized by high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. Glucose is acquired through food. With the help of insulin (a hormone produced by the pancreas), it enters the cells and produces the energy the body requires.
When insufficient insulin is produced, glucose stays in the blood and its buildup causes health effects, such as a compromised immune system, allowing bacteria to grow. Taking medicines for diabetic people is required. We have a comprehensive guide about diabetes and metformin. Side effects and management tips are explained in this article.
The most frequent different types are:
Type 1 diabetes
A condition in which the body does not produce insulin because the immune system attacks the cells of the pancreas that produce it. Those with this diagnosis must use insulin to maintain the balance of their health.
Type 2 diabetes
The body does not make or use insulin. This type occurs most often in people over 45 and older adults.
Some of the consequences derived from a high blood sugar level are:
• Cerebrovascular accidents
• Heart disease
• Dental diseases
• Eye conditions
• Nerve damage
• Renal problems
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 347 million people were diagnosed with this illness worldwide in 2019; and it is estimated that by 2030 that number will reach 366 million.
In 2020, the US National Diabetes Statistics Report noted that at that time 34.2 million people had some form of diabetes.
Effects of on Oral Health
Diabetics are prone to various injuries that affect their oral health.
The increase in sugar level is reflected in the amount of glucose that reaches the saliva, making it easier for the bacteria present in the mouth to feed that favors the following:
• Gum abscess
• Parotid salivary gland enlargement
• Taste disturbance
• Dry mouth from a low saliva level
• Oral candidiasis
• Caries
• Periodontal disease
• Ulcers in the mouth
If a diabetic does not have a treatment for its control, the useful life of their teeth may be affected. In addition, the increase in glucose levels decreases blood flow, which deteriorates the soft tissues that connect the tooth to the jaw, increasing the chances of periodontal disease.
In turn, gum disease makes it more difficult to control blood sugar levels, leading to a high-risk cycle of pathology that hampers the required dental treatment.
Necessary Care in Dental Extraction
Tooth extractions in diabetic persons require some pre-procedure procedures and specific post-procedure care.
In the pre-extraction stage
The dentist must be informed about this health condition and the medications received before starting any dental treatment. This will make it easier to take the corresponding preventive measures and avoid complications afterward.
It is relevant to measure the level of glucose in the blood, as well as monitor the practice of careful oral hygiene. In some cases, antibiotic dental prophylaxis is prescribed to facilitate a better oral condition during the procedure.
It is recommended that this intervention be carried out in the morning to reduce the risk of a drop in glucose level (hypoglycemia).
In the post-extraction stage
It should be taken into account that diabetic people have longer healing times since the high level of sugar affects blood coagulation, a situation that can cause the cavity to dry out, thereby increasing the possibility of infection (osteomyelitis).
Regularly, antibiotic treatment is prescribed to prevent infection and facilitate recovery.
Some of the complications that can occur after extraction are delayed healing, severe pain, and bleeding.
To reduce the possibility of these incidents, it is suggested:
• In the following 72 hours, avoid tobacco use, alcoholic beverages, and contact with irritating substances, such as mouthwashes containing alcohol.
• Brush your teeth at least twice a day, with a soft bristle brush.
• Flossing to prevent plaque buildup and reduce the chances of infection.
• If prostheses are used, it is necessary to clean the parts daily.
• The practice of physical exercise and consuming a healthy diet ensure better oral health.
• Schedule regular checks of blood sugar levels.
• Periodically visit the dentist to monitor the recovery process.
Interconsultation is Pertinent and Healthy
Diabetes and dental extraction require preparation before the intervention to facilitate a successful procedure, without complications. Likewise, post-exodontia care is important to achieve recovery without setbacks and maintain the best health condition.
It is relevant for the dentist to know the patient’s clinical history. In some cases, it is recommended to have a dialogue between the dentist and the doctor who guides the diabetes treatment (an inter-consultation), to make the necessary adjustments in the corresponding therapeutic protocol to facilitate a good outcome.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a diabetic person get his teeth extracted?
Diabetic patients may need dental extractions if they suffer from severe tooth decay, gum disease, or infections that cannot be treated with other dental procedures. However, due to their condition, special care and preparation are necessary to manage the extraction process safely and effectively.
How are dental treatment and diabetes related?
The diabetics are at a higher risk for tooth extraction due to their increased susceptibility to oral infections, gum disease, and tooth decay. High blood sugar levels can lead to a compromised immune system and poor blood circulation, which can exacerbate oral health issues and make tooth extraction more likely.
Does diabetes mellitus affect the cavities of dental extractions?
Yes, diabetes mellitus can affect tooth extraction sockets by slowing down the healing process and increasing the risk of complications such as infections and dry socket. High blood sugar levels can impair blood clotting and reduce blood flow to the gums, making it more difficult for the extraction site to heal properly.
Why do we prefer to call a diabetic patient in the morning to extract a tooth?
Preparing for dental extractions with diabetes involves several important steps:
- Inform the dentist about your diabetes and any medications you are taking.
- Ensure your blood sugar levels are well-controlled before the procedure.
- Schedule the extraction in the morning to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
- Maintain good oral hygiene and possibly use antibiotic prophylaxis as recommended by your dentist.
- Follow any specific instructions provided by both your dentist and healthcare provider to minimize risks and complications.
Diabetes and Oral Health
Diabetes significantly impacts oral health by increasing the risk of various dental issues, including gum disease, cavities, dry mouth, and oral infections. High blood sugar levels create an environment that promotes bacterial growth in the mouth, leading to these complications. Managing diabetes effectively and maintaining good oral hygiene practices are crucial for preventing and controlling these issues.
Share:
References
1. American Dental Association (Enero 24 de 2022) Diabetes – Key points / https://www.ada.org/resources/research/science-and-research-institute/oral-health-topics/diabetes
2. Arteta Ingrid, Arroyo Dayanna (December 2019) Diabetes mellitus, manifestations in oral cavity. A theme review / http://www.scielo.org.co/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0122-06672019000200105
3. Giath Gazal (Enero de 2020) Management of an emergency tooth extraction in diabetic patients on the dental chair / https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6950840/
4. Guzmán Cristian, Jefferson Angel (March 24, 2023) exodontia type II diabetes mellitus complications of dental extraction / http://dspace.unach.edu.ec/handle/51000/10548
5. National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (March 2019) Diabetes and Oral Health / https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/espanol/temas-de-salud/la-diabetes-y-la-salud-oral
6. Sanz-Sánchez I., Bascones-Martínez A. (October 2009) Diabetes mellitus: Its implication in oral and periodontal pathology / https://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0213-12852009000500003
-
Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...