Last Updated on: 10th December 2025, 06:11 am
What is dentin? What function does it fulfill? What is its relationship with dental sensitivity? How to take care of it? These are some of the questions that are answered in this account.
One of the parts that requires greater care for good oral health is not visible, although it does influence the color of teeth. This is dentin, one of the layers of the dental structure that is not well known, although it has a relevant function in oral health.
What is Dentin?
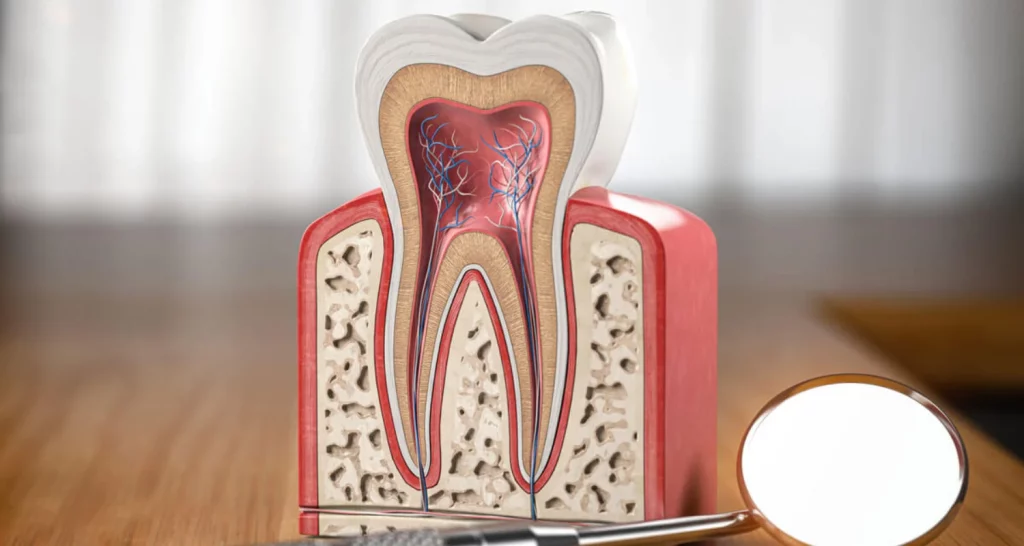
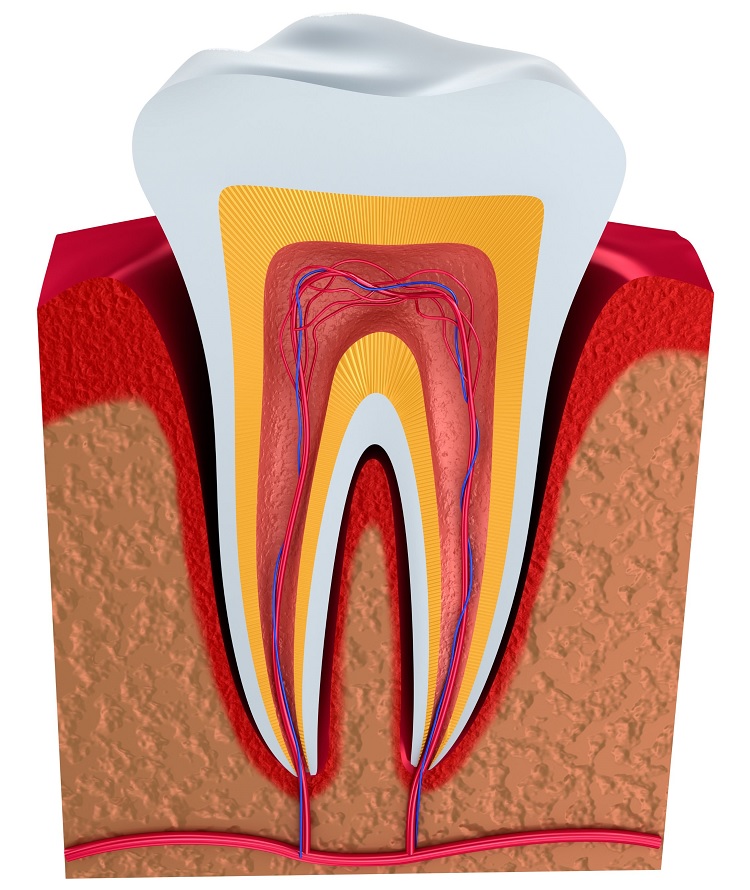
1. Dentin is a calcified tissue that is found beneath the enamel of the tooth and represents the majority of dental tissue.
2. Dentin is located beneath the dental enamel. It is the second layer of the tooth structure, that is, it is between the enamel and the dental pulp.
3. An important characteristic of dentin is that its production is constant throughout life and it regenerates, reducing the impact of wear or deterioration.
4. This second layer of dental structure is formed from dentinogenesis, a process in which odontoblasts (specialized cells in the production of dentin) produce predentin, a substance that later matures into dentin.
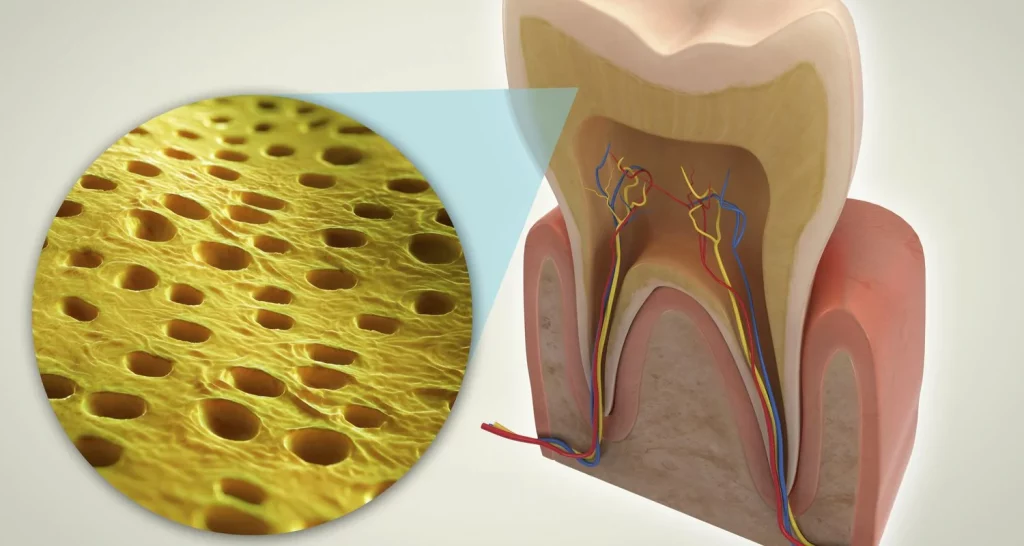
5. Dentine is in the crown of the tooth, covered by enamel, and inside it are dentinal tubules, channels that go from the enamel to the pulp and transmit sensations of heat, cold, stimuli of acidic or sweet foods to the inside of the tooth. In the root zone, dentin is covered by dental cement.
What Is The Function Of Dentin?
Dentin supports enamel and protects pulp. It also transmits impulses (sensations/stimuli) from the enamel or root to the dental pulp, made up of a set of blood vessels and nerves. Dentin is the layer that gives color to the tooth and provides protection against cavities.
Dentin Composition And Characteristics
Dentin is less translucent than enamel because it has a lower degree of mineralization, a factor that determines the color of the tooth.
It shows a white color with a yellowish tone, an aspect that presents variations depending on the degree of mineralization, pulp vitality, and the age of the person.
Different Types of Dentin
According to its location in the tooth structure, there are three types of dentin:
1. In the outermost part is primary dentin (predentin). It is in contact with the enamel and establishes the delimitation of the dental piece with the pulp chamber.
2. Secondary dentin is in the root, in contact with cement. Its formation does not decrease throughout the tooth’s life cycle. It is also known as orthodentin or regular dentin.
3. Tertiary dentin, also called reparative dentin, is formed internally and its function is to isolate the pulp from any oral lesion, such as a dental cavity and dental wear.
What Products Does Dentin Need In Its Care To Be Healthy?

Products recommended to preserve the good condition of dentin are those products that we use in our oral health routine, which are the following:
1. Toothbrush: Brush teeth after every meal. It is suggested to use a soft-bristled brush and not apply too much force, as this can affect the dental enamel. Circular motions are recommended.
2. Dental Floss: Use dental floss and mouthwash to contribute to hygiene, which are good complements to brushing.
3. Interdental Brush: Clean interdental spaces and the gum line well.
4. Toothpaste: Use toothpaste with fluoride.
Do not use teeth as tools to manipulate objects, such as cutting adhesive tapes or opening containers. This wears down the enamel and generates fissures that affect dentin.
Dentin Sensitivity and Treatment Options
Ever experience a sharp twinge of pain when you bite down on something cold or sugary? That could be dentin sensitivity, a common dental issue affecting millions of people.
What causes tooth sensitivity?

Dentin has a layer of tissue that is linked to the tooth nerve. When the gums recede, the dentin is exposed, leading to tooth sensitivity, a common circumstance that causes discomfort when consuming very cold or too hot foods/beverages, as they stimulate the dental nerve and trigger a reaction.
Damage to dental enamel can leave the dentin exposed. This is the case with dental caries, which first affects the enamel and then progresses to dentin, causing pain.
If the cavity goes untreated, it destroys dentin and can advance to the pulp, bone, and gums.
Generally, tooth sensitivity is a manifestation of tooth enamel wear or root exposure. In some cases, discomfort is due to a cracked or chipped tooth, a filling that needs to be renewed, or gum disease.
These are some of the situations that cause tooth sensitivity:
● Bruxism. This affects both enamel and dentin.
● Periodontal disease that causes gum recession.
● A diet with plenty of sugary, acidic, or spicy foods.
● Using a toothbrush with very stiff bristles or brushing too hard.
● After a teeth whitening process, sensitivity may be present for a few days.
What is the treatment for tooth sensitivity?

To solve the discomfort caused by tooth sensitivity, it is recommended to consult a dentist for an evaluation and prescribed treatment.
Some recommendations that can help manage the situation are:
● Avoid excessive alcohol consumption.
● Avoid using wooden toothpicks.
● Do not consume very cold or too hot foods/beverages.
● Do not consume acidic or spicy foods.
● Reduce consumption of high-sugar foods.
● Use toothpaste for sensitive teeth.
Other therapeutic procedures that a dentist may perform include:
● Applying fluoride to sensitive areas to strengthen dental enamel.
● Applying adhesive resin to sensitive roots.
● If gum tissue has been lost, gingival grafting may be an option, which is a surgical procedure that requires greater management.
● In the case of teeth with considerable sensitivity that have not been controlled with other treatments, the option is a root canal treatment.
When to consult your dentist?

Taking care of dental enamel and dentin is fundamental to maintaining good oral health. If any indication of tooth sensitivity arises, it is recommended to consult a dentist as soon as possible to apply the corresponding treatment and avoid the condition impacting internal parts of the tooth with greater complexity effects.
Practicing oral hygiene habits in combination with regular visits to the dentist is a prevention strategy that allows for timely diagnosis and required attention.
Conclusion
Dentin is essential for oral health, supporting tooth enamel and influencing sensitivity. It requires proper care through gentle brushing, fluoride toothpaste, and avoiding habits that damage enamel.
Tooth sensitivity, often linked to dentin exposure, can be managed with desensitizing products and professional dental treatments. Regular dental visits and good oral hygiene are key to maintaining dentin health and preventing discomfort.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is dentin and where is it located?
Dentin is a calcified tissue beneath the tooth’s enamel, serving as the second layer between the enamel and dental pulp. It forms the majority of dental tissue and plays a crucial role in the overall structure and health of the tooth.
How does dentin affect tooth color and sensitivity?
Dentin is less translucent than enamel and has a natural yellowish hue, which influences the color of teeth. It contains tubules that transmit sensations from the tooth surface to the nerve, making teeth sensitive to temperature and certain foods.
What are the types of dentin and their functions?
There are three types of dentin: primary, secondary, and tertiary. Primary dentin forms the initial structure adjacent to the enamel. Secondary dentin adds layers throughout life, providing ongoing support. Tertiary dentin develops in response to trauma or decay, protecting the pulp.
How should dentin be cared for to prevent tooth sensitivity and decay?
To maintain healthy dentin and prevent sensitivity, use a soft-bristled toothbrush, fluoride toothpaste, and gentle brushing techniques. Regular use of dental floss and mouthwash can help clean hard-to-reach areas and reduce the risk of decay and sensitivity.
What treatments are available for tooth sensitivity due to exposed dentin?
Treatments for sensitive teeth include using desensitizing toothpaste, applying fluoride or adhesive resins to strengthen enamel and dentin, and, in severe cases, undergoing root canal treatment or gingival grafting to cover exposed roots and reduce sensitivity.
Share:
References
1. Espinoza J, González, Ruiz P (2013). Treatment of dentin hypersensitivity post periodontal therapy, using two desensitizing dentifrices / https://www.scielo.cl/pdf/piro/v6n2/art06.pdf
2. Facultad de Estudios Superiores IZTACALA – UNAM (2013). EMBRIOLOGY, HISTOLOGY AND PULPAR PHYSIOLOGY – Dentin-pulp complex / https://www.iztacala.unam.mx/rrivas/NOTAS/Notas6Histologia/comdentina.html
3. Fuentes María V. (March 2004) Mechanical properties of human dentin – Avances en Odontoestomatología Journal https://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0213-12852004000200003
4. Gernhardt Crhistian (December 2012) Dentin hypersensitivity: causes and treatment of dentin neck sensitivities / https://www.elsevier.es/es-revista-quintessence-9-articulo-hipersensibilidad-dentinaria-causas-tratamiento-sensibilidades-S0214098512002188
5. Keijo Luukko, Berggreen Ellen (2011) Structure and Functions of the Dentin-Pulp Complex / https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/immunology-and-microbiology/dentin
6. Mandal Ananya (January 20, 2023) What is Dentin / Dentine? /https://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Dentin-Dentine.aspx
7. Salinas Thomas (December 7, 2021) What causes tooth sensitivity and how can I treat it / https://www.mayoclinic.org/es-es/healthy-lifestyle/adult-health/expert-answers/sensitive-teeth/faq-20057854
8. Simon Flury, Anne Peutzfeldt, Patrick R. Schmidlin, Adrian Lussi (January 12, 2017) Exposed Dentin: Influence of Cleaning Procedures and Simulated Pulpal Pressure on Bond Strength of a Universal Adhesive System / https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5233420/
-
Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...Recent Posts