Last Updated on: 27th December 2025, 05:36 am
Tooth infection spreading to the bone has multiple causes, such as genetic conditions, having a disease that compromises the immune system and weakens it, metabolic diseases such as diabetes and dental extraction, or gum disease not treated on time.
An infection is a process during which pathogens such as bacteria, fungi, or viruses invade a vulnerable area of the body, multiply, and cause a disease.
Tooth infections in most cases are caused by bacteria infecting the innermost layer of the tooth called the pulp or dental nerve. It also occurs when there is an accumulation of plaque at the gum line, generating gingivitis, which later worsens and becomes periodontitis.
When tooth infection is not treated early, it can spread rapidly from the tooth to the surrounding bone, causing a serious and life-threatening condition known as osteomyelitis.
Tooth infection is alarming especially when it can spread to the whole body. We have a comprehensive guide about the symptoms of tooth infection spreading to the body. Also, the complications and treatments are explained well in this article.
Causes of a Tooth Infection
The increase in bacteria that cause tooth infections can occur for a variety of reasons, including:
1. Advanced dental caries
The acid produced by bacteria destroys the hard tissues of the tooth (enamel and dentin) and leaves the dental nerve exposed.
2. Fractured or cracked teeth
Bacteria easily enter the dental pulp through any opening.
3. Gum disease (gingivitis and periodontitis)
Accumulation of plaque or tartar in the space between the gum and the tooth that generates inflammation. Check this article about gum diseases. This will help you understand the signs, symptoms, and treatments for gum diseases.
4. Dental trauma (blows, falls)
During trauma, the dental pulp can be injured, causing nerve death or making the tooth more susceptible to infection.
5. Tooth extraction
The extraction of a tooth can cause infection, possibly due to poor oral hygiene or no antibiotics given after the extraction.
6. Dental implants
The infection associated with regeneration surgery done with bone grafting can be generated, due to the excessive use of cement during the placement of a crown on an implant, which does not allow for adequate healing and bone recovery. We have a complete guide about dental implant procedures to help you understand more.
Some conditions can be triggers for tooth infections, including:
• Poor dental hygiene: The main reason for an infection in the mouth is poor oral hygiene. It is described as not brushing your teeth at least 2 times a day and not using dental floss.
• Food with a high sugar content: Contributes to the formation of dental caries.
• Dry mouth or Xerostomia: When saliva is decreased, protection against bacteria is lost. This condition is associated with the use of some medications, aging, or systemic diseases.
• Smoking
• Weakened immune system: is associated with some diseases, such as HIV, diabetes, lupus, etc. when the body cannot effectively fight bacteria.
Signs and Symptoms of Tooth Infection
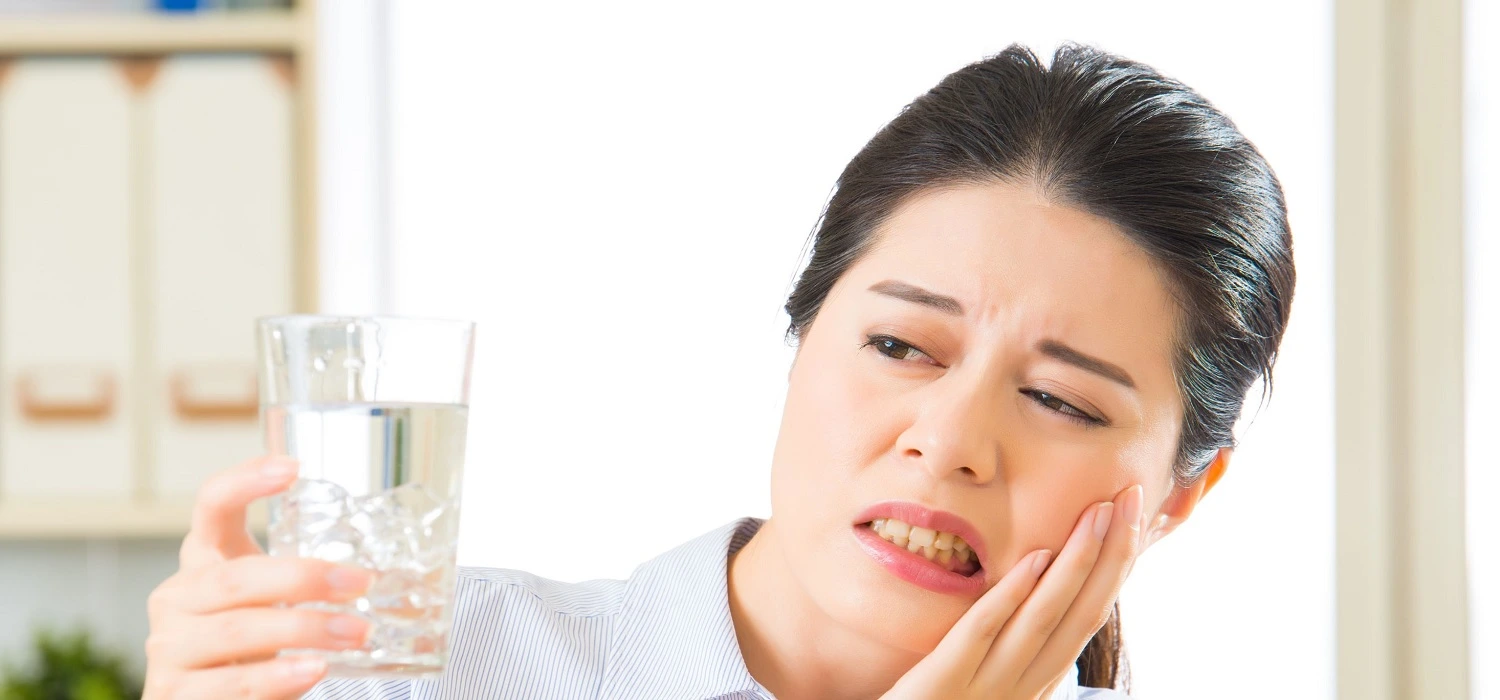

• The most common symptoms of a tooth infection are: tooth sensitivity to acid, cold, heat, and a sweet taste
• Unpleasant odor and taste
• Severe, throbbing pain, which may spread to the ear and/or neck on the same side as the tooth and worsens when lying down
• Swelling of the face
• Gum redness
• Fever
• Fistula: purulent discharge
When a tooth infection spreads to the bone or other parts of the body, the following symptoms may occur:
• general malaise, fatigue, ear and headaches, dizziness, and lightheadedness.
• fever, sweating or chills, reddening of the skin, or rashes.
• intense swelling of the face, difficulty in opening the mouth, swallowing, and breathing correctly.
• severe gum swelling, pain, and bleeding.
• diarrhea, vomiting and abdominal pain
• increase of cardiac heartbeat frequency
• increase of respiratory frequency
• dehydration
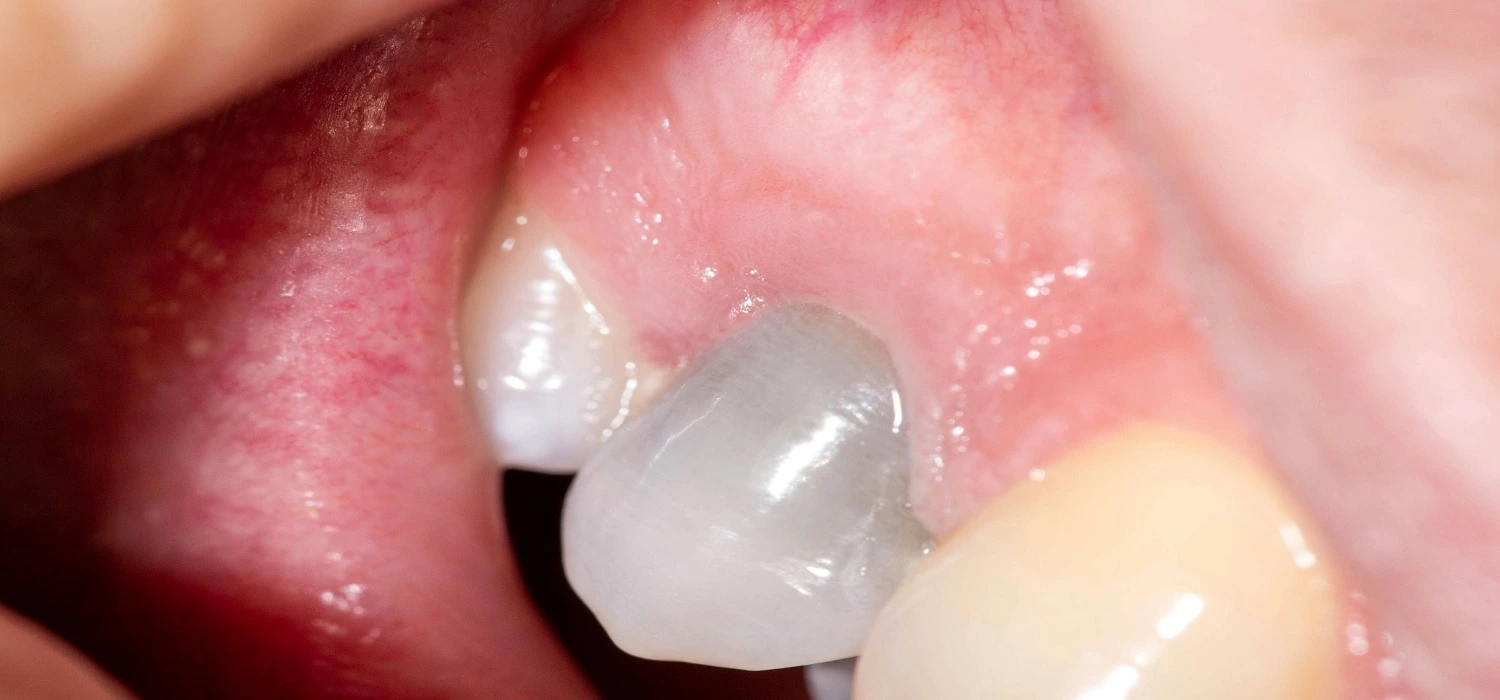
Tooth Infection Spreading to the Bone
In general, when there is a tooth infection, an accumulation of pus in what is known as an abscess appears. The stages are:
1. Gingival: an infection develops in the gums but it does not affect the tooth or bone structures.
2. Periapical: an infection that forms at the tip of the root of a tooth when a cavity or fracture touches the dental nerve and it dies. The infection spreads to the bone in that area and an abscess forms.
3. Periodontal: The tissues that support the teeth are affected by an infection, and the gum disease known as periodontitis appears.
When the infection has advanced to the bone, osteomyelitis may occur.
What is Osteomyelitis?
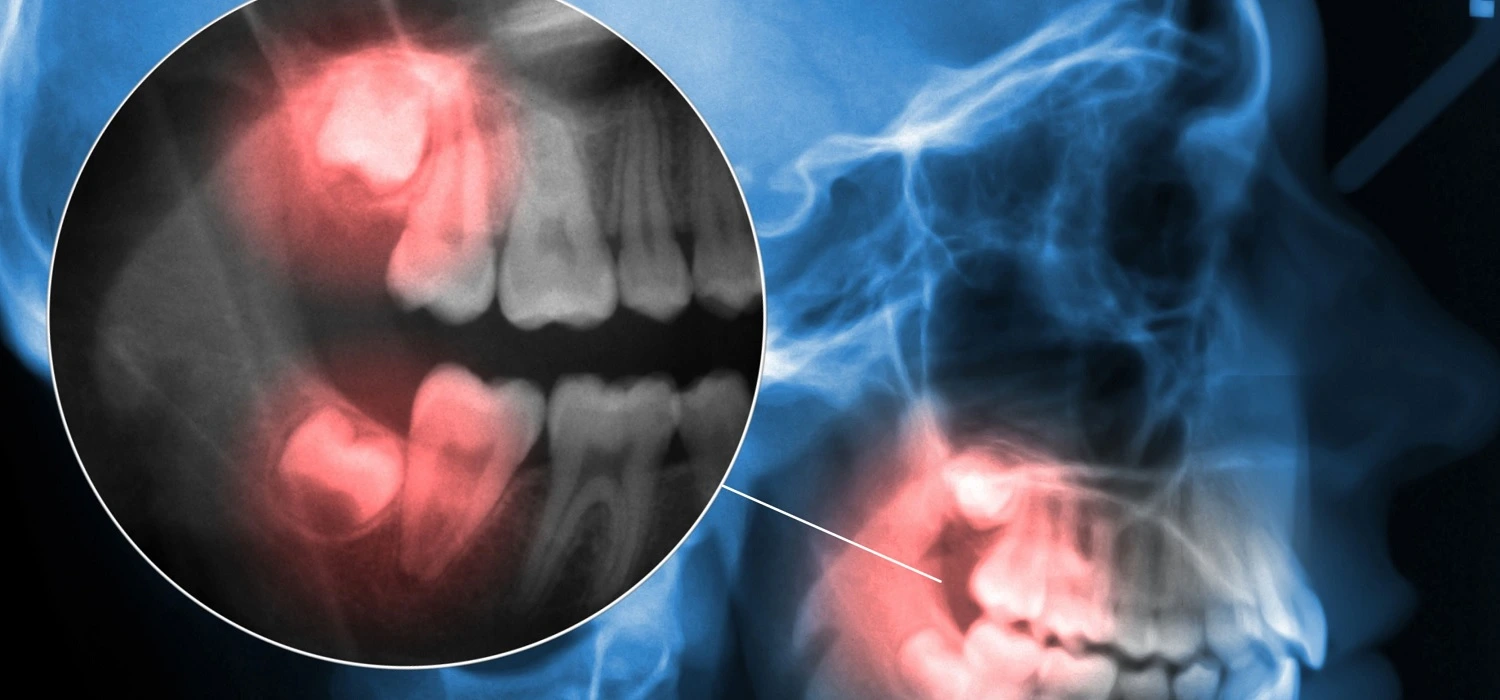
It is an infection of the bone tissue caused by bacteria. It occurs as a consequence of a chronic periapical infection or disease that obstructs blood flow, causing bone death or necrosis. It is classified as:
1. Acute suppurative osteomyelitis
Intense pain, inflammation, sensitivity, increased temperature, mobility of the teeth involved in the osteomyelitis area, and pus secretion.
2. Chronic suppurative osteomyelitis
It is usually asymptomatic and presents fistulas through which pus comes out with bone particles detached from the bone.
3. Chronic Focal Sclerosing Osteomyelitis
It is asymptomatic and occurs in a specific area of the bone. It is more common in young patients.
4. Chronic diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis
Its origin is associated with a weakened immune system. It is more common in older adult patients.
When to seek professional help?
It is important to visit the dentist at the first signs of a tooth infection. Depending upon the level of advancement of the infection and the causes of its appearance, the dentist may order tests such as X-rays, computed tomography, histopathological examination, and thermal tests.
Treatment of a Tooth Infection Spreading the Bone
To treat the symptoms of a tooth infection that spreads to the bone, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the infection. Some treatment options are:
1. Root canal treatment or endodontics
The procedure involves the extraction of the infected pulp inside the tooth, followed by a thorough cleansing of the canals. The resulting space is then filled with a specialized material to seal the tooth and eliminate the infection. This treatment is administered in cases where the infection has not yet spread to the underlying bone. This information is relevant when discussing root canals and their relationship to cancer.
2. Apical surgery
Consists in uncovering the root of the tooth and cutting part of it at the same time that the abscess and the infected bone are removed surgically, then the root is sealed.
3. Drainage of the abscess
An incision is made and the pus is drained. Sometimes an elastic band is placed to keep the perforation open so it can continue to drain. The abscess can also be drained at home. Click the article to find out more.
4. Tooth extraction
When it is not possible to save the tooth, it is extracted along with all the tissue affected by the infection.
5. Medicines
Depending on how advanced the infection is, the dentist will prescribe antibiotics to manage it while performing other types of treatments. It may be necessary to perform a biopsy and a histopathological study of the affected bone area to determine what type of bacteria causes the infection and send an antibiotic that attacks it directly. In more serious cases, it may require hospital management.
How to Prevent a Tooth Infection from Spreading to the Bone?
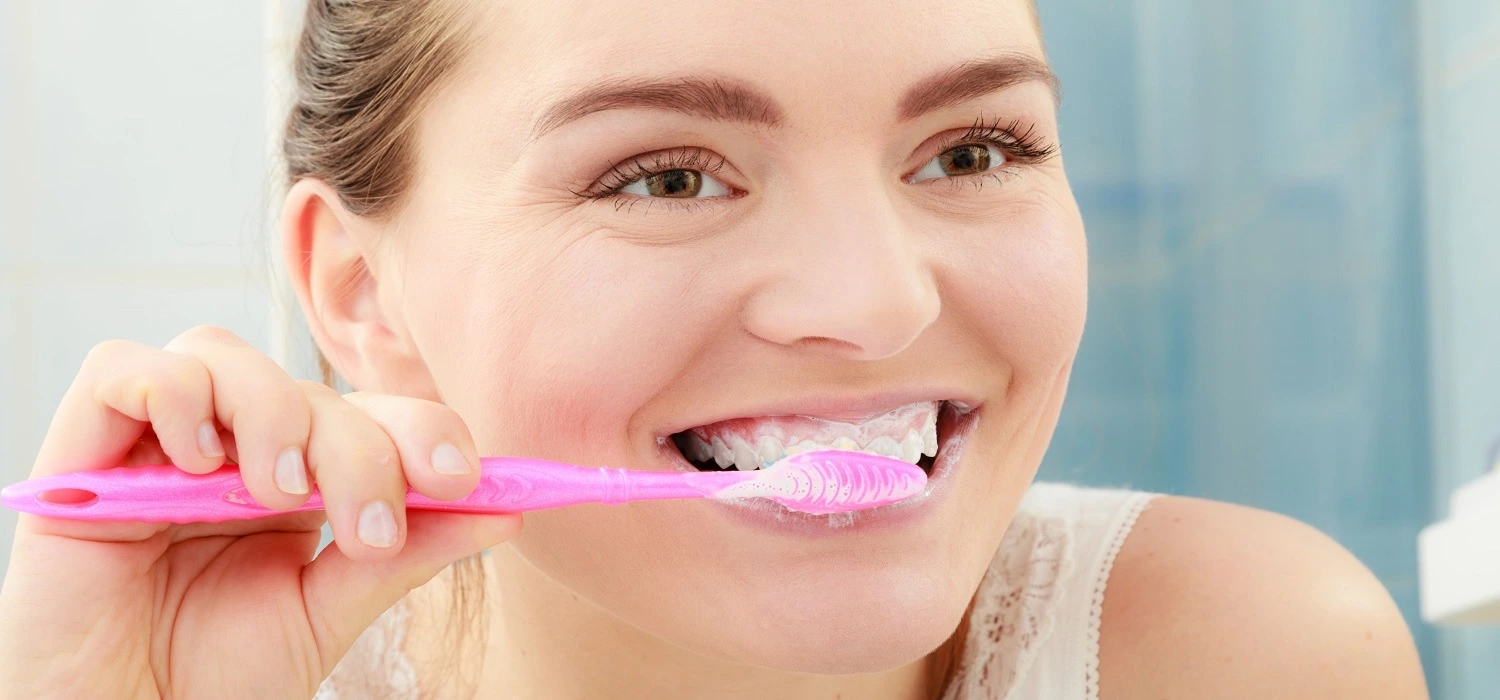

To avoid tooth infections, some useful tips to follow include:
• Proper oral hygiene: use fluoride toothpaste, a good toothbrush, and dental floss at least 2 times a day; also use mouthwash after brushing.
• Change the toothbrush every 2 or 3 months and when it looks or feels deteriorated.
• Maintain a balanced diet with lots of fruits and vegetables, and reduce the consumption of sugars.
• Avoid habits such as cigarette smoking or alcohol.
• Schedule periodic visits to the dentist at least 2 times a year for checkups and professional cleanings.
A tooth infection can be easily treated in its early stages, so try to visit the dentist at the first signs of alarm or pain. In this way, you will avoid complications such as the spread of infection to the bone and even to other areas of the body.
On our site, you will find an article titled “Best Antibiotic for Tooth Infection“. There, when to use those antibiotics and the possible side effects are explained. Thanks for reading our article.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of a jaw bone infection?
A jaw bone infection primarily arises from poor dental hygiene or untreated dental cavities. Bacteria settle in the area, leading to an infection that, if left untreated, can severely damage the affected areas and cause significant health problems. Symptoms include redness and swelling, pain in the mouth and jaw, and the drainage of pus from the infected site.
What causes a dental infection to spread to the bone?
A dental infection can spread to the bone when bacteria from untreated dental issues such as advanced cavities, gum disease, or dental trauma invade the surrounding bone tissue, leading to a serious condition called osteomyelitis.
What are the symptoms of a dental infection spreading to the bone?
Symptoms of a dental infection that has spread to the bone include severe, throbbing pain that may radiate to the ear or neck, swelling of the face, fever, gum redness, pus discharge, general malaise, fatigue, difficulty swallowing and breathing, and increased heart and respiratory rates.
How is a dental infection that has spread to the bone treated?
Treatment options include root canal therapy, apical surgery, abscess drainage, tooth extraction, and antibiotics. The specific treatment depends on the severity and progression of the infection.
How can dental infections that spread to the bone be prevented?
Preventive measures include maintaining proper oral hygiene, using fluoride toothpaste, flossing regularly, reducing sugar intake, avoiding smoking and alcohol, and scheduling regular dental checkups at least twice a year.
Share:
References
1. Abscess Tooth: Symptoms, Causes & Treatments. (Reviewed: March 27, 2023). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10943-abscessed-tooth
2. Agarwal, A., Kumar, N., Tyagi, A. K., & De, N. (2014).Primary chronic osteomyelitis in the mandible: a conservative approach. Case Reports. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2013-202448
3. Frothingham, S. (May 28, 2019). What Are the Symptoms of Tooth Infection Spreading to Your Body? Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/symptoms-of-tooth-infection-spreading-to-body
4. Newman, T. (December 4, 2017). What’s to know about dental abscesses? Medical news today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/170136
5. Nezafati, S., Ghavimi, M. A., & Yavari, A. (2009).Localized osteomyelitis of the mandible secondary to dental treatment: report of a case. Journal of dental research, dental clinics, dental prospects. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3517289/
6. Osteomyelitis – Symptoms and causes. (November 8, 2022). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/osteomyelitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20375913
7. Tooth abscess – Symptoms and causes. (June 29, 2022). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tooth-abscess/symptoms-causes/syc-20350901
- Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...Recent Posts