Last Updated on: 27th December 2025, 07:44 am
Symptoms of Tooth Infection Spreading to Body: Complete Guide
Many people think that it is not important to pay attention to dental infections, but the reality is a different matter. These infections and the symptoms of tooth infection spreading to body are dangerous and can even be fatal if not treated on time. If you would like to read more about tooth diseases, you can visit the article here.
It is essential to learn what dental infections are, what causes them, their symptoms, what happens if they spread to other parts of the body, and how to know when this is happening. Knowing about this topic will help you identify a dental infection when to go to the dentist and thus avoid serious future complications.
Tooth infections are particularly concerning as they have the potential to extend into our bones. Refer to this article, “Tooth Infection Spreading to the Bone” for further information.
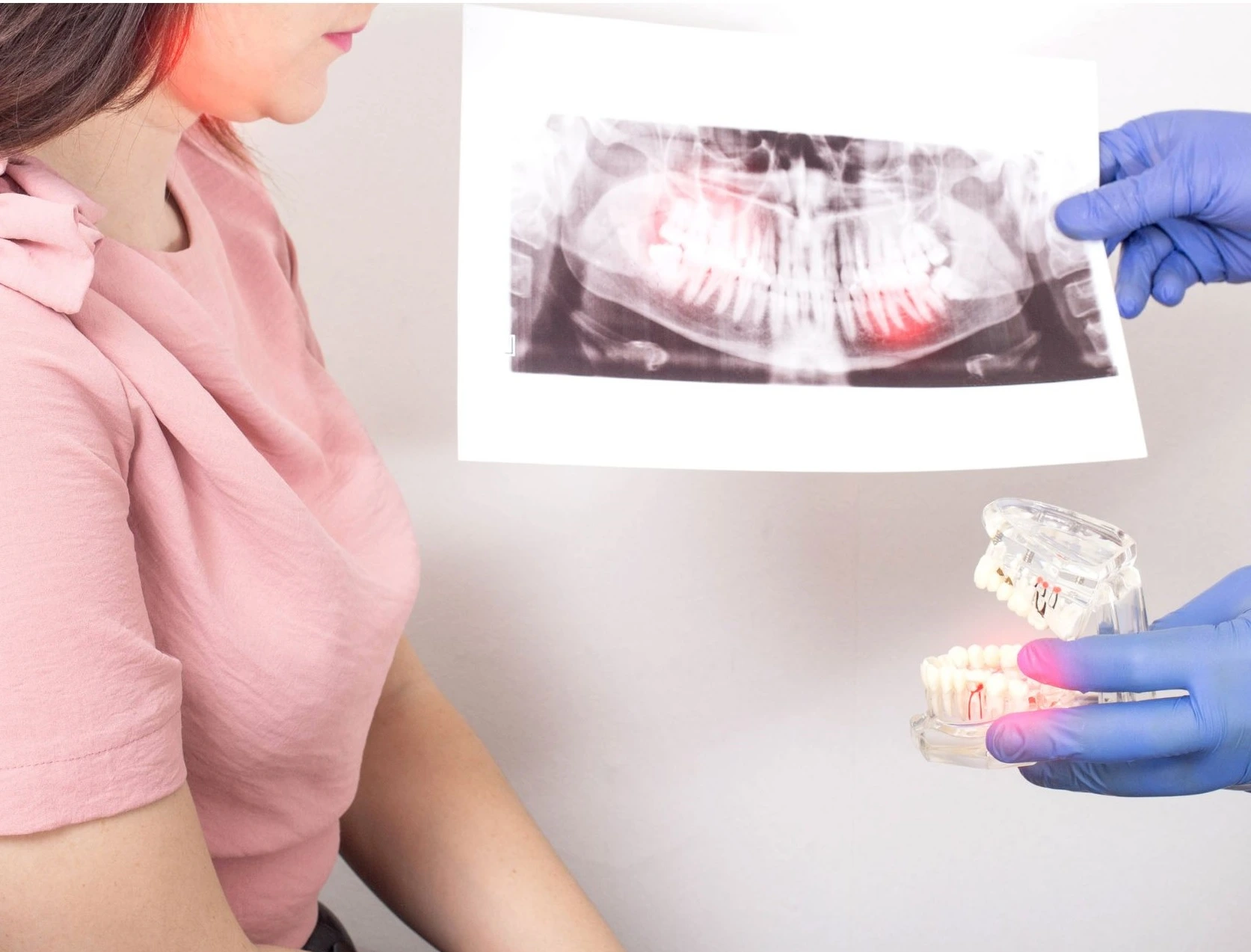
What is a dental infection?
Infections are a condition in which pathogenic microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, or fungi) colonize living tissue. In the case of dental infections in an advanced state, there is an accumulation of pus known as a dental abscess.
Before an abscess appears, dental infections can be almost imperceptible since most of the time they are asymptomatic.
Depending upon the origin of the infection, dental abscesses can be observed in different parts of the mouth:
• The gums
• The roots of the teeth
• The maxillary or mandibular bone
Why do dental infections appear and what are the symptoms?
The increase in bacteria that cause dental infections can occur for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Advanced dental caries
Tooth decay is caused by acid produced by bacteria in the mouth. This acid destroys the hard tissues of the tooth: the enamel and dentin. When a cavity is not treated in time, it progresses until it affects the dental nerve.
Symptoms: Initially, when the caries are close to the nerve, there is intense sporadic and throbbing pain (like the beating of the heart), swelling of the face, and sensitivity to acid, sweets, cold, and heat.
Later, when the caries touch the nerve, it dies and the dental abscess appears (at the level of the root of the tooth). Pain occurs when biting and chewing.
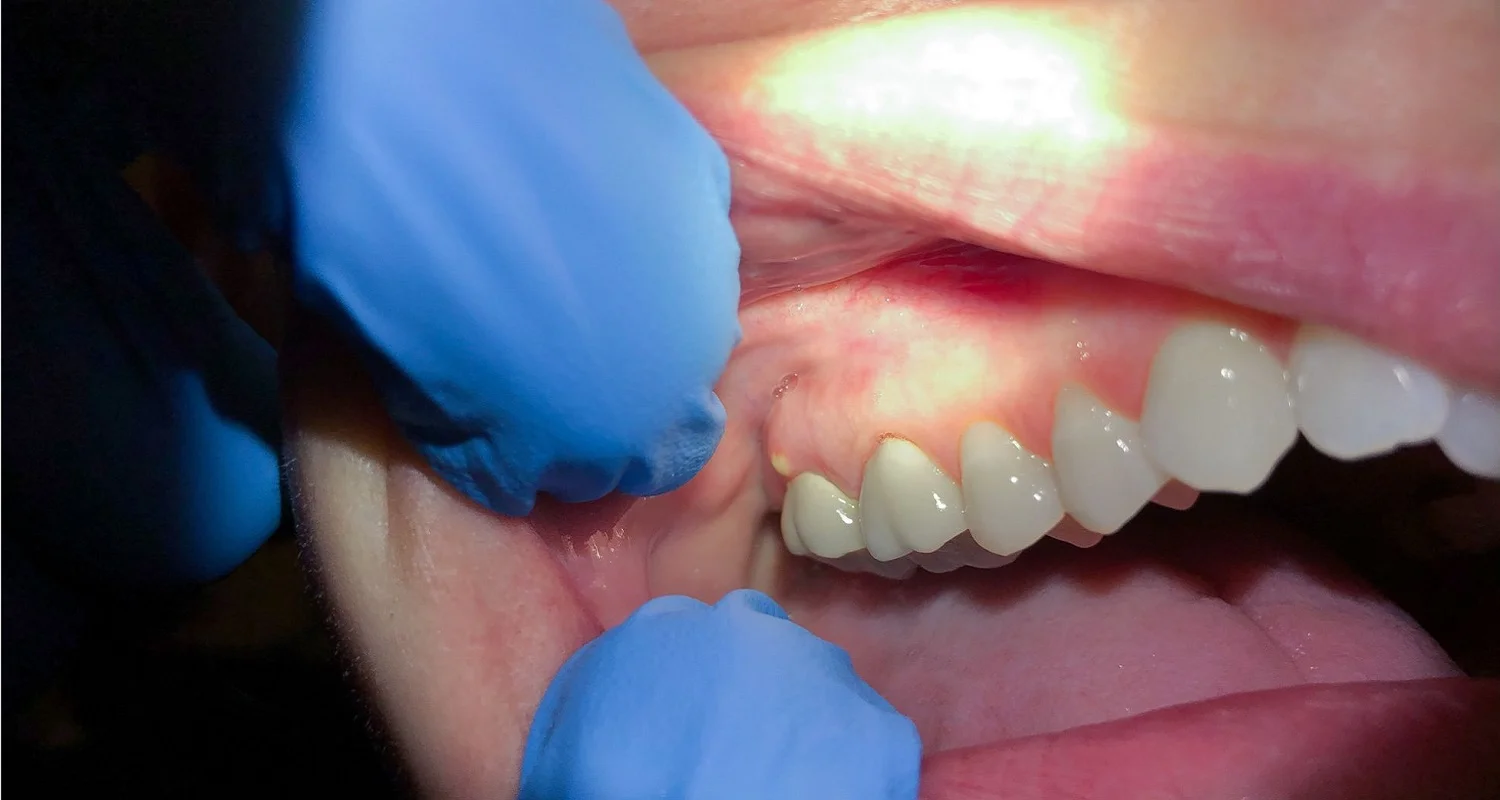
2. Gum disease
Gum disease is known as gingivitis and periodontitis. They manifest when there is an accumulation of plaque or tartar in the space between the gum and the tooth. This condition causes an inflammation that, if not treated in time, becomes an infection and an abscess appears at the gum level.
Symptoms: Redness, inflammation, and bleeding of the gums, dental sensitivity, mobility, and loss of teeth.
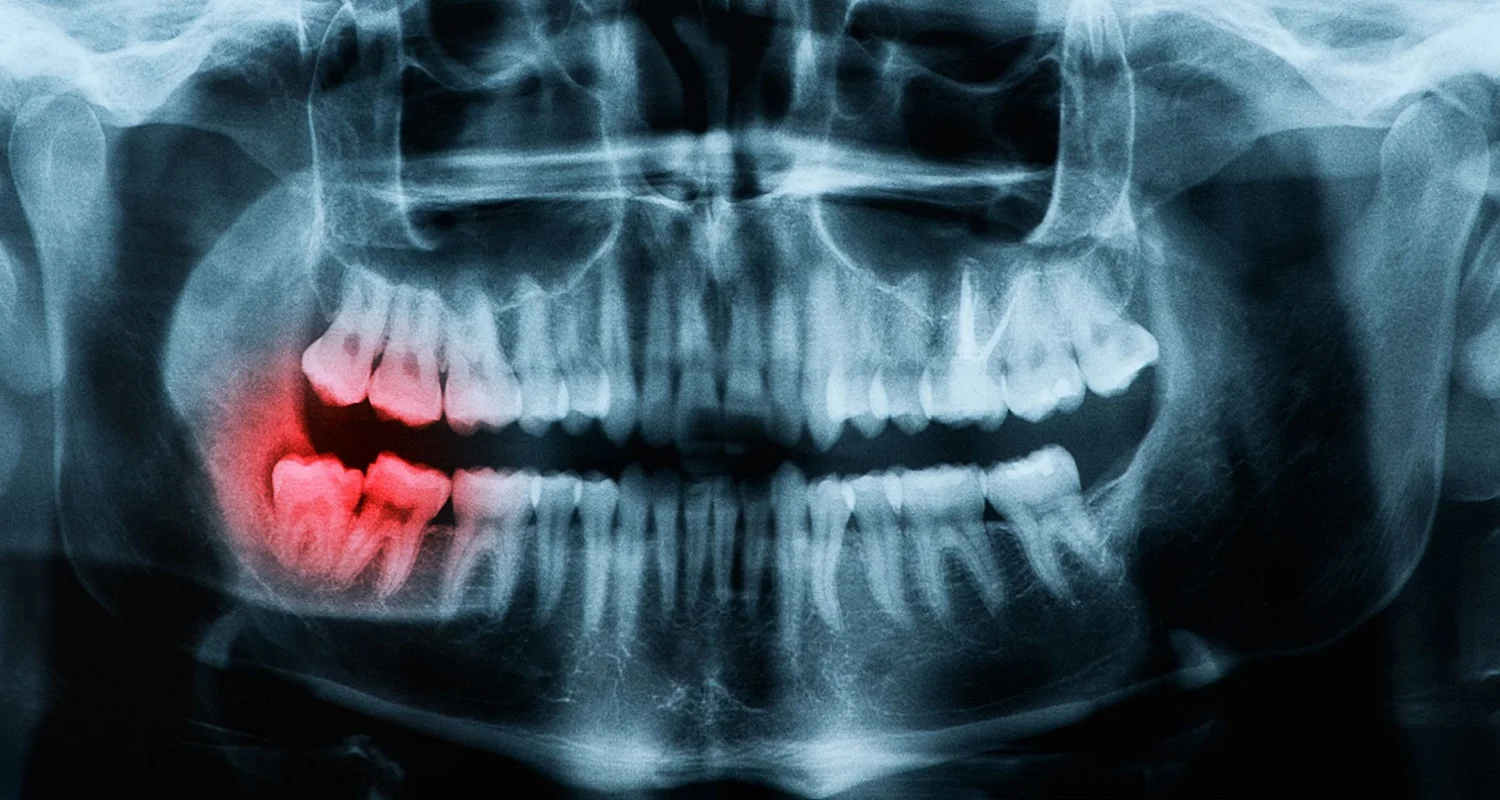
3. Wisdom teeth
The infection that occurs in wisdom teeth is called pericoronitis. It occurs when bacteria or food debris is introduced into the gums that cover these teeth in the process of eruption.
Symptoms: Pain, redness, suppuration of the gum, swelling of the face, and dental sensitivity.
4. Dental trauma (blows and falls)
In many cases, when a person suffers a fall or blows to the mouth, the teeth can be affected. They can be fractured or the dental nerve may die. In both cases, the risk of infection is high, since even a small fracture can harbor dental caries and progress.
It is recommended whenever a dental trauma occurs, go to the dentist as soon as possible for an examination.
Symptoms: Tooth discoloration (dark or grayish), throbbing pain, tooth sensitivity, gum redness, and tooth mobility.
5. Inflammation of the dental nerve
This is known as pulpitis; It occurs when advanced caries or a dental fracture reaches the dental nerve and when a restoration (shim) mismatches or is dislodged and not rebuilt.
Symptoms: Moderate pain that comes and goes, sensitivity to cold and heat; and in more advanced cases, throbbing pain especially when lying down.
Other conditions can trigger dental infections
Bad habits and dental care
The main reason why an infection occurs in the mouth is poor oral hygiene. It means you do not brush your teeth at least two times a day and do not use dental floss. Poor oral hygiene is at the root of most tooth and gum diseases.
High sugar diet
Eating and drinking foods high in sugars can contribute to the formation of dental caries, which in advanced stages can cause infections and dental abscesses.
Dry mouth (xerostomia)
Having a dry mouth increases the risk of dental cavities. The condition is related to the use of some medications, aging, or diseases such as Sjögren’s syndrome (an autoimmune disease that attacks the glands that produce moisture in the eyes, mouth, and other parts of the body).
Other common symptoms of dental infections:
• Bad smell and taste in the mouth
• Fever
• Difficulty swallowing, chewing, and breathing.
• Swollen lymph nodes: The glands in the jaw and neck swell.
• Gingival fistula: A lesion on the gum, with the appearance of a pimple that drains pus.
When it bursts, the pain decreases, but the infection is still present and the pimple fills up with pus again.
A dental infection not treated in time can present multiple complications:
• Tooth loss
• Blood infection
• Spread of infection to soft tissue
• Spread of infection to the jaw
• Spread of infection to other areas of the body

What happens if a dental infection spreads to the body?
Many situations can trigger a dental or oral infection. These infections, when not treated in time, can cause serious damage since they spread to the level of the maxillary or mandibular bone, affecting the blood vessels while entering the blood (that runs through the entire human body) and spreading through it.
This spread of infection to the body can cause multiple health complications and may even be fatal.
Oral complications
• Osteomyelitis: An infection in the bone surrounding the teeth.
• Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Infection in the blood vessels of the paranasal sinuses due to the spread of bacteria from facial or oral infections.
• Cellulitis: An inflammatory and painful process located in the skin and the fatty tissue below it caused by a poorly treated dental abscess.
• Parapharyngeal abscess: Deep neck infection
Systemic complications
• Sepsis: this serious medical condition is the immune system’s response to a blood infection; it is exaggerated and causes damage to its tissues.
• Endocarditis: The infection travels to the heart through the bloodstream and lodges on the inside of the heart valves.
• Bacterial meningitis and stroke: The infection travels through the blood vessels and reaches the brain.
• Brain abscesses
These are the most common systemic complications, but oral infections can also cause diseases of the kidneys, joints, and respiratory and gastric systems.
What are the symptoms of tooth infection spreading to body?
Among the most common symptoms are:
1. General discomfort: Fatigue, earaches and headaches, dizziness, and lightheadedness.
2. Fever: Accompanied by sweating or chills, redness of the skin, or rashes.
3. Intense swelling of the face: Difficulty opening your mouth, swallowing, and breathing properly.
4. Severe gum swelling: Accompanied by pain and bleeding.
5. Stomach problems: Diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain
6. Increase of cardiac frequency: This may be accompanied by chest pain.
7. Increase of respiratory frequency: More than 25 breaths per minute.
8. Dehydration: Dry mouth, darker urine, and less frequent urination.
9. Increased body temperature
10. Changes in vision, seizures, drifting in and out of consciousness: Symptoms of a brain abscess.
If you present one or more of these symptoms, it is recommended to visit the emergency room to receive immediate attention, as your life may be in danger.

What is the treatment for infections?
Depending upon the complexity of the infection, it may require treatments such as:
• Endodontics (root canal treatment)
• Surgery
• Abscess drainage
• Tooth extraction
• Drug prescription
• Hospitalization
In the website section on Treatment, You will find detailed information about the different options for treating an infection that may require dental or medical intervention.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if my tooth infection is spreading?
If you’re concerned about a tooth infection potentially spreading, keep an eye out for the following indicators and seek prompt medical assistance if you experience any of them: intense pain in your mouth or tongue, noticeable swelling in your face, cheeks, or neck, and challenges with swallowing.
How do you Detecting Signs of a Tooth Infection in the Bloodstream?
To identify if a tooth infection has entered your bloodstream, watch out for symptoms of bacteremia, which might include mild fever, feelings of nausea, and signs of infection in distant areas of the body. In some cases, bacteremia might resolve without medical intervention, but it could also advance into septicemia, a more severe blood infection characterized by symptoms such as chills, high fever, rapid heartbeat, intense nausea, vomiting, and confusion.
How long is it estimate on the Duration for a Tooth Infection to Spread to the Body?
If left unaddressed, a tooth abscess will gradually extend to nearby tissues and potentially further, causing detrimental effects on both your oral and general health. The timeframe for this spread can vary, spanning from weeks to months, and it’s challenging to predict precisely how long it will take for the infection to progress.
What is the mortality rate associated with tooth infections?
Based on the findings, around 1 in 150 cases admitted for oral and maxillofacial infections resulted in death. The majority of individuals who passed away had diabetes and were affected by severe or necrotizing infections. It’s crucial to give special consideration to patients exhibiting these characteristics.
Is it possible to endure a tooth infection for an extended period?
Neglecting to address a tooth infection can result in bacteria entering the bloodstream, a condition often referred to as blood poisoning, bacteremia, or septicemia. If not properly managed, septicemia can escalate into sepsis, a critical systemic infection that poses a risk to life.
Share:
References
1. Erazo D, Whetstone D. (Updated September 26, 2022) Dental Infections. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542165/
2. Frothingham, S. (May 28, 2019). What Are the Symptoms of Tooth Infection Spreading to Your Body? Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/symptoms-of-tooth-infection-spreading-to-body
3. Kandola, A. (April 3, 2020).Signs and symptoms of tooth infection spreading to the body. Medical news today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/symptoms-of-tooth-infection-spreading-to-body
4. Newman, T. (December 4, 2017). What’s to know about dental abscesses? Medical news today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/170136
5. Semenovskaya, Z., MD. (August 3, 2022).Symptoms Of a Tooth Infection Spreading To The Body. K Health. https://www.khealth.com/learn/dental-infection/spreading-to-the-body/
6. Tooth abscess. (s. f.). National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001060.htm
7. Tooth abscess – Symptoms and causes. (June 29, 2022). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tooth-abscess/symptoms-causes/syc-20350901
- Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...Recent Posts