Last Updated on: 22nd December 2025, 10:23 am
Oral health and liver disease are closely linked in ways that often go unnoticed. From gum problems to changes in saliva, liver conditions can have a significant impact on the oral cavity. This blog article explores this little-known connection and highlights the importance of a comprehensive approach to healthcare, where doctors and dentists work together to improve patient’s overall health.
What is Liver Disease?
The term “liver disease” is used to refer to various conditions of the liver. These diseases range from hepatic steatosis (fat buildup in the liver) to more serious conditions such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
The liver performs essential functions for digestion, storage of vitamins and minerals, defense against infections, and blood coagulation, among other processes.
Therefore, any liver dysfunction can have a significant impact on the general health of the individual, and its relationship with oral health is an emerging aspect of research and medical care.

Exploring the Link Between Oral Health and Liver Disease
Does liver disease affect your teeth?
Yes, liver diseases can affect your teeth in several ways:
1. Training defects: If liver diseases occur during childhood, permanent teeth may form with defects and stains.
2. Vitamin deficiency: When the liver does not function properly, the body may have difficulty absorbing and using certain essential nutrients, such as vitamin D, which is essential for the absorption of calcium and strengthening the teeth. A study published in 2015 showed that 87% of patients with chronic liver disease had vitamin D deficiencies.
3. Alterations of the immune system: Liver conditions can lead to a weakened immune system, making the mouth’s natural defenses less effective against cavity-causing bacteria.
4. Acid reflux: Gastroesophageal reflux, which often occurs along with chronic liver disease, can cause erosion of tooth enamel.
Can liver disease cause oral thrush or ulcers?
Yes, liver disease can contribute to the development of oral thrush or ulcers. Liver dysfunction can cause iron and vitamin B12 deficiency, which, added to low saliva production, predisposes to the formation of ulcers and other diseases of the oral mucosa. These lesions can be uncomfortable and make it difficult to eat food and maintain proper oral hygiene, which, in turn, can worsen oral health.
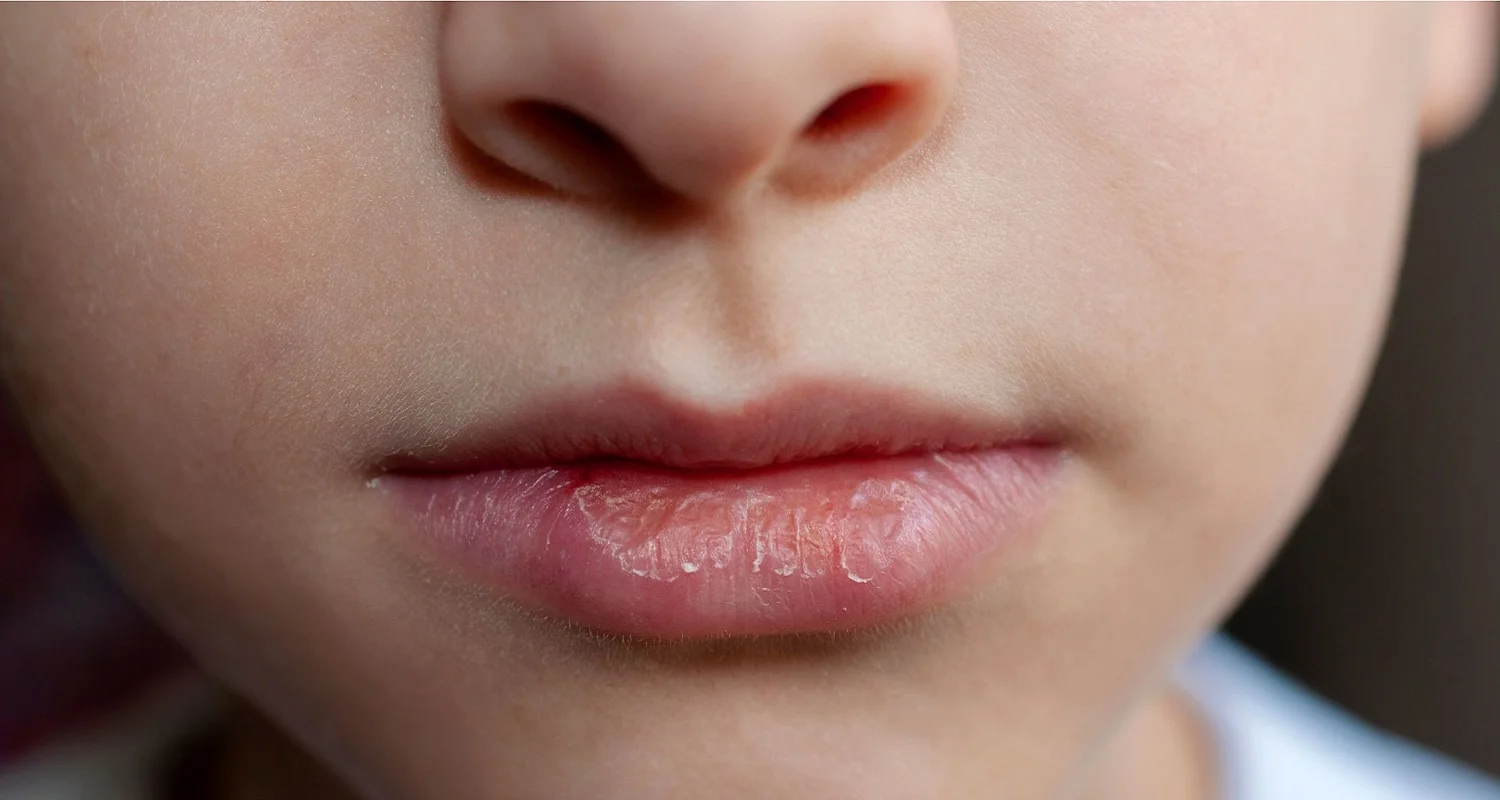 Why does liver disease cause dry mouth?
Why does liver disease cause dry mouth?
Dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, is another common side effect of liver disease. The liver breaks down chemicals and produces bile, which is essential for digestion. When the liver does not function properly, there can be a buildup of toxins in the body that affects the salivary glands, decreasing saliva production. A lack of saliva can increase the risk of cavities and gum problems, as saliva plays a crucial role in protecting teeth and gums from bacteria.
Can liver health affect gum health?
Yes, liver health and gum health are interconnected. Liver disease can increase systemic inflammation in the body, which in turn can contribute to gum inflammation, known as periodontitis. Additionally, liver problems can weaken the immune system, making the gums more susceptible to infections and periodontal diseases.
In 2018, a group of researchers published a study where he found a particular population of bacteria in patients suffering from periodontitis and cirrhosis. It is believed that this could be caused by alterations in the immune system, which allow a greater number of bad bacteria to multiply in the mouth.

Oral Hygiene Practices for Liver Health
Maintaining optimal oral hygiene is not only essential for a radiant smile, but it can also have a positive impact on liver health. Research has shown that preventing periodontal disease and tooth decay can help reduce the burden on the liver and minimize inflammation throughout the body.
Here are some key practices that can contribute to a healthy mouth and, therefore, a healthier liver:
1. Brushing and flossing regularly: These basic practices help prevent the buildup of harmful bacteria that can enter the bloodstream and affect the liver.
2. Sugar control: Limiting sugar consumption reduces the risk of cavities and, at the same time, decreases liver burden as the liver processes sugar.
3. Avoid alcohol and tobacco: Alcohol and tobacco are known for their negative impact on oral and liver health. Reducing or eliminating its consumption benefits both systems.
4. Maintain a balanced diet: A diet rich in nutrients, especially vitamins and minerals, contributes to a healthier mouth and liver.
5. Control periodontal disease: Treating gum conditions early reduces oral inflammation and potentially systemic inflammation, easing the burden on the liver.
6. Regular dental visits: Regular dental exams allow early detection and treatment of oral problems, avoiding liver complications.
Conclusion
The relationship between oral health and liver diseases is undeniable. The comprehensive health care of our patients must take this connection into account, and dental professionals must work hand in hand with hepatologists to provide a comprehensive and effective approach to medical care.
In the next sections, we will further explore how maintaining a healthy smile can be an indicator of a healthy liver and what steps can be taken to prevent and address these problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do liver conditions affect oral and dental health?
This narrative review addresses the various connections between long-term liver diseases and oral and dental health. Symptoms in the oral cavity such as xerostomia, ulcers, erosions, and abnormal linguistic conditions are particularly common in individuals suffering from chronic liver disorders.
Can liver disorders lead to dental health complications?
Studies have revealed that alterations in the oral mucosa are noticeably more common in patients with liver cirrhosis, and these individuals usually have markedly reduced salivary production. According to experts, as the condition of the liver worsens, the chances of the individual having teeth with cavities, missing teeth, or requiring fillings increase.
Does an infection in the mouth have an impact on liver health?
Clinical and scientific evidence is increasing regarding the long-term adverse effects that a chronic gum infection can have on various liver conditions. This includes the development and progression of diseases such as NAFLD, the formation of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, as well as influencing the success of a liver transplant.
What is the reason why dental extractions are not recommended in cases of liver cirrhosis?
In a group of patients, hemorrhagic complications after tooth extraction were observed in 4.4% of cases. Surgical extraction operations and removal of multiple teeth in a single session were significantly associated with an increased risk of bleeding (p < .05). However, both preventive platelet transfusion and post-transfusion platelet count were not shown to have a significant impact on this risk.
Share:
References
1. Golla, K., Epstein, J. B., & Cabay, R. J. (2004). Liver disease: current perspectives on medical and dental management. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology, 98(5), 516-521.
2. Fernández, N. F., Torres, P. L., Matias, D. J., Plaza, F. J., & Goñi, J. L. O. (2016). Vitamin D deficiency in chronic liver disease, clinical epidemiological analysis and after vitamin supplementation.Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 39(5), 305-310.
3. Åberg, F., & Helenius-Hietala, J. (2022). Oral Health and Liver Disease: Bidirectional Associations—A Narrative Review. Dentistry Journal, 10(2), 16.
4. Cutler, N., & Ac., L. (2012). What does our tongue tell us about our liver? Liversupport.com. https://www.liversupport.com/what-does-our-tongue-tell-us-about-our-liver/
5. Liver disease & liver problems. (s/f). WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/hepatitis/liver-and-hepatic-diseases
6. Nall, R., MSN, & CRNA. (Apr 2, 2018). What does the liver do? Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/what-does-the-liver-do
-
Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...Recent Posts