Last Updated on: 2nd January 2026, 09:05 am
Root canal treatment, also known as endodontics, is a dental procedure that involves removing diseased or damaged tissue from inside a tooth and then replacing it with artificial material. This procedure is often used to treat teeth that are infected, decayed, or otherwise damaged. But, some people claim root canals and cancer have a connection with each other.
It has been hypothesized that there may be an association between endodontics and cancer. The exact cause of this link is still unknown, but it is believed that bacteria present in the root canal may be responsible for this consequence since the root of the tooth is connected to the nerves in the mouth.
The bacteria present release toxins that travel through those nerves into the bloodstream, then spread and presumably become cancerous.
This article will explain what an endodontic treatment is, how likely it is that root canal treatments will cause cancer, and other myths about this treatment.
What is a root canal?
A root canal treatment is a common dental procedure used to treat teeth damaged by decay, trauma, or infection.
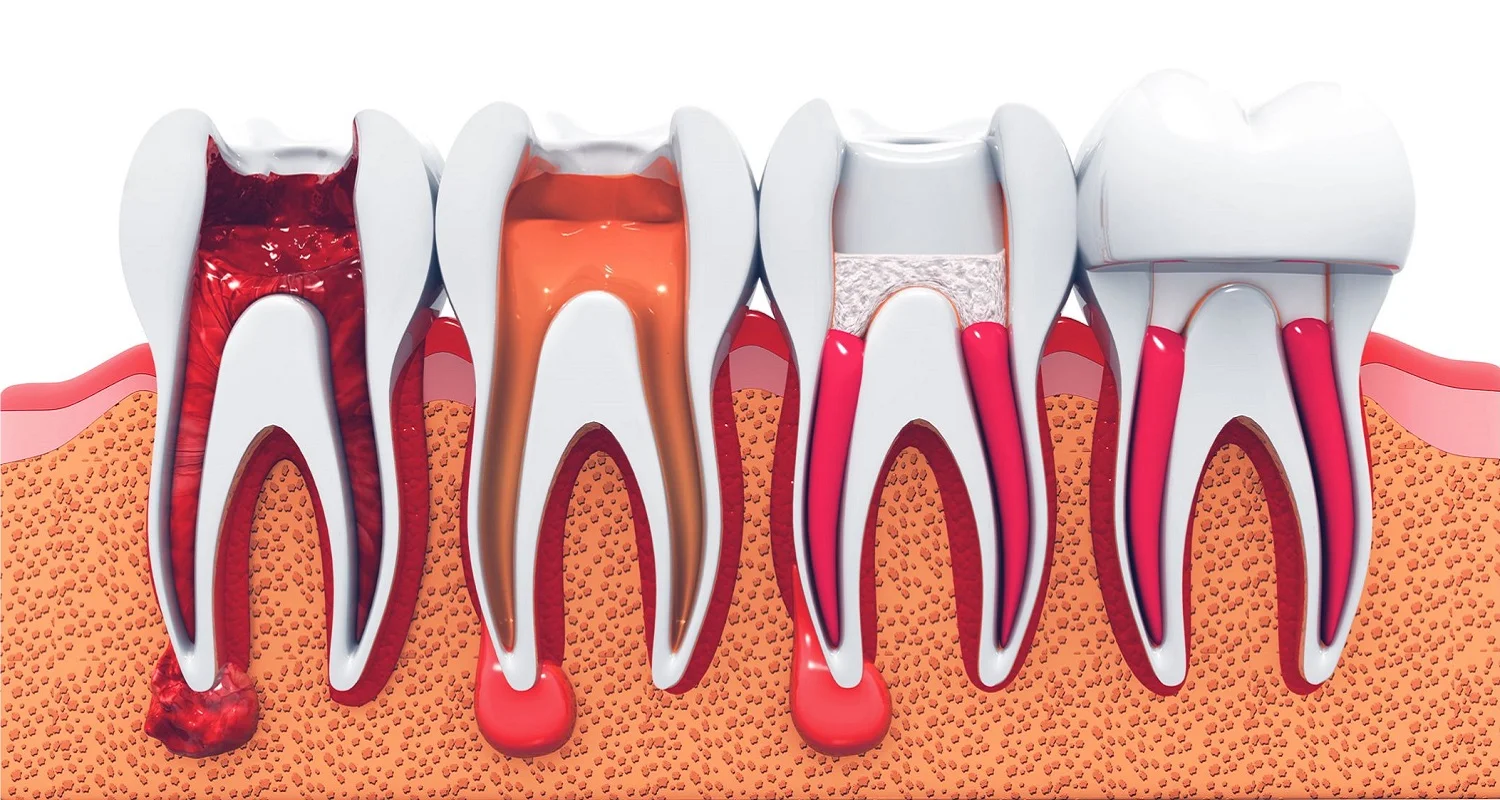
The tooth is made up of 3 layers:
• Enamel: The outermost area is the hardest tissue of the human body. If you want to know more about enamel, you can visit our article here.
• Dentin: Intermediate zone that lies between the enamel and the dental nerve.
• Pulp dental: the innermost tissue that contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue cells. It is located along the roots of the teeth in an area known as the root canal.
If a cavity or trauma affects the enamel or dentin, it is unlikely that an infection will develop. But when that damage affects the dental nerve, bacteria easily enter the root canal, causing an infection and subsequent nerve death.
Symptoms of a dental infection
• Pain when biting and chewing
• Increased sensitivity when eating food or drinking hot or cold drinks
• Swelling and redness of the gum
• Abscess in the gum near the tooth (with pus)
• Swelling of the face
• Throbbing pain in the tooth
When the dental nerve is affected, one or more of these symptoms may occur. If this is the case, it is necessary to carry out an endodontic surgery or treatment, which consists of extracting the infected dental nerve from the inside of the tooth, cleaning and disinfecting the root canal, and finally filling it with a special material.
After this process, a restoration is made to prevent problems from occurring in the future. The goal of a root canal treatment is to save the tooth, preserving its natural structure and function. It is a safe and effective way to keep the tooth and eliminate an existing infection.
Can root canals cause cancer?
There is no evidence that root canals cause cancer. This myth began in the 1920s when a dentist named Weston Price carried out a series of experiments and published essays with the results obtained. He related root canals to the appearance of cancer.
The teeth after treatment still contain harmful toxins that, in his opinion, travel to other areas of the body and contribute to the development of cancer and other diseases.
This study was poorly designed, so its results are not reliable. Some of the defects were:
• Little control of the conditions of the experiments.
• Tests were performed in non-sterile environments.
• No investigator has been able to recreate the results of the study.
• It did not involve the use of control groups and the other standard requirements of a modern scientific study.
Later in 2019, a documentary on Netflix called “RootCausee” generated great commotion. It explained the theory of focal infection, in which bacteria are transported through the bloodstream from distant places and generate multiple systemic problems, including cancer.
The documentary claims that 97% of breast cancer patients had an endodontically treated tooth on the same side of the jaw.
The truth about root canals and cancer
The AAE (American Association of Endodontists) published an article about the safety of root canal treatments. Points to highlight are:
1. Every year 25 million root canal treatments are performed around the world effectively and safely. If it were true that root canals cause cancer, there would be much more scientific information about it, and it would not be the treatment of choice to save teeth.
2. There is no valid scientific evidence linking root canal treatment to diseases in other parts of the body. It is true that some people with cancer may have had a root canal at some point in their lives. but it does not mean that this procedure is related to the development of cancer.
3. In 2013, a study published in a journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA Otolaryngology—Head & Neck Surgery) found that a patient’s cancer risk does not change after undergoing root canal treatment. The author even mentions that people who had undergone multiple root canals were less likely to have head and neck cancer.
4. Technological advances in medicine have made root canal treatments more predictable and successful today.
Other myths about root canals
1. Root canals are painful: This treatment does not cause pain; on the contrary, it removes it. Anesthetics are used to make the procedure as comfortable as possible.
2. Extractions are preferable to root canals: Saving the tooth is the best option. Every missing tooth must be replaced, which is costly and time-consuming; If not replaced, it can create a collapsed bite.
3. Root canal treatments cause other diseases such as Alzheimer’s: It is not possible to contract a disease from having a root canal; this theory is unfounded and cannot be validated.
The bacteria found around a root canal-treated tooth are the same as those found throughout the mouth, so there is no valid, scientifically proven reason to say that root canal treatment causes diseases such as cancer.
It is normal to have doubts and ask questions about this type of treatment.
Ideally, seek information from reliable and scientifically backed sources and always consult a dentist about this and other questions you have.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is getting a root canal bad for your health?
There’s no need to worry about root canals causing health issues. In fact, skipping this treatment could be more detrimental. The American Dental Association (ADA) advises that deep cavities, cracks, or fractures can allow bacteria to reach the inner part of your tooth (the pulp), leading to an infection.
Is there a link between root canals and cancer?
There is no scientific evidence to support the claim that root canals cause cancer. This misconception seems to originate from misinterpreted studies and unfounded theories. Multiple rigorous research studies and systematic reviews have concluded that there is no connection between root canals and cancer development.
Where does the myth about root canals and cancer come from?
The myth about root canals and cancer may have its origins in a study from several decades ago that found a higher incidence of cancer among people who had received root canal treatments. However, this study had significant methodological limitations and could not establish a causal relationship. Subsequent studies with more robust methodologies have found no association between root canals and cancer.
Why is it important to debunk the myth about root canals and cancer?
It is crucial to debunk this myth because it can have negative consequences for people’s oral health. Unfounded fear of cancer could lead people to postpone or avoid necessary root canal treatments, which can lead to serious complications such as dental infections, tooth loss, and chronic pain.
What are the risks of not treating a damaged tooth that might require a root canal?
Not treating a damaged tooth that might need a root canal can carry significant risks to both oral and overall health. Untreated dental infections can spread to other parts of the body, causing problems such as abscesses, bone infections, and heart problems. In addition, persistent pain and sensitivity can negatively impact quality of life.
When is a root canal necessary?
A root canal is necessary when the dental pulp, the living tissue inside the tooth, is damaged or infected. This can happen due to deep cavities, dental trauma, or fractures. Common symptoms that indicate the need for a root canal include severe tooth pain, sensitivity to hot or cold, swelling in the gums, and darkening of the tooth.
It is important to consult with a dentist to obtain an accurate diagnosis and determine if a root canal is the right treatment.
Share:
References
1. American Association of Endodontists. (November 15, 2022). Myths About Root Canals. https://www.aae.org/patients/root-canal-treatment/myths-root-canals/
2. American Association of Endodontists. (2014). Root canal safety talking points. AAE. https://www.aae.org/specialty/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2017/06/rootcanalsafetytalkingpoints.pdf
3. Ames, H. (March 23, 2020). Root canal procedures do not cause cancer: This is why. Medical news today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/root-canals-and-cancer
4. Canadian Cancer Society. (s. f) Do root canals cause cancer? CCS. https://cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/reduce-your-risk/myths-and-controversies/do-root-canals-cause-cancer
5. Snyder, A. (March 15, 2019). Root Canals and Cancer. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/root-canal-and-cancer
6. Tezal, M., Scannapieco, F.A., Wactawski-Wende, J., Meurman, J.H., Marshall, J.R., Rojas, I.G., Stoler, D.L., & Genco, R.J. (2013).Dental Caries and Head and Neck Cancers. JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery, 139(10), 1054. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2013.4569
-
Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...