Last Updated on: 30th December 2025, 06:03 am
What is Anodontia?
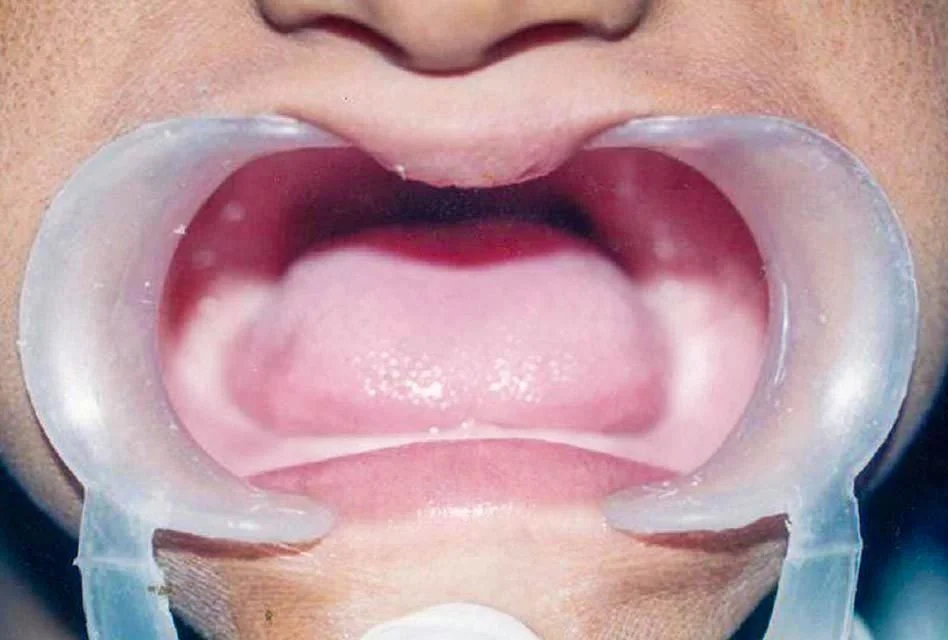
Anodontia refers to the absence of all permanent or primary teeth. It is a rare condition in which the teeth never form and therefore never emerge in the mouth. It is not to be confused with tooth loss, in which teeth form but are extracted or lost due to accidents, tooth decay, or gum disease.
What are the Causes of Anodontia?
Anodontia is caused by a genetic mutation, that is, a change in the formation of a particular gene. In the vast majority of cases, this mutation is the same one that gives rise to a condition called ectodermal dysplasia, where abnormal development occurs in the skin, hair, nails, sweat glands, and total absence of teeth.
Ectodermal dysplasia is inherited when both parents carry the defective gene, even though they do not necessarily have the disorder.
In very rare cases, only anodontia may occur without the other symptoms of ectodermal dysplasia. It is believed this is due to a mutation in a yet unknown gene.
How and when is Anodontia Detected?
A patient can be suspected of having anodontia in two cases:
• When a baby is over one year old and has not developed any teeth.
• When a child is in pre-adolescence and has not started dental replacement, that is, when no permanent teeth have yet erupted.
In either of these two situations, during a consultation with a dentist, a physical examination and x-rays will be performed to verify whether the teeth have formed or not.
Why is it Important to have Teeth?
Teeth are small, solid organs that have several functions:
• Chewing: The teeth grind food before it is swallowed. This process is essential for good digestion, since for the stomach and intestines to function properly, they must receive well-chewed food.
• Phonation: The teeth help in the correct pronunciation of words, regulate the passage of air, and serve as a support for the tongue when articulating different phonemes.
• Aesthetics: The teeth are responsible for the aesthetics of the smile. These are very important for the lower third of the face. A beautiful and healthy smile engenders self-esteem and helps develop interpersonal relationships. By contrast, the total absence of teeth can give the appearance of an aged face.
How can Anodontia Affect People’s Health?
The total absence of teeth could cause:
• Digestive problems due to not being able to chew food properly.
• Disadvantages in speech.
• Self-esteem problems, when aesthetics are affected.
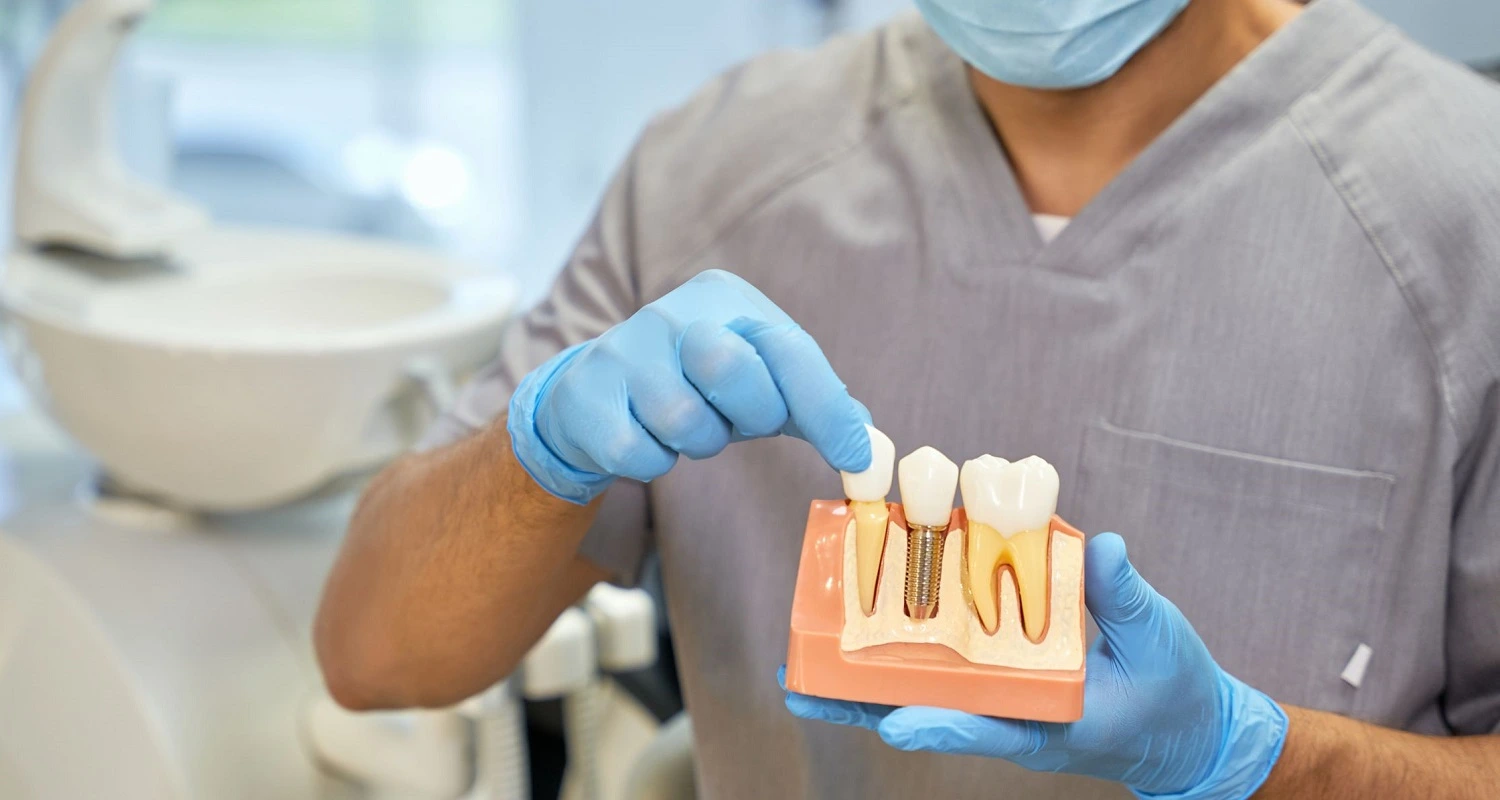
What is the Treatment for Anodontia?
In cases where the teeth have not formed, the dentist can offer several alternatives:
• Dental implants
• Full dentures supported on dental implants
• Total dentures supported on the gums
If you would like to learn more about dental implants, you can explore this related article.
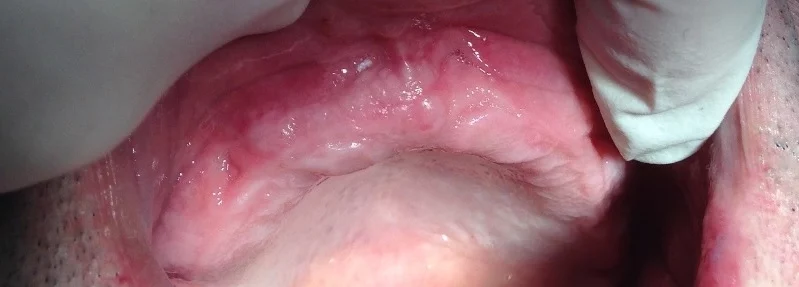
Is there Partial Anodontia?
In some cases, some teeth will form, while others do not. Although some people may refer to this as “partial anodontia”, the correct term is “dental agenesis”. It indicates a condition in which some teeth do not form. Thus, depending on the number of missing teeth, dentists will mention:
• Hypodontia: When between 1 and 5 teeth are not formed.
• Oligodontia: When 6 or more teeth are not formed.
While anodontia is defined as the absence of all teeth, there are cases where a condition that causes too many teeth to grow in your mouth exists, and it’s called hyperdontia. If you’re interested, you can check out this article.
Conclusion
Anodontia is a rare condition caused by a genetic mutation. It is generally part of a disorder called ectodermal dysplasia and occurs with other symptoms caused by failure to develop hair, nails, and skin, among other things. Because the presence of teeth in the mouth is very important for chewing, speaking, and aesthetics, various alternatives allow patients to chew, speak, and smile with peace of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is complete anodontia?
Complete anodontia is the absence of all permanent or primary teeth, a rare genetic condition where teeth never form and emerge in the mouth.
What is partial anodontia?
Partial anodontia, or dental agenesis, is when some teeth are missing. Hypodontia refers to 1-5 missing teeth, while oligodontia refers to 6 or more missing teeth.
Is anodontia a congenital absence?
Yes, anodontia is a congenital condition present from birth, typically caused by a genetic mutation often associated with ectodermal dysplasia.
How does anodontia affect my oral and overall health?
Anodontia can cause digestive problems due to improper chewing, speech difficulties, and aesthetic concerns that may affect self-esteem and social interactions.
What are the treatment options for anodontia?
Treatment options include dental implants, full dentures supported on dental implants, and total dentures supported on the gums. These treatments help restore chewing function, speech, and aesthetics.
Share:
References
1. Wiener, C. R. (Abr 1, 2019). Hypodontia, Oligodontia and Anodontia in West Virginia Appalachia. Journal of Dental Hygiene. https://jdh.adha.org/content/93/2/34.short
2. Anodontia: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment. (Sep 15, 2022). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24168-anodontia
3. Bhat, V., Bhat, V. S., Vadakkan, J., Bhat, S. S., Shetty, S., & Hegde, S. K. (Jul, 2021). Prosthodontic Management of Congenital Hypothyroidism with Anodontia: A Case Report. International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry, 14(4), 586. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8585887/
4. What Is Anodontia? (Feb 11, 2022). Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/what-is-anodontia-5214570
5. Muñoz, J. V. A., Báez, T. D. M., & Lancón, R. D. V. (Jan 7, 2021). Prosthetic rehabilitation in a pediatric patient with ectodermal dysplasia.Latin American Journal of Pediatric Dentistry, 11(2). https://revistaodontopediatria.org/index.php/alop/article/view/248
6. Castle , MA , Drager , MD , Maudet , A , & Leiva , A (Oct 12, 2022). Aesthetic and functional rehabilitation of a girl with Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia. Report of a case. InXXI Latin American Congress of Pediatric Dentistry (Vol. 12, No. Supplement).https://congreso.revistaodontopediatria.org/index.php/alop/article/view/235
-
Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...