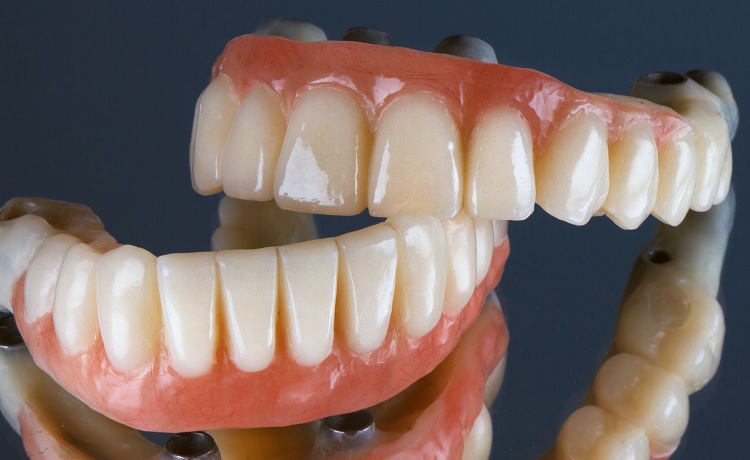
Last Updated on: 17th December 2025, 10:05 am
Permanent dental prostheses have become a lifesaver. The loss of one or more teeth affects not only the function of the oral cavity but also the aesthetics of a person’s face. It can generate low self-esteem and insecurity.
What are Dentures for?
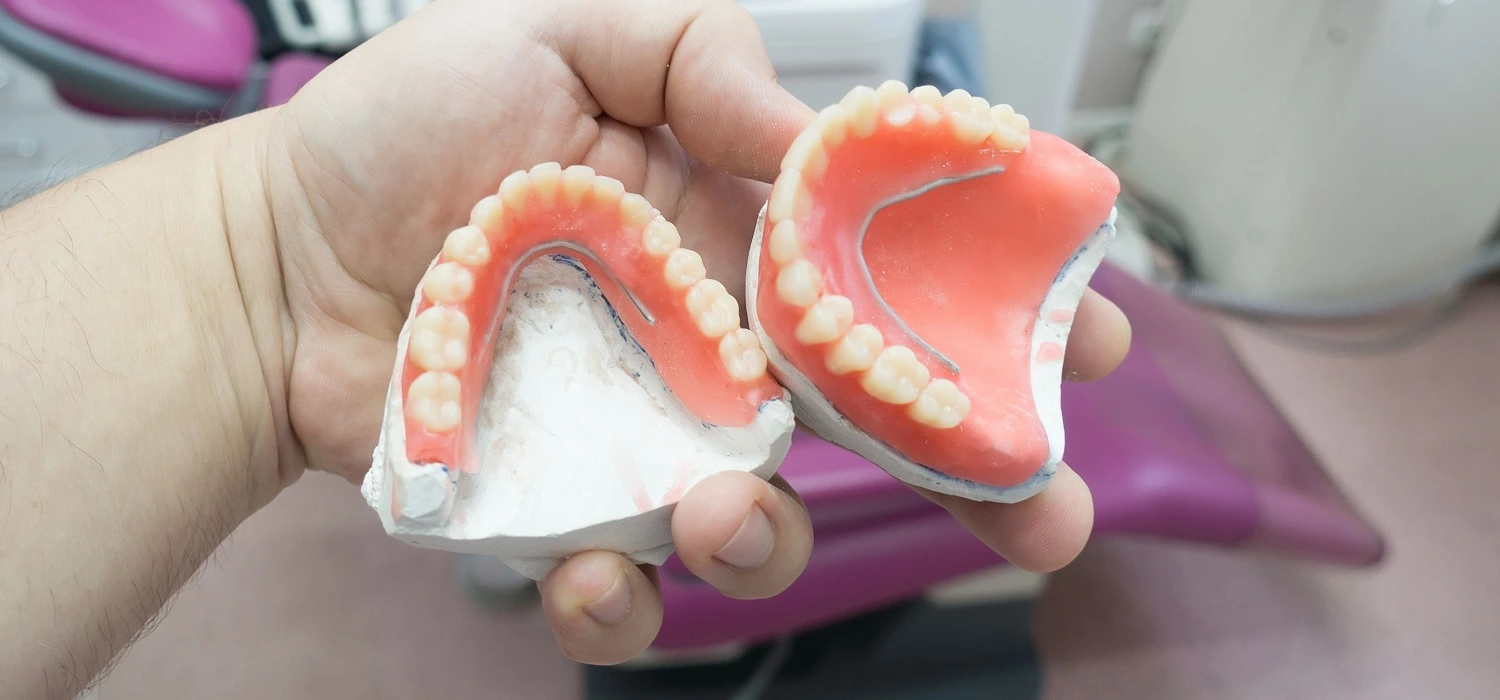
Generally, when teeth are lost, those that remain in the mouth lean and change position to try to close the space. Also, the facial muscles lose their support and the appearance of the face changes. People look older when the shape of the face changes when speaking.
Dental prostheses are made to look as similar as possible to the original teeth to restore the function, aesthetics, stability, and support of the oral cavity.
There are traditional dentures, called removable dentures, which are generally removed for cleaning and sleeping, and then put in again during the day.
There are also permanent dental prostheses, which are fixed to the teeth, or dental implants that cannot be removed. This article will talk about the various options, how many types there are, their benefits, and how to care for them. We invite you to read on.
What are Permanent Dental Prostheses?
Also known as fixed prostheses, they are used permanently to replace missing teeth; they allow people to show off a beautiful smile, and serve to fulfill all the functions of the oral cavity such as speaking, eating, and laughing normally.
Depending upon each case, there are multiple fixed prostheses to choose from. Depending upon how many teeth have been lost, the general condition of your mouth, and your overall budget, the dentist will give you one or several alternatives.
Types of Permanent Dental Prostheses
1. Individual prostheses
Known as dental crowns, they act like a coating placed on a tooth or an implant. They are very similar to the shape and color of natural teeth. They are indicated to replace any missing dental pieces.
The most common crowns are:
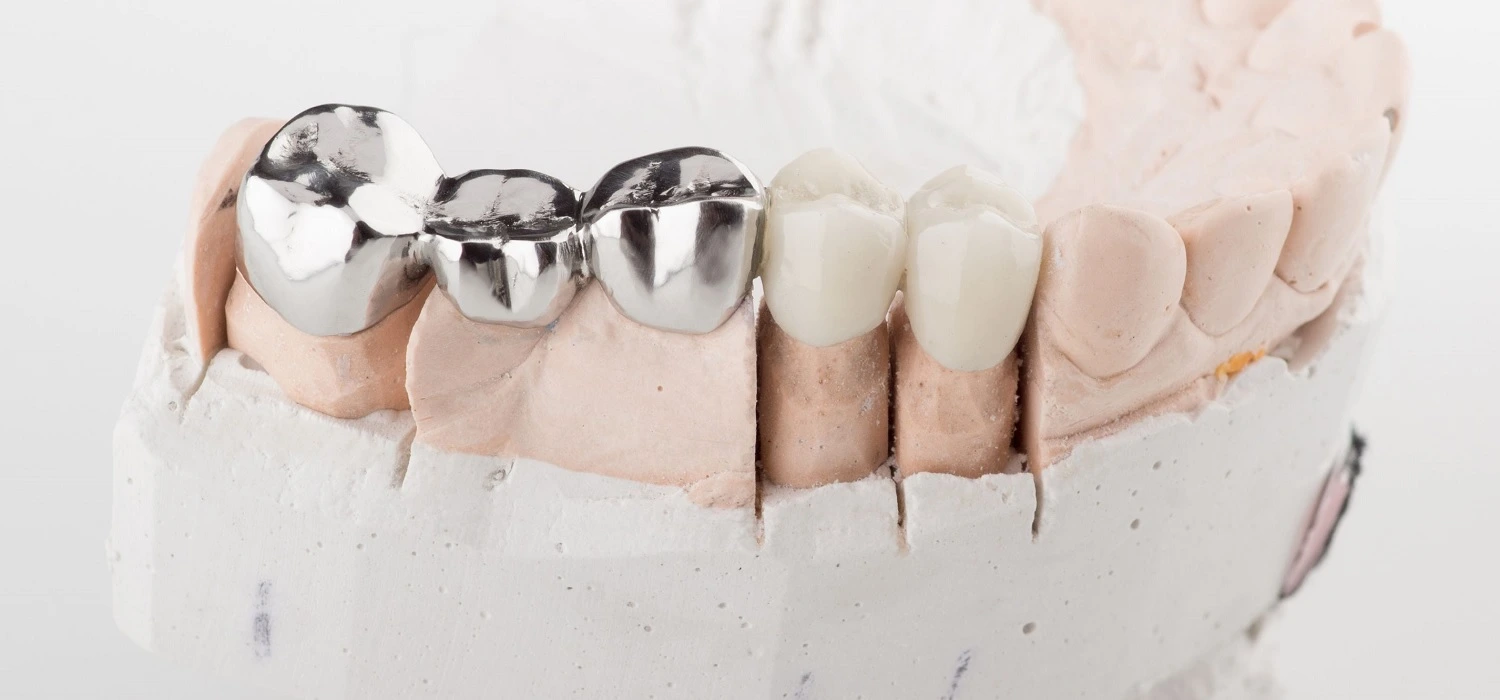
• Metal-porcelain: An internal metal layer is covered by a porcelain layer of the same color as the tooth. They are resistant, but not particularly aesthetic, which is why they are indicated mainly for the posterior teeth.
• Zirconium crowns: These are a type of white metal, so they are very resistant to daily wear and tear.
• Porcelain crowns (lithium disilicate – feldspar): as highly aesthetic materials, they are indicated to replace the anterior teeth, which are seen when smiling.
• Metallic crowns: They are stainless steel. They are usually used in children when they have lost dental structure due to caries and the teeth must be kept for a long period.
2. Partial dentures
Known as dental bridges, they replace one or more adjacent teeth. They consist of a series of crowns, joined together and supported on the root of a natural tooth or a dental implant.
Dental bridges can be:
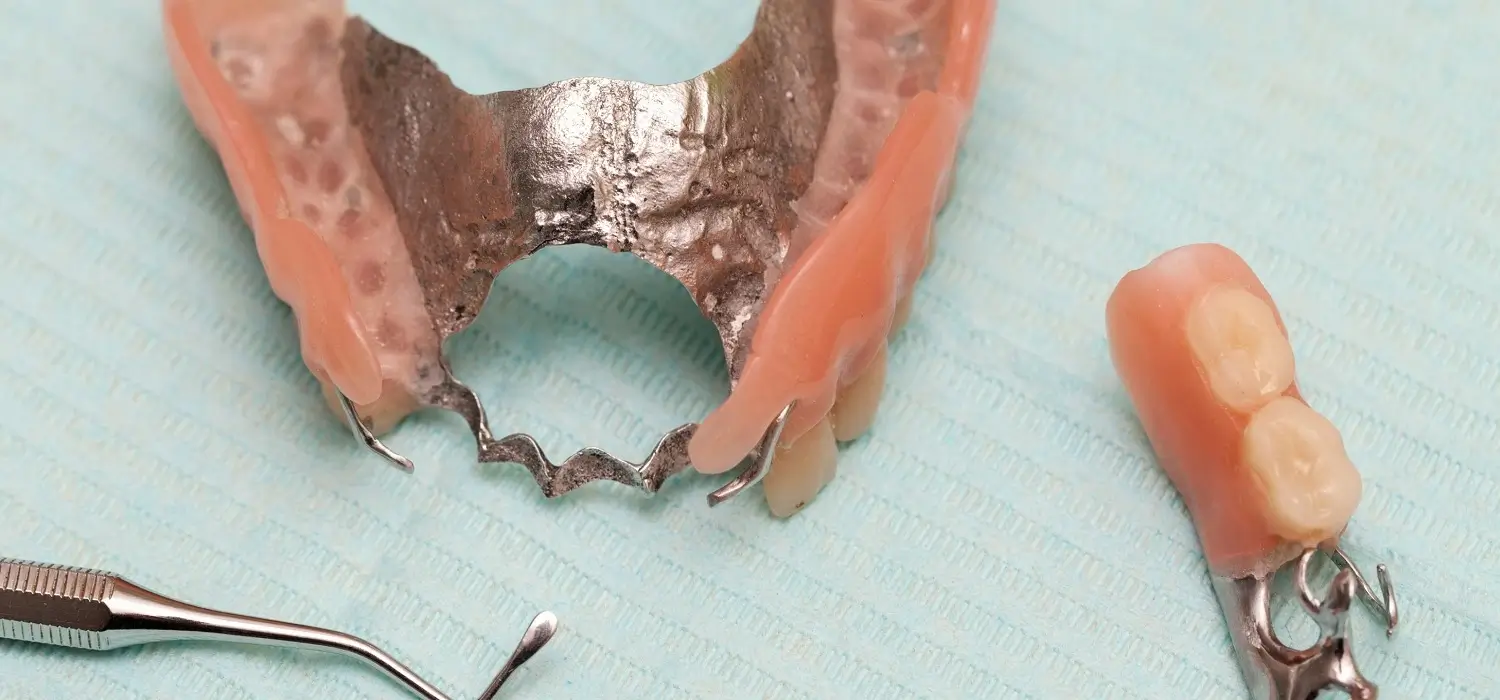
• Traditional: The dentist must carve the two teeth adjacent to the missing tooth to create a space where the bridge is to be placed. This is done so that the natural teeth (like pillars) support the artificial tooth (pontic).
• Maryland: Replaces the missing tooth using the neighboring teeth as support.
• Cantilever: The dentist carves one of the teeth next to the missing tooth to use it as an abutment for the missing tooth.
• Implant supported: When several contiguous teeth have been lost, implants can be placed at the ends of the edentulous area, and a crown bridge can be made over them.
3. Total dentures
These are known as implant-supported or hybrid total dentures. When a person has lost all their teeth, they are replaced with a full denture. It is difficult for patients to adapt to the use of conventional prostheses since they move or may cause discomfort and pain. As an alternative, prostheses supported on dental implants can be placed; generally, 4 to 6 upper or lower implants are placed, and the prostheses are then supported by them.
What are the Advantages?
The advantages of these prostheses include:
1. Exceptional stability
They do not move while the patient performs.s their daily activities, allowing them to speak with greater confidence and eat without worrying that the prosthesis is going to fall out at any moment. In addition, a permanent prosthesis generates a greater bite force.
2. Jaw stimulation
Unlike traditional dentures, fixed prostheses offer protection against bone loss and prevent damage to the jaw bone.

3. Improves quality of life
Permanent dentures give a more natural-looking smile, adhere more precisely to the gum line, which decreases discomfort and irritation, and provide support to the lips and cheeks, so the face no longer appears sunken. Self-esteem and confidence improve remarkably.
4. Cost
depending upon the needs of the patient and the type of denture or prosthesis required, there may be a variation in cost. For example, a complete denture can run from $1,300 to $3,000 if it is only one side or both.
On average, the range can be between $700 to $30,000. However, it may be more economical in the long run to purchase one that does all the required functions since you won’t have to change dentures frequently.
Care of Permanent Dental Prostheses
The duration of a fixed prosthesis and the general health of the oral cavity will depend mainly on the care you take. In that regard, the following tips will be useful:
• Avoid biting very hard things or foods (nuts with shells, shellfish, among others).
• Hygiene immediately after each meal and before going to bed; will help keep the dentures and teeth clean.
The correct way to clean a permanent prosthesis is:
• Brush the accessible area of the prosthesis with toothpaste and a toothbrush (just as you do with natural teeth).
• Clean the area between the politics and the gum. You can use dental floss to sweep away the plaque and any food debris that remains trapped there since they can ferment and cause halitosis (bad breath).
• The spaces between the teeth and the gum can be cleaned with interdental brushes; they are also used between widely-spaced teeth. In areas where this brush cannot enter, dental floss is best used.
• Use an alcohol-free dental rinse.
Permanent dentures are the best option so you can permanently forget about dental discomfort and related problems. They will last longer and provide a better fit than traditional prostheses.
If you are considering getting dentures, check with your dentist about the different options for your case to make the best decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of dental prosthesis?
There are several types of permanent dental prostheses, including dental crowns for individual teeth, dental bridges to replace one or more contiguous teeth, and implant-supported total dentures for people who have lost all their teeth. The choice of the appropriate type will depend on the number of missing teeth, the general condition of the mouth and the patient’s budget.
What are permanent dental prostheses?
Permanent dental prostheses, also known as fixed prostheses, are devices used to replace missing teeth permanently. They provide a natural-looking smile and restore the full functionality of the oral cavity, such as speaking, eating, and laughing normally.
What are the benefits of permanent dental prostheses?
Permanent dental prostheses offer exceptional stability, preventing movement during daily activities, and providing greater bite force. They also stimulate the jaw, protect against bone loss, and improve the quality of life by giving a more natural-looking smile, reducing discomfort, and providing support to the lips and cheeks.
How should permanent dental prostheses be cared for?
To ensure the longevity of permanent dental prostheses and overall oral health, it is essential to avoid biting very hard foods, maintain hygiene immediately after each meal and before bed, brush the prosthesis with toothpaste and a toothbrush, clean between the pontics and gum with dental floss, use interdental brushes for wider spaces, and rinse with an alcohol-free dental rinse.
How long do permanent dental prostheses last?
The longevity of permanent dental prostheses depends on proper care and maintenance. With good oral hygiene practices and regular dental check-ups, these prostheses can last many years, often over a decade. Regular cleaning, avoiding hard foods, and following your dentist’s recommendations will help extend their lifespan.
Share:
References
1. Dental Crowns: Why Would You Need One? (Reviewed: April 14, 2023). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/10923-dental-crowns
2. FOR. (s. f.). Implant overdentures, introduction. foundation for oral rehabilitation. https://experts.llu.edu/en/publications/implant-overdentures-foundation-for-oral-rehabilitation
3. Frothingham, S. (June 13, 2018). Dental Bridge. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/dental-bridge
4. Gaviria, L., Salcido, J., Guda, T., & Ong, J. L. (2014).Current trends in dental implants. Journal of The Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons, 40(2), 50. https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.2.50
5. National Library of Medicine. (s. f.). Dentures. https://medlineplus.gov/dentures.html
6. Your Options When Considering Dentures and Dental Implants. (Reviewed: April 15, 2022). WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/ss/slideshow-dentures-implants
7. Willans, K. (Feb 19, 2023). Permanent Dentures Cost. NewMouth. https://www.newmouth.com/dentistry/restorative/dentures/permanent/
-
Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...