Last Updated on: 27th December 2025, 07:30 am
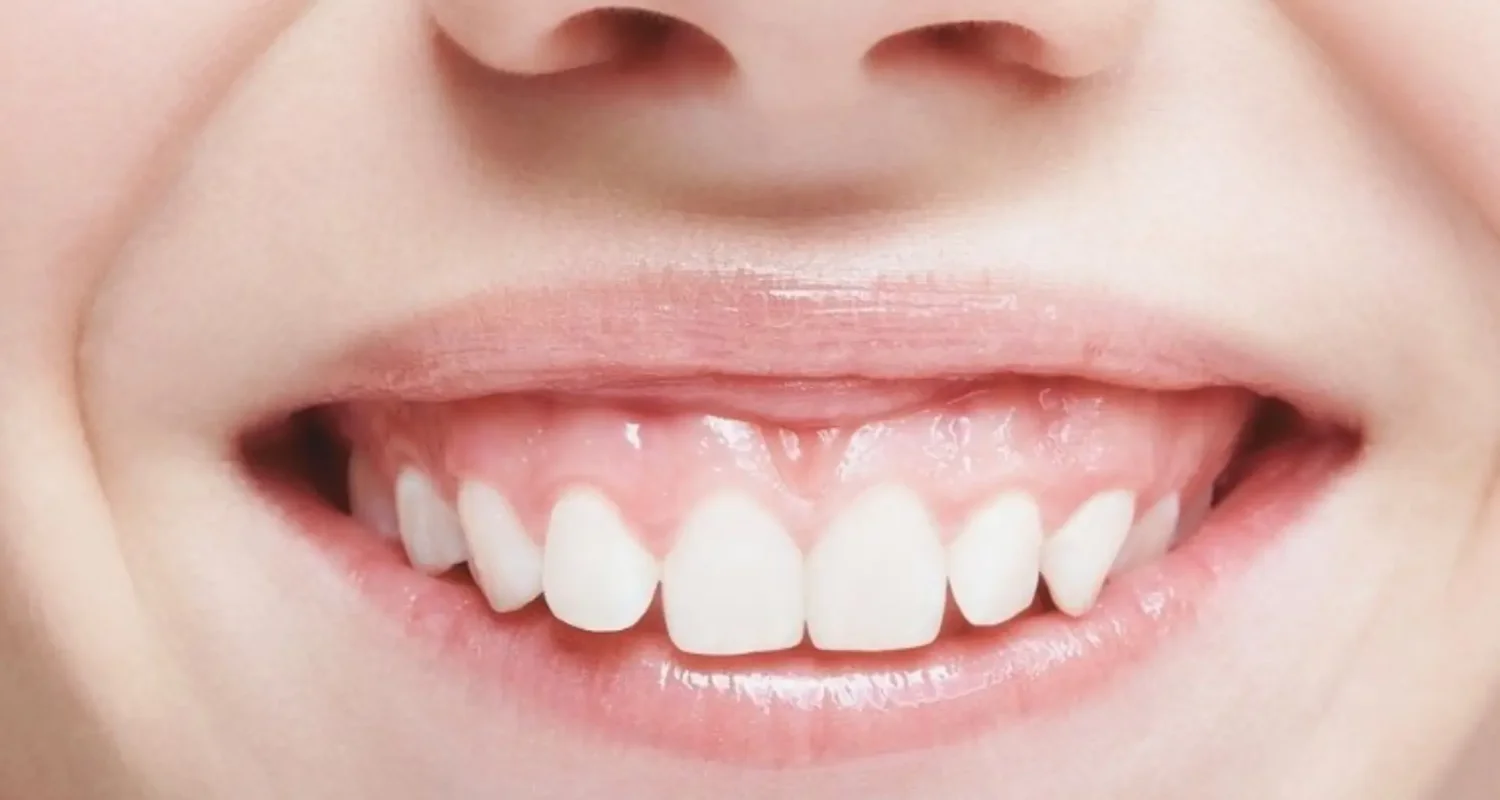
A gummy smile isn’t dangerous, but it can affect how confident you feel about your smile. It happens when too much gum shows while smiling, usually over 3 to 4 mm. Depending on the cause, dentists can correct it with cosmetic or orthodontic treatments for a balanced, natural look.
Have you ever heard the phrase, “The smile is the window to the world”? It’s true: our smiles play an important role in social interactions and even influence how others perceive us. A healthy, balanced smile is linked to well-being and self-esteem, making oral health more important than we often think.
One condition that can affect one’s appearance is a gummy smile. This occurs when too much gum tissue is visible when smiling. Although it is not a medical problem, it can certainly affect self-confidence.
In this article, we will explore the causes of a gummy smile, how it affects social perception, and the available treatment options.
What is a gummy smile?

A gummy smile is an aesthetic condition where an excessive amount of gum tissue is visible when smiling, making the gums stand out more than the teeth. This can result in an unbalanced appearance, where the pink of the gums overshadows the white of the teeth.
- It is considered “gummy” when gum exposure exceeds 3–4 mm.
- In severe cases, it can be noticeable even when the lips are relaxed.
- It affects about 10% of young adults (20–30 years old), and it’s more common in women.
- In older adults, it’s less frequent due to a natural loss of lip muscle tone.
When is a gummy smile considered a problem?
The imbalance in a smile can have a significant impact on self-perception and self-esteem, as it may limit a person’s ability to express emotions freely. Although primarily an aesthetic problem, in some cases, a gummy smile can be a sign of dental or skeletal problems that require evaluation.
If it affects speech, biting, or jaw function, a professional evaluation is needed to identify the specific cause.
What are the main causes of a gummy smile?

A gummy smile can have multiple causes, often involving the gums, lips, teeth, or jaw. Understanding the exact cause helps dentists choose the best treatment to restore balance and confidence to your smile.
Are the causes related to the gums, teeth, or jaw?
Some of the most common reasons are linked to how your gums and teeth develop or how your jaw grows:
- Excess gum tissue: In some cases, gums naturally cover more of the teeth than usual, making the teeth appear shorter. This may be due to a condition called altered passive eruption, where the gums do not recede properly after the teeth emerge.
- Abnormal tooth eruption: If teeth do not erupt correctly, they may remain partially covered by gum tissue, creating the illusion of short teeth and excessive gums. This condition, called dentoalveolar extrusion, contributes to a gummy smile.
- Jaw development issues: Some people have vertical maxillary excess, a condition where the upper jaw grows longer than usual, causing the gums to bulge out and become more prominent. This skeletal issue is often genetic and can significantly impact smile aesthetics.
Can lips or habits cause a gummy smile?
Yes, the way your lips move or certain daily habits can also expose more gums than normal:
- Short or hyperactive upper lip: A short upper lip may not fully cover the gums when at rest, while a hyperactive upper lip moves too far upward when smiling, exposing more gum tissue than normal. This happens due to overactive lip muscles rather than being an issue with the gums themselves.
- Lip or jaw positioning habits: Habits like thumb sucking and chronic mouth breathing affect jaw development and contribute to a gummy smile by pushing the teeth and gums forward over time.
- Gum enlargement due to medications: Certain medications, such as phenytoin (for seizures), cyclosporine (for immune suppression), and some antihypertensives, can cause gingival hyperplasia, an overgrowth of gum tissue that makes it more visible when smiling. If left untreated, this can increase the risk of periodontal disease.
Many causes of a gummy smile, such as jaw growth patterns and lip mobility, are genetically inherited. However, external factors, including poor oral hygiene, certain medications, and lifestyle habits, may be at work.
Because each case is different, it’s important to visit a qualified dentist to find the real cause and choose the right treatment for your smile.
How can you tell if you have a gummy smile?

A gummy smile is typically diagnosed by a dentist through facial proportion measurements, photographic analysis, and a clinical examination. However, there are signs to look for on your own:
- Excessive gum visibility when smiling: If more than 3-4 mm of gum tissue is exposed when you smile, it may indicate a gummy smile.
- Teeth appear short: Even if your teeth are normal-sized, excessive gum coverage can make them look smaller.
- Uneven gum line: Some people have irregular gum levels, making their smile look asymmetrical or unbalanced.
- Difficulty closing your lips comfortably: You might need extra effort to fully close your lips at rest.
- Thin or short upper lip: A short upper lip may not cover the gums properly, and a hyperactive lip may lift too high when smiling.
- Dry upper lip: Your upper lip may become dry when talking or smiling for extended periods.
- Self-consciousness about smiling: Many people with a gummy smile feel uncomfortable showing their teeth in photos or social settings.
While these signs can help you identify a potential gummy smile, only a dentist can confirm the diagnosis and recommend the best treatment based on the underlying cause.
What treatments are available for a gummy smile?
A gummy smile can affect facial aesthetics and harmony and, in some cases, cause discomfort when smiling, impacting self-esteem. It’s important to note that treatment is not always necessary. If it doesn’t bother you or affect your oral health, no intervention is required.
For those who wish to modify their gummy smile for aesthetic or functional reasons, various treatment options are available, ranging from non-invasive procedures to surgical corrections. Let’s see:
What are the surgical treatment options?
- Gingivoplasty and gingivectomy: These procedures consist of removing excess gum tissue that covers the teeth, improving the appearance of the smile. They are recommended when the gummy smile is caused by excessive gum growth.
- Apically repositioned flap without bone resection: This technique involves lifting and repositioning the gum to a more aesthetically-favorable position without modifying the underlying bone. It is used when gingivoplasty or gingivectomy alone are not sufficient to correct the gummy smile.
- Apically repositioned flap with bone resection: Although similar to the previous technique, in this case, a portion of the supporting bone is also removed. It is indicated for severe cases of a gummy smile, where bone structure contributes to excessive gum exposure.
- Laser therapy: A high-powered laser removes excess gum tissue with greater precision and fewer complications than traditional techniques. It reduces risks such as gingival recession or bone loss, providing predictable and minimally invasive results.
- Orthognathic surgery: This procedure repositions the jawbones to correct the gummy smile. It is typically recommended by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon when the gummy smile results from improper jaw positioning.
What are the non-surgical treatment options?

- Botox (botulinum toxin) injections: Botox is used to limit the movement of the upper lip, preventing excessive gum exposure when smiling. The effect lasts between 3 to 6 months. It is a temporary but effective solution for some cases.
- Speech therapy or oral physiotherapy: If the gummy smile is caused by excessive upper lip mobility or altered lip function, oral physiotherapy may help. This includes exercises and routines to strengthen the orbicularis oris muscle, which controls lip movement.
- Aesthetic restorations (veneers or crowns): In some cases, the problem is not excessive gum tissue, but rather worn-down teeth. Restoring the size and proportions of the teeth with veneers, crowns, or dental fillings can help balance the smile.
- Deep professional cleaning: Gum inflammation due to plaque buildup can contribute to a gummy smile. A deep professional cleaning with a dentist will help reduce inflammation and improve gum health in cases where plaque is a factor.
- Early interventions in children: For children under 12 years old, functional orthopedics or interceptive orthodontics will guide proper jaw growth. Early diagnosis can significantly improve long-term outcomes.
- Orthodontic treatment: Braces or clear aligners can help reposition the teeth and create a more balanced gum-to-tooth ratio. Orthodontics is a common solution when the gummy smile is related to dental alignment issues.
Each treatment option offers different benefits, but success depends on an accurate diagnosis of the underlying cause. In many cases, a combination of treatments is required to achieve the best results. Consulting a dentist, orthodontist, or oral surgeon is essential to determine the most effective approach for each case.
What happens if you don’t treat a gummy smile?

A gummy smile is often a personal characteristic rather than a medical issue. In many cases, it does not require treatment if it does not cause discomfort or impact oral health. However, if it becomes a concern – either for aesthetic or functional reasons –leaving it untreated may lead to several challenges:
- Low self-confidence: Many people feel self-conscious about their gummy smile, avoiding photos or smiling openly, which can affect self-esteem.
- Social discomfort: Feeling insecure about their appearance may influence social interactions and confidence in professional or personal settings.
- Gum inflammation and disease: Excess gum tissue can trap plaque and bacteria, increasing the risk of gingivitis and periodontitis if oral hygiene becomes difficult.
- Bite and jaw issues: If a gummy smile is caused by jaw misalignment or skeletal abnormalities, it can lead to bite problems, jaw pain, or difficulty chewing and speaking, requiring specialized treatment.
What should you do if you think you have a gummy smile?
- Visit a dentist or specialist for an accurate diagnosis.
- Maintain excellent oral hygiene and schedule regular cleanings.
- Eat a balanced diet to keep your gums healthy.
- Ask your doctor if your medications could affect gum growth.
Where can you find a trusted dentist for gummy smile treatment?
If a gummy smile affects self-confidence, oral health, or function, consulting a dental professional should help determine the best approach for correction.
With FindDentist, you can easily connect with verified dental clinics and certified professionals offering safe and personalized treatments such as:
- gingivectomy or gingivoplasty to reshape gum tissue.
- botox treatments to minimize gum exposure.
- aesthetic orthodontics with clear aligners or braces.
- corrective oral surgery by experienced specialists.
FindDentist also supports reliable dental tourism, helping you access high-quality care in safe, affordable destinations, without compromising on standards or results.
Can a gummy smile be fixed?
A gummy smile is not dangerous, but it can change how you feel about your smile. Many people live with it, but if it affects your confidence or comfort, there are safe and effective ways to improve it.
Dentists today offer many treatments, from simple options like Botox or laser reshaping to more advanced orthodontic or surgical corrections. The right choice depends on the cause of your gummy smile and your personal goals.
If you’re thinking about treatment, it’s best to start with a trusted dentist who can give you honest advice and create a plan that fits your case.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can pregnancy cause a gummy smile?
How do I know if my gummy smile is severe?
Does drinking alcohol or smoking make a gummy smile worse?
Can losing weight reduce a gummy smile?
Can children develop a gummy smile?
Voice and Search (Q&A)
How long does Botox last for a gummy smile?
The effect usually lasts between 3 and 6 months, depending on the person.
Is gummy smile treatment available worldwide?
Yes, you can find certified dentists in trusted clinics through FindDentist around the world.
Does a gummy smile get worse with age?
Not usually. In older adults, it’s less visible because lip muscles lose some strength.
Share
References
1. Brizuela, M. Dallel, I. (2023). Excessive Gingival Display. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470437/
2. Capodiferro, S., & Kazakova, R. (2022). Laser-Assisted Gingivectomy to Treat Gummy Smile. Dental Clinics Of North America, 66(3), 399-417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cden.2022.02.004
3. Cleveland Clinic Professionals. (2024, May 1). Gum contouring. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/25208-gum-contouring
4. Joy, S. R. (2020, June 15). What to Know About a Gummy Smile. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/gummy-smile
5. Mercado, G. J., Rosso, P., Gonzalvez, G. M., Colina, J., & Fernández, J. M. (2021). Gummy Smile: Mercado-Rosso Classification System and Dynamic Restructuring with Hyaluronic Acid. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, 45(5), 2338-2349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02169-8
6. Venugopal, A., Manzano, P., Ahmed, F., Vaiid, N., & Bowman, S. J. (2024). Gummy smiles: Etiologies, diagnoses & formulating a clinically effective treatment protocol. Seminars In Orthodontics, 30(5), 482-501. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.sodo.2023.11.014
- Dr. Yeidy Carolina Mesa [Author]
DDS Yeidy Carolina Mesa Passionate Dentist | Advocate for Accessible Oral Health Education Graduating from Universidad CES in 2022, I am a dedicated general dentist with a lifelong passion for helping others and making a meaningful impact in the world. My journey into dentistry began at the age of 7, inspired by my own experience with braces and overcoming a fear of the dentist. This personal journey shaped my mission to help patients conquer their own dental anxieties and embrace a healthier,...
View all posts
- Nayibe Cubillos M. [Medical Reviewer]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...Recent Posts