Last Updated on: 5th November 2025, 06:00 am
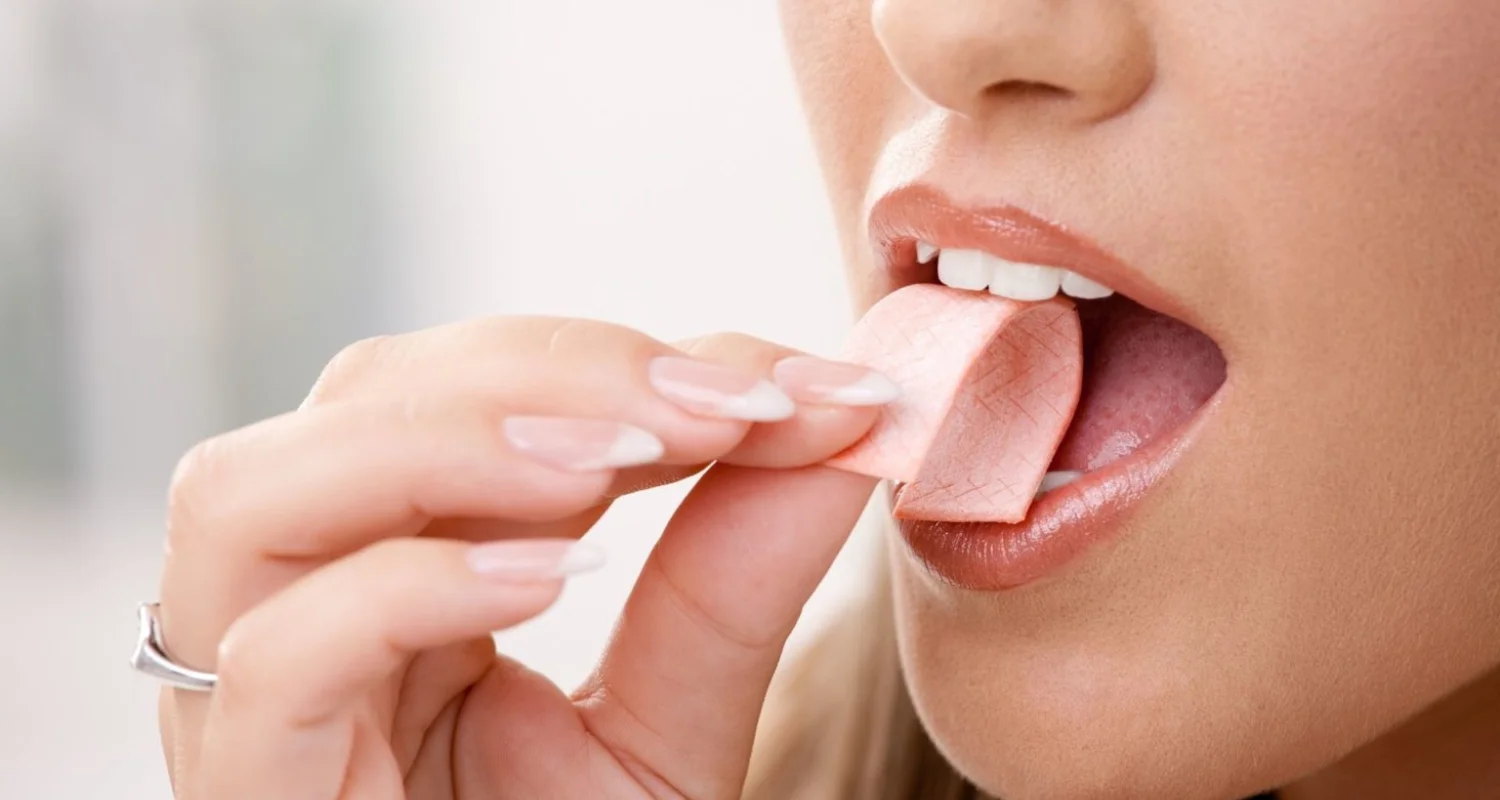
Yes, chewing sugar-free gum, especially with xylitol, can reduce the risk of cavities. Why? It increases saliva, balances mouth pH, and helps with enamel repair. Chewing gum is not a substitute for brushing and flossing; it is a simple and effective complement to better oral health.
Tooth decay is one of the most common health problems worldwide. Studies estimate that more than 2.3 billion people are affected in their permanent teeth, while over 530 million children have cavities in their baby teeth.
Because of these numbers, experts continue to explore simple and effective preventative methods. Recently, sugar-free chewing gum has gained attention as a practical option.
What are cavities?
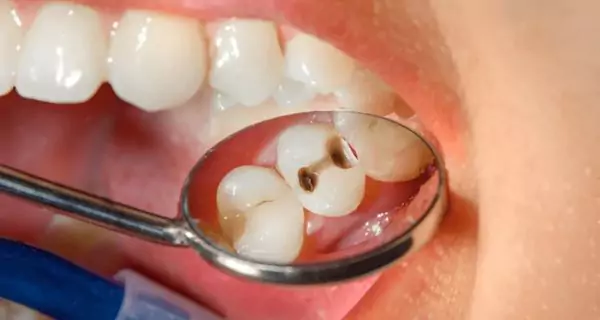
Cavities are tiny holes in teeth caused by acid attacks. When sugar from food or drinks meets bacteria in plaque, the bacteria produce acid. Over time, this acid wears down the enamel, causing permanent damage.
Why do cavities form?
Cavities have multifactorial causes and tooth decay can happen for different reasons:
- frequent intake of sugary or sticky foods
- inconsistent brushing and flossing
- weak enamel or lack of fluoride
- dry mouth or low saliva flow
If untreated, cavities can lead to pain, infection, and even tooth loss; but you can prevent them with good habits.
How can cavities be prevented day to day?
Cavity prevention is about balance: controlling sugar intake, keeping teeth clean, and supporting the natural defenses of the mouth.
Some daily prevention tips:
- Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss at least once daily.
- Use fluoride mouthwash if recommended by your dentist.
- Limit soda, juice, and sweets.
- Visit the dentist twice a year for cleanings.
With good oral hygiene and practicing sound habits, you can avoid cavities in your teeth. There is a product that helps by giving you a valuable extra layer of protection: sugar-free gum.
Does chewing gum really protect teeth?

Yes, but only when it is sugar-free gum. Research since the 1970s shows that chewing sugar-free gum after meals stimulates saliva, neutralizes acids, and even helps enamel repair itself.
Chewing gum protects teeth by:
- boosting saliva production
- neutralizing harmful acids in the mouth
- washing away food particles
- delivering minerals like calcium and phosphate to the enamel
The most important thing is to opt for chewing sugar-free gum. It is beneficial whereas regular gum can be harmful.
What is the difference between regular gum and sugar-free gum?
Not all gums are the same, and this difference is important for oral health.
Regular gum
Regular gum contains sugar, which feeds bacteria. As the bacteria break it down, it releases acid that weakens enamel and promotes decay.
Problems with regular gum:
- feeds harmful bacteria
- produces acid that erodes enamel
- increases cavity risk
Sugar-free gum

Sugar-free gum uses sweeteners like xylitol, sorbitol, or mannitol that do not cause decay. Instead, they support saliva flow and reduce bacterial growth.
The benefits of sugar-free gum:
- does not feed cavity-causing bacteria
- saliva to protect enamel
- helps restore minerals to weakened teeth
Regular gum acts like candy, while sugar-free gum supports oral health.
What do studies say about sugar-free gum and cavities?
Scientific evidence strongly supports sugar-free gum as a cavity-prevention tool. Of note:
- In Finland, xylitol gum is used in school programs to protect children’s teeth.
- The American Dental Association (ADA) has approved sugar-free gum with polyols for its oral health benefits.
- Clinical studies show gum reduces plaque and strengthens enamel when used after meals.
In short, sugar-free gum is a simple, affordable, and proven way to lower cavity risk.
Why are xylitol, sorbitol, and mannitol important?

These sugar substitutes, called sugar alcohols, look like sugar but act differently in the mouth.
What makes xylitol special?
- found naturally in fruits and vegetables
- blocks bacteria from sticking to teeth
- increases saliva and balances mouth pH
- shown in studies to reduce cavities in children and adults
How do sorbitol and mannitol work?
- provide sweetness without causing decay
- do not allow bacteria to produce harmful acid
- help reduce plaque formation
All sugar alcohols are safer than sugar, but xylitol offers the strongest cavity protection.
What are the extra benefits of sugar-free gum?

Sugar-free gum does more than help to prevent cavities. Let’s see the other important benefits:
- relieving dry mouth (xerostomia).
- freshening breath by neutralizing odors.
- reducing stress or improving focus while chewing.
- lowering the risk of transmitting cavity-causing bacteria from parents to children.
Making chewing gum a daily habit can be beneficial for all family members, improving both comfort and oral health.
Is sugar-free gum helpful for children?
Yes, when they are old enough to chew safely without swallowing. Gum can be especially helpful after school lunches or snacks when brushing isn’t possible.
Tips for parents
- Choose xylitol gum for better protection.
- Supervise children to avoid swallowing gum.
- Limit other sugary snacks and drinks.
- Encourage brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste.
Sugar-free gum is an extra line of defense, but supervision and good brushing habits remain essential.
Can teenagers benefit from chewing gum?

Definitely. Teens face higher risks due to soda consumption, busy schedules, and various braces. Orthodontic appliances make cleaning harder, which increases plaque buildup.
Why teens should chew sugar-free gum
- helps clean around braces after meals
- neutralizes acids from soft drinks
- freshens breath during social activities
- adds protection when brushing is less convenient
For teens, sugar-free gum is an easy, practical way to keep their teeth healthier.
Why should adults consider sugar-free gum?
Adults often deal with unique issues such as dry mouth from medications, gum disease, or enamel wear. Sugar-free gum can provide comfort and protection.
Benefits for adults
- relieves dryness and discomfort
- protects enamel from acid damage
- keeps breath fresh at work or in social settings
For adults, sugar-free gum is more than just about preventing cavities; it’s also good for maintaining comfort and oral health long-term.
How should sugar-free gum be used safely?
Sugar-free gum is safe for most people when used safely. Some recommendations for safe use are:
- Chew for about 20 minutes after meals.
- Pick xylitol gum when available.
- Avoid gum if you have jaw pain (TMJ problems).
- Do not give gum to very young children.
Remember that chewing gum to prevent cavities is possible, but it is only a helper; brushing, flossing, and dental visits remain essential.
Find the Right Specialist for Your Cavity Care
Thinking about getting treatment for cavities outside your city or even abroad? At Find Dentist, we bring together top dentists and clinics across Latin America so you can compare options, check prices, and view real photos of their facilities—all in one place. Make an informed, confident choice and take the first step toward a healthier, cavity-free smile today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can sugar-free gum replace brushing and flossing?
How long should I chew gum after meals?
Are there any side effects of chewing sugar-free gum?
Is sugar-free gum safe for children?
Voice and Search (Q&A)
Is chewing gum good after drinking coffee?
Yes, sugar-free gum helps remove coffee acids, reduces staining, and keeps the mouth fresher after drinking coffee or tea.
Is all sugar-free gum the same?
No, not all sugar-free gums have the same effect. Those with xylitol offer extra cavity protection as compared to gums with other sweeteners.
How many times a day should I chew sugar-free gum?
Chewing sugar-free gum 2 to 3 times a day, especially after meals, is considered safe and beneficial for oral health.
Share
References
1. ADA. (2023, May 4). Chewing gum. American Dental Association. https://www.ada.org/resources/ada-library/oral-health-topics/chewing-gum
2. BDJ Team. (2015). The oral health benefits of sugarfree gum. British Dental Journal 2(1–8). https://doi.org/10.1038/bdjteam.2015.151
3. Ramasubbu, D., & Duane, B. (2024). Do chewing gums and sweets containing xylitol prevent caries in children? Evidence-Based Dentistry, 25(2), 89–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41432-024-01018-2
4. Whelan, C. (2018, March 14). Are there any benefits to chewing Sugar-Free Gum? Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/sugar-free-gum
5. Yeung, C. Y., Chu, C., & Yu, O. Y. (2023). A concise review of chewing gum as an anti-cariogenic agent. Frontiers in Oral Health, 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/froh.2023.1213523
- Dr. Yeidy Carolina Mesa [Author]
DDS Yeidy Carolina Mesa Passionate Dentist | Advocate for Accessible Oral Health Education Graduating from Universidad CES in 2022, I am a dedicated general dentist with a lifelong passion for helping others and making a meaningful impact in the world. My journey into dentistry began at the age of 7, inspired by my own experience with braces and overcoming a fear of the dentist. This personal journey shaped my mission to help patients conquer their own dental anxieties and embrace a healthier,...
View all posts
- Nayibe Cubillos M. [Medical Reviewer]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...Recent Posts
















