Last Updated on: 26th January 2026, 05:34 am
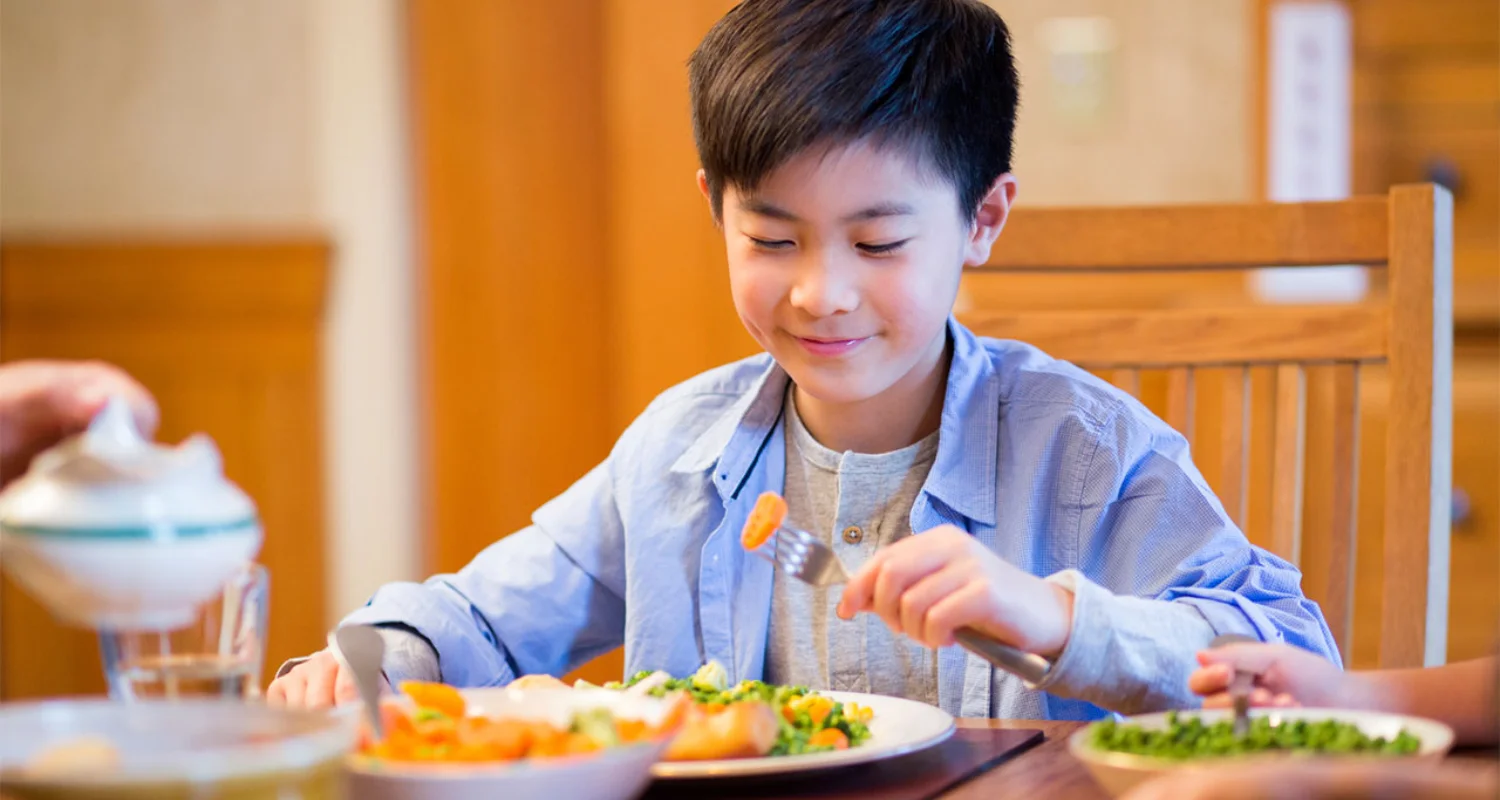
Healthy eating habits directly support your child's oral health by strengthening teeth and gums, stimulating saliva production, and reducing sugar intake. Foods rich in calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D protect enamel, while crunchy fruits and vegetables clean teeth naturally. Limiting sugary snacks and drinks lowers the risk of cavities and gum disease.
A healthy diet from an early age is the foundation for a strong body, an active mind, and healthy teeth. Good nutrition plays a key role in your child’s overall growth and development, including their child’s oral health.
It’s important to understand that poor nutrition isn’t just about not eating enough—it also includes frequent consumption of:
- Added sugars
- Highly processed foods
- Low-nutrient products
This type of diet can harm the body and increase the risk of cavities, plaque buildup, and other dental problems.
At World of Dentistry, we encourage parents and caregivers to pay close attention to children’s daily meals and promote foods rich in vitamins and minerals. Doing so helps prevent tooth damage, reduces plaque formation, and supports healthy growth and development.
How does diet impact your child’s oral health?
Diet plays a crucial role in your child’s oral health: the foods they eat directly influence the state of their teeth and gums. Promoting good oral hygiene alongside proper nutrition:
- Provides essential nutrients for tooth development.
- Strengthens teeth and gums.
- Helps prevent cavities and other oral diseases.
Eating a diet rich in healthy foods contributes to strong teeth and maintaining a healthy oral environment. In addition, proper nutrition supports the production of saliva, which is essential for neutralizing acids and removing food debris.
How do unhealthy eating habits affect a child’s oral health?
Sugars and acidic foods can cause serious damage to teeth. Sugars and fermentable carbohydrates, especially from processed foods:
- Are metabolized by bacteria in the mouth
- Produce acids that lower the pH of the dental biofilm
- Attack tooth enamel, leading to demineralization of dental tissues.
A balanced diet is vital in preventing cavities and keeping your child’s oral health in optimal condition.
What foods should be avoided for better children’s oral health?
To improve oral health, it is important to avoid certain foods that increase the risk of cavities and other dental problems. Below are foods to limit:
Sticky and chewy foods
- Sugary foods such as gummy worms, caramel, lollipops and hard candy.
- White bread, chips, and other sticky snacks.
These foods tend to adhere to teeth, promoting bacterial growth and cavities.
If you give any of these foods to your children, it is recommended to do so directly after a meal since saliva production at this time is greater and helps sweep bacteria off tooth surfaces.
Sugary treats
- Ice cream, cookies, and any sugary snacks should be consumed in moderation.
- Sugar is metabolized and turns into acid – increasing the risk of enamel erosion and causing demineralization of dental tissue.
Children should brush their teeth after eating desserts.
Sugary drinks and juices
- Soft drinks, sports drinks, sweetened fruit juices and milk with added sugar.
- High sugar content and acidic pH increase the risk of cavities and enamel erosion.
It is recommended for children to consume water, ideally fluoridated.
Snacks between meals
- Frequent snacking increases bacterial load, plaque formation, and risk of cavities.
- Many snacks are high in sugar and low in nutrients.
If your children eat snacks between meals, it is recommended to brush after eating, in addition to the general recommendation to brush in the morning and at night.
What are the best foods for children’s oral health?
Developing healthy eating habits is essential for protecting children’s oral health. The best foods for healthy teeth are those that strengthen enamel, stimulate saliva production, and help fight the bacteria responsible for cavities.
Below are some key food groups that support strong teeth and gums.
Crunchy fruits and vegetables
Crunchy fruits and vegetables like apples, carrots, pears, cucumbers and celery are natural allies for children’s oral health.
- They provide nutrients as fiber, water and antioxidants (Vitamin C and beta-carotene).
- They help clean the teeth while being chewed and stimulate saliva production, which neutralizes acids and washes away food particles.
- They reduce inflammation and support gum health.
How to include them more often:
- Offer sliced fruits and vegetables as daily snacks.
- Pair them with low-sugar peanut butter for added nutrients and satiety.
- Include them in school lunches and family meals.
Low-fat dairy products
Dairy products such as cheese, milk, and yogurt, are rich in calcium, phosphorus, protein and probiotics. They help to:
- Strengthen tooth enamel
- two essential minerals for strengthening tooth enamel.
- Promote enamel remineralization after acid exposure
- Help inhibit bacterial growth and reduce plaque buildup
How to include them more often:
- Serve yogurt with fresh fruit instead of sugary desserts.
- Add cheese to meals or offer it as a snack.
- Choose unsweetened or low-sugar dairy options.
Lean meats, nuts and other protein sources
Proteins such as lean meats, eggs, nuts, seeds and legumes are essential for the development of strong dental and oral structures in growing children. Those foods are full of protein, iron, zinc and vitamin D that are essential to:
- Support tooth and jaw development.
- Help maintain healthy oral tissues.
- Strengthen enamel by supporting mineral absorption.
How to include them more often:
- Incorporate lean meats into balanced meals.
- Offer nuts or nut butters as snacks (age-appropriate).
- Combine protein with fruits or vegetables for balanced snacks.
Fluoride and drinking water
Water is essential for overall health and plays a key role in protecting children’s teeth.
- Fluoride, which is found in drinking water and some toothpastes, helps remineralize enamel.
- Water also rinses away food debris and sugars and supports saliva production.
- Water and fluoride help to reduce the risk of cavities, protect enamel from acid attacks and maintain a healthy oral environment.
How to encourage better intake:
- Offer water as the main beverage throughout the day.
- Limit sugary drinks and juices.
- Encourage drinking water after meals and snacks.
What strategies help children develop healthy eating habits?
Building healthy eating habits can be challenging, but small and consistent strategies can help. Let’s see some practical tips for parents and caregivers.
- Be a role model by choosing healthy foods yourself.
- Offer a variety of foods and repeat exposure without pressure.
- Make meals colorful and fun to increase interest.
- Avoid using sweets as rewards.
- Keep healthy snacks easily accessible at home.
- Encourage regular meal times to reduce frequent snacking.
- Involve children in grocery shopping and meal preparation.
Creating a positive relationship with food helps children develop lifelong habits that support both their oral health and overall well-being.
How do healthy eating habits support children’s oral health?
Healthy eating habits are essential for maintaining children’s oral health. A balanced diet supports strong enamel, healthy gums, and proper dental development, while regular meals and adequate water intake help create a protective oral environment.
By encouraging nutritious food choices from an early age, parents and caregivers can support children’s oral health, overall well-being, and long-term healthy smiles.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should you eat and avoid for your child's teeth?
What should I avoid for my kid to maintain good oral health?
What are the best foods for strong teeth in children?
How can water benefit my child's oral health?
Which nutrients are most important for healthy teeth in children?
Voice and Search (Q&A)
How does nutrition affect a child’s oral health?
Good nutrition strengthens enamel, supports healthy gums, stimulates saliva, and reduces cavities and other dental problems.
Do fruits and vegetables really help clean teeth?
Yes, crunchy fruits and vegetables naturally clean teeth and increase saliva production while chewing.
How often should children consume sugary foods?
Sugary foods should be limited and offered occasionally, preferably after meals.
Share
References
1. American Academy of Pediatrics. (2020, February 4). Healthy Teeth and Your Child’s Diet. Healthy Children. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/healthy-living/oral-health/Pages/Healthy-Teeth-and-Your-Childs-Diet.aspx
2. Chandan, S. N., Rao, S. (2022). Dietary interventions and nutritional impact on oral health and development: a review. 13;60(6):1666–1673. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10169943/
3. Hancock, S., Schofield, G., & Zinn, C. (2022). Healthy Food, Healthy Teeth: A Formative Study to Assess Knowledge of Foods for Oral Health in Children and Adults. Nutrients, 14(14), 2984. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142984
4. Naidoo, S., & Myburgh, N. (2007). Nutrition, oral health and the young child. Maternal And Child Nutrition, 3(4), 312-321. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1740-8709.2007.00115.x
5. Pugle, M. (2022, December 19). Pediatricians update guidelines for children’s dental health. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health-news/pediatricians-update-guidelines-for-childrens-dental-health
-
Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...