Last Updated on: 16th December 2025, 11:02 am
Learn how toothache and sinus infection are connected, including their symptoms and ways to find relief. Discover when to see a dentist or doctor for effective treatment.
If you’ve ever experienced a toothache that doesn’t seem to have an obvious dental cause, it may be linked to something higher up: a toothache sinus infection. Sinusitis can often cause discomfort that mimics tooth pain, particularly in the upper molars. This overlap between dental and sinus health can make it difficult to determine whether the pain originates in the teeth or is the result of sinus pressure.
Let’s explore how sinus infections can lead to toothaches, how to differentiate between the two, and the best ways to find relief.
What is a Sinus Infection?
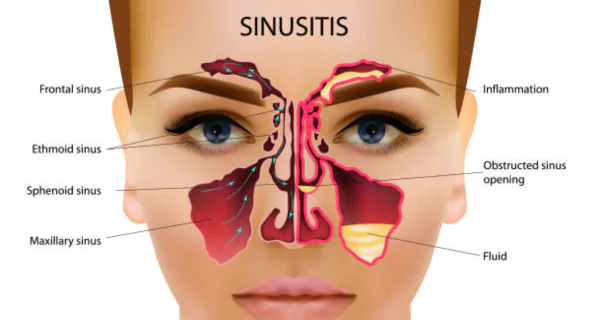
A sinus infection, also known as sinusitis, occurs when the sinuses, hollow cavities in the skull, become inflamed. These infections are typically caused by bacteria, viruses, or allergens that irritate the lining of the sinuses, resulting in symptoms such as congestion, facial pressure, and nasal discharge.
Types of sinus infections
Sinusitis can be categorized based on the duration and frequency of symptoms:
- Acute sinusitis: a short-term inflammation lasting less than four weeks, usually caused by a cold or viral infection. Symptoms include nasal congestion, facial pain and nasal discharge.
- Subacute sinusitis: The symptoms persist for one to three months. It can occur as an intermediate stage between acute and chronic sinusitis, often due to prolonged inflammation.
- Chronic sinusitis: a long-lasting inflammation that persists for more than 12 weeks, even with treatment. Often associated with allergies or structural issues in the nasal passages. It may result in persistent nasal congestion, facial pressure, and reduced sense of smell.
- Recurrent sinusitis: Multiple episodes of acute sinusitis occurring throughout the year, indicating an underlying vulnerability to sinus infections, such as weakened immunity or structural issues.
How a Sinus Infection Causes Tooth Pain

The relationship between a sinus infection and tooth pain is rooted in anatomy. The maxillary sinuses, a pair of cavities located behind the cheekbones, are positioned just above the roots of the upper molars and premolars, creating a close connection between these structures.
- Sinus pressure and toothache: When the sinuses become inflamed, they swell and fill with mucus, increasing pressure within the sinus cavities. This pressure can press down on the roots of the upper teeth, causing a dull ache or sensitivity that feels remarkably similar to a traditional toothache.
- Referred pain: In some cases, sinus-related tooth pain may not be isolated to a single tooth. Instead, the discomfort can spread across multiple teeth. This phenomenon, known as referred pain, occurs because the nerves in the area share common pathways, making it challenging for the brain to determine the exact source of the discomfort.
Toothache and Sinus Infection: How to Tell the Difference
Tooth pain can be caused by sinus infections or dental issues, but distinguishing between the two is crucial for seeking the appropriate treatment. Understanding the connection between sinus infections and tooth pain helps individuals identify their symptoms and decide whether to consult a dentist or a healthcare provider.

Key indicators of sinus tooth pain
- Pain in multiple teeth: Sinus-related tooth pain often affects several teeth on the same side of the upper jaw. This is due to the pressure exerted by inflamed sinuses on multiple tooth roots simultaneously.
- Worsening pain with movement: Activities such as bending over, lying down, or making sudden head movements can intensify sinus-related tooth pain. These actions cause shifts in sinus pressure, leading to increased discomfort.
- Associated sinus symptoms: A toothache sinus infection is usually accompanied by other sinus symptoms, such as:
- nasal congestion or a blocked nose
- postnasal drip (mucus drainage from the back of the nose)
- Facial tenderness around the cheeks, eyes, or forehead
- Bad breath caused by mucus buildup and bacteria in the sinuses
Signs of a true toothache
- Localized pain: Dental toothaches are typically isolated to one tooth, often caused by cavities, fractures, or gum infections.
- Sensitivity to temperature: Dental pain triggered or worsened by consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods is a key indicator of a true toothache
- Gum swelling or redness: Visible swelling or irritation in the gums near the affected tooth suggests a dental problem rather than sinus-related pain.
Shared symptoms between sinus infections and toothaches
- pain in upper teeth
- facial pressure or discomfort
- persistent aching
Unique symptoms of sinus infections
- nasal congestion: Difficulty breathing due to blocked nasal passages.
- postnasal drip: Mucus draining into the throat.
- facial tenderness: Soreness around the cheeks, eyes, and forehead.
- bad breath: Caused by mucus buildup and bacterial activity in the sinuses.
How to differentiate
If your tooth pain is localized, sensitive to temperature, or accompanied by gum swelling, it’s likely a dental issue. However, if the pain affects multiple teeth, worsens with movement, and is accompanied by sinus symptoms like congestion or facial tenderness, a toothache sinus infection is the probable cause. Recognizing these distinctions helps determine whether you should visit a dentist or a healthcare provider for effective relief.
Home Remedies for toothache With Sinus Infection
When tooth pain is caused by a sinus infection, the key to relief lies in reducing sinus inflammation and pressure. Here are practical strategies to alleviate both sinus pressure and tooth pain.

Relieving sinus pressure
- Steam Inhalation: Inhale steam from a bowl of hot water or take a warm shower to loosen mucus and reduce sinus pressure.
- Saline nasal sprays: Rinse your nasal passages with a saline solution to clear mucus and alleviate congestion.
- Warm compress: Apply a warm compress to your cheeks or forehead to soothe facial pain and improve sinus drainage.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to thin mucus, making it easier to drain from your sinuses. Warm drinks like tea or soup can provide additional comfort and relief.
- Use a humidifier: A humidifier adds moisture to the air, which helps to thin mucus and calm irritated airways, making it easier for your sinuses to drain.
- Spicy foods: If you can tolerate them, spicy foods like those with hot peppers or mustard can stimulate mucus drainage and open up nasal passages.
Managing tooth pain
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate both sinus pressure and tooth pain.
- Avoid chewing on the affected side: Reduce strain on the sensitive teeth by eating softer foods and avoiding the side with discomfort.
By focusing on reducing sinus inflammation and pressure, these remedies can effectively relieve the toothache sinus infection. If symptoms persist, consider consulting a healthcare provider or dentist to rule out underlying issues.
Medical Treatments for Sinus Infections and Tooth Pain
While home remedies can provide temporary relief, some situations require professional care to fully address the problem.
Sinus infection treatments
- Antibiotics: prescribed for bacterial sinus infections to eliminate the infection and reduce symptoms.
- Antihistamines and decongestants: help manage sinusitis caused by allergies or excessive mucus production.
- Steroid nasal sprays: reduce inflammation and promote sinus drainage for chronic sinus issues.
When dental treatment Is needed
If your tooth pain persists after sinus treatment, it’s important to consult your dentist. The underlying issue may involve a dental abscess, cavity, or gum disease requiring professional intervention.
Complications of Untreated Sinus Infections
Ignoring sinus infections can lead to complications that impact both your sinus and dental health.
Impact on dental health
Persistent sinus pressure can worsen tooth sensitivity and aggravate existing dental issues. If not treated, these problems can escalate, potentially leading to further oral health concerns, such as prolonged discomfort or damage to teeth and gums.
Spread of infection
In severe cases, untreated sinus infections can spread to nearby areas, such as the eyes or brain, posing significant health risks. Conditions like orbital cellulitis (eye socket infection) or meningitis (inflammation of the brain’s protective membranes) can develop. Timely medical intervention is essential to avoid these serious complications.
Preventing a Toothache Sinus Infection

Adopting good sinus and dental care habits can help minimize the likelihood of experiencing sinus-related tooth pain.
Maintaining sinus health
- Stay hydrated to keep mucus thin and promote drainage.
- Avoid allergens and irritants that trigger sinus inflammation.
- Practice good nasal hygiene with regular saline rinses.
Dental care practices
- Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and floss regularly to maintain healthy teeth and gums.
- Schedule routine dental check-ups to catch and address any potential issues early.
- Use a mouthguard at night if you grind your teeth, as this can worsen existing tooth pain.
Conclusion
Sinus infections and toothaches share a close connection, demonstrating how oral health and sinus health are intricately linked. Recognizing the symptoms and underlying causes of sinus-related tooth pain will help pinpoint the source of your discomfort and guide you toward the right solution.
If you are suffering a toothache sinus infection, reducing sinus inflammation through home remedies or medical treatment can bring relief. However, if the pain persists or becomes severe, it’s important to seek professional advice from a doctor or dentist to protect your overall health and well-being.
Practicing good sinus and oral hygiene habits can help you avoid future issues, ensuring both your sinuses and your smile remain healthy and pain-free.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a sinus infection cause a toothache on one side?
How do I know if my tooth pain is from a sinus infection?
What can I do at home to relieve sinus tooth pain?
When should I see a doctor or dentist for sinus tooth pain?
Can a sinus infection lead to tooth damage?
Share
References
1. Cronkleton, E. (2022, october 4). Can a Sinus Infection Cause a Toothache? Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/dental-and-oral-health/sinus-toothache
2. Henson, B., Drake, T. M., & Edens, M. A. (2023, july 24). Anatomy, Head and Neck, Nose Sinuses. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513272/
3. Psillas, G., Papaioannou, D., Petsali, S., Dimas, G. G., & Constantinidis, J. (2020, december 24). Odontogenic maxillary sinusitis: A comprehensive review. Journal Of Dental Sciences, 16(1), 474-481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jds.2020.08.001
4. Zhou, C. (2023, march 7). Sinus infection and toothache: Any connection?. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/acute-sinusitis/expert-answers/toothache/faq-20058299
- Nayibe Cubillos M. [Author]
Pharmaceutical Chemestry |Pharmaceutical Process Management | Pharmaceutical Care | Pharmaceutical Services Audit | Pharmaceutical Services Process Consulting | Content Project Manager | SEO Knowledge | Content Writer | Leadership | Scrum Master
View all posts
A healthcare writer with a solid background in pharmaceutical chemistry and a thorough understanding of Colombian regulatory processes and comprehensive sector management, she has significant experience coordinating and leading multidisciplina...Recent Posts















