Gum Disease Treatments
What is gum disease?
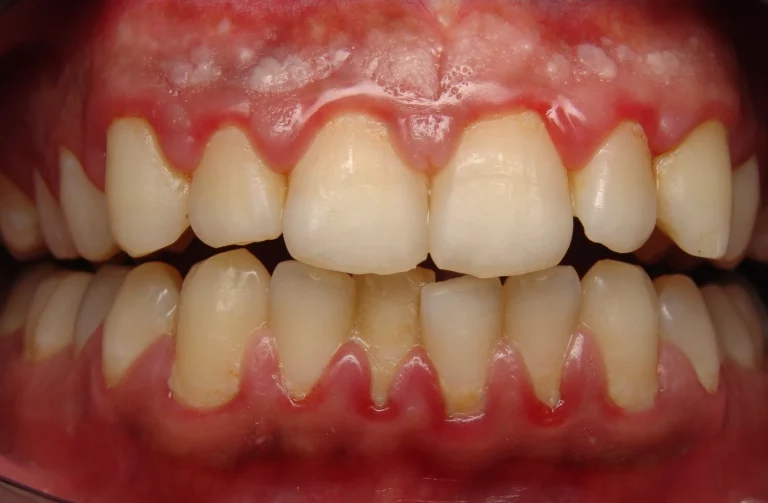
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that impacts the gums and the tissues that support the teeth.
Gum disease can be very painful and cause permanent damage if not treated properly.
Risk factors
There are several risk factors that increase the chance of developing gum disease:
Smoke

Excessive alcohol consumption

Diseases that compromise the immune system, such as type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and HIV.

Gum disease can be hereditary. In other words, some people may be more prone to developing it than others.
Assessment and diagnosis
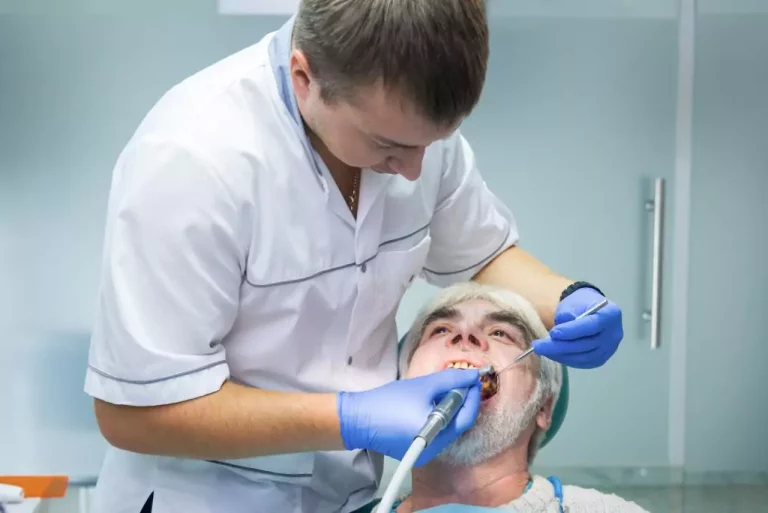
In restorative dentistry, there are several treatments available for gum disease.
The first step in the treatment of gum disease is a complete evaluation of dental health. A periodontist dentist performs a detailed examination of the gums and teeth to determine the severity of gum disease. In this assessment, the depth of the periodontal pockets is measured, which are spaces between the teeth and the gums that are formed when the gums move away from the teeth. X-rays may also be taken to assess the health of the teeth and the bones that support them.

19 Natural Antibiotics to Ward Off Any Dental Infection
Sign up to receive daily email dentist tips and challenges, as well as our comprehensive Better smile Guidebook.
Available Treatments for Gum Disease
The next step is treatment, the route of which depends on the diagnosis obtained in the initial assessment:
Scaling and root planing
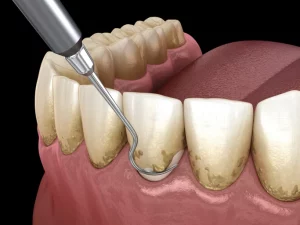
A deep dental cleaning is done. This procedure removes plaque and tartar that have built up on the teeth and gums. Generally, deep dental cleaning is done under local anesthesia.
After a dental cleaning, antibiotics may be prescribed to help reduce inflammation and prevent infection.
Periodontal surgery
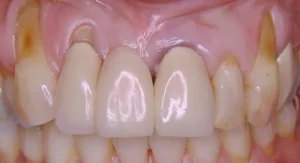
In severe cases, a surgical intervention is performed to remove plaque and tartar under the gums, and repair damaged tissue. Surgery may involve removing gum tissue or repairing the bones that support the teeth. Local anesthesia is applied for this intervention.
Gum graft
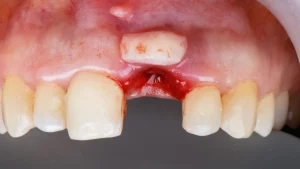
In this procedure, gum tissue is taken from another area of the mouth and placed in the areas where the gums have moved away from the teeth. The graft helps reduce tooth sensitivity and improves the appearance of the gums.
Extraction of impacted teeth
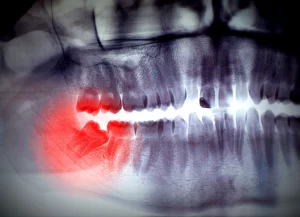
It is the therapeutic alternative in extremely serious cases. Extraction is necessary if the teeth are too damaged to repair or if gum disease has caused significant bone loss. After tooth extraction, the missing pieces are replaced with dental implants or another type of prosthesis.
Conclusion
Prevention and timely care
Treatments for gum disease in restorative dentistry help prevent tooth loss, reduce inflammation and pain associated with the pathology.
If periodontal disease develops, it is essential to seek treatment as soon as possible to avoid permanent damage to the teeth and gums.
If you require an evaluation to diagnose the condition of your gums, our directory of dental professionals offers different service alternatives in the area of periodontics. Consult it and select the care option that meets your expectations.

19 Natural Antibiotics to Ward Off Any Dental Infection
Sign up to receive daily email dentist tips and challenges, as well as our comprehensive Better smile Guidebook.
Our Doctor
Meet Doctor

19 Natural Antibiotics to Ward Off Any Dental Infection
Sign up to receive daily email dentist tips and challenges, as well as our comprehensive Better smile Guidebook.






